Annamaria R. Varkonyi-Koczy
Intelligent Road Inspection with Advanced Machine Learning; Hybrid Prediction Models for Smart Mobility and Transportation Maintenance Systems
Jan 18, 2020



Abstract:Prediction models in mobility and transportation maintenance systems have been dramatically improved through using machine learning methods. This paper proposes novel machine learning models for intelligent road inspection. The traditional road inspection systems based on the pavement condition index (PCI) are often associated with the critical safety, energy and cost issues. Alternatively, the proposed models utilize surface deflection data from falling weight deflectometer (FWD) tests to predict the PCI. Machine learning methods are the single multi-layer perceptron (MLP) and radial basis function (RBF) neural networks as well as their hybrids, i.e., Levenberg-Marquardt (MLP-LM), scaled conjugate gradient (MLP-SCG), imperialist competitive (RBF-ICA), and genetic algorithms (RBF-GA). Furthermore, the committee machine intelligent systems (CMIS) method was adopted to combine the results and improve the accuracy of the modeling. The results of the analysis have been verified through using four criteria of average percent relative error (APRE), average absolute percent relative error (AAPRE), root mean square error (RMSE), and standard error (SD). The CMIS model outperforms other models with the promising results of APRE=2.3303, AAPRE=11.6768, RMSE=12.0056, and SD=0.0210.
Applying ANN, ANFIS, and LSSVM Models for Estimation of Acid Solvent Solubility in Supercritical CO$_2$
Nov 21, 2019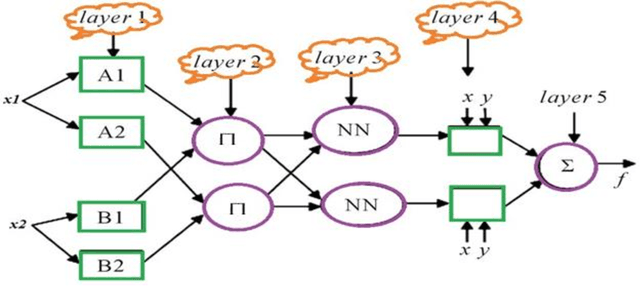
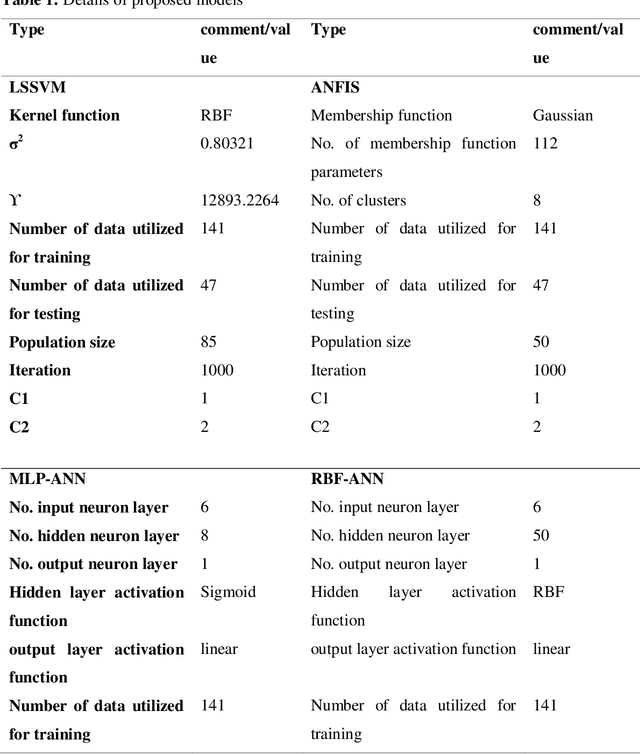
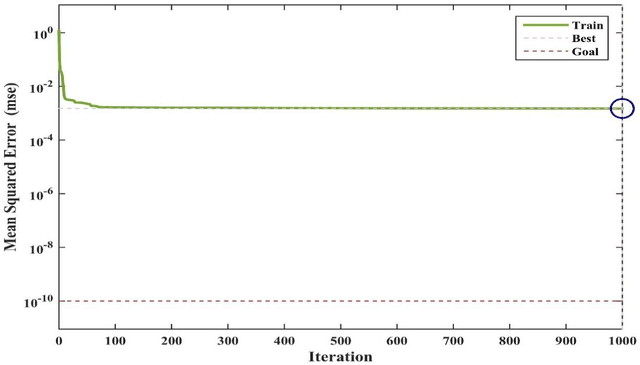
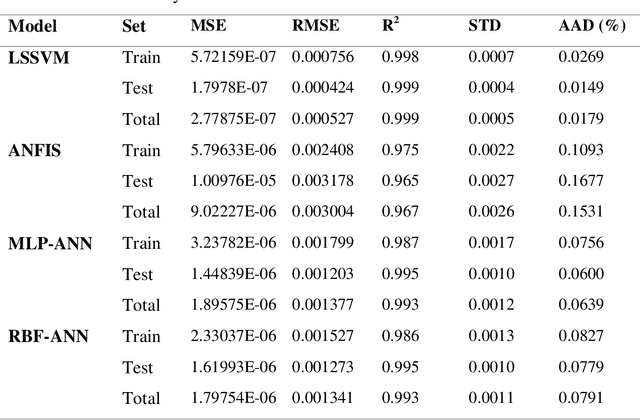
Abstract:In the present work, a novel and the robust computational investigation is carried out to estimate solubility of different acids in supercritical carbon dioxide. Four different algorithms such as radial basis function artificial neural network, Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network (ANN), Least squares support vector machine (LSSVM) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) are developed to predict the solubility of different acids in carbon dioxide based on the temperature, pressure, hydrogen number, carbon number, molecular weight, and acid dissociation constant of acid. In the purpose of best evaluation of proposed models, different graphical and statistical analyses and also a novel sensitivity analysis are carried out. The present study proposed the great manners for best acid solubility estimation in supercritical carbon dioxide, which can be helpful for engineers and chemists to predict operational conditions in industries.
Performance Evaluation of Supervised Machine Learning Techniques for Efficient Detection of Emotions from Online Content
Aug 05, 2019



