Shahab Shamshirband
A Mobile Cloud-Based eHealth Scheme
Apr 15, 2020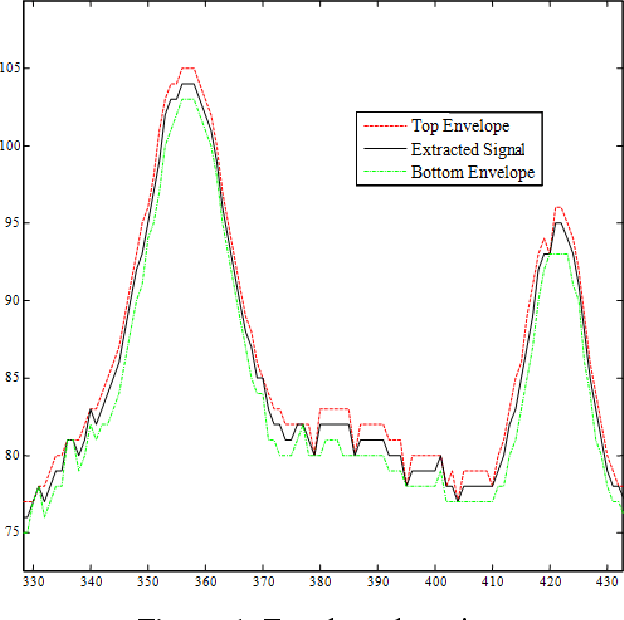