Abstract:Emotion detection from the text is an important and challenging problem in text analytics. The opinion-mining experts are focusing on the development of emotion detection applications as they have received considerable attention of online community including users and business organization for collecting and interpreting public emotions. However, most of the existing works on emotion detection used less efficient machine learning classifiers with limited datasets, resulting in performance degradation. To overcome this issue, this work aims at the evaluation of the performance of different machine learning classifiers on a benchmark emotion dataset. The experimental results show the performance of different machine learning classifiers in terms of different evaluation metrics like precision, recall ad f-measure. Finally, a classifier with the best performance is recommended for the emotion classification.
Modeling Daily Pan Evaporation in Humid Climates Using Gaussian Process Regression
Aug 01, 2019



Abstract:Evaporation is one of the main processes in the hydrological cycle, and it is one of the most critical factors in agricultural, hydrological, and meteorological studies. Due to the interactions of multiple climatic factors, the evaporation is a complex and nonlinear phenomenon; therefore, the data-based methods can be used to have precise estimations of it. In this regard, in the present study, Gaussian Process Regression, Nearest-Neighbor, Random Forest and Support Vector Regression were used to estimate the pan evaporation in the meteorological stations of Golestan Province, Iran. For this purpose, meteorological data including PE, temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and sunny hours collected from the Gonbad-e Kavus, Gorgan and Bandar Torkman stations from 2011 through 2017. The accuracy of the studied methods was determined using the statistical indices of Root Mean Squared Error, correlation coefficient and Mean Absolute Error. Furthermore, the Taylor charts utilized for evaluating the accuracy of the mentioned models. We report that GPR for Gonbad-e Kavus Station with input parameters of T, W and S and GPR for Gorgan and Bandar Torkmen stations with input parameters of T, RH, W, and S had the most accurate performances and proposed for precise estimation of PE. Due to the high rate of evaporation in Iran and the lack of measurement instruments, the findings of the current study indicated that the PE values might be estimated with few easily measured meteorological parameters accurately.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge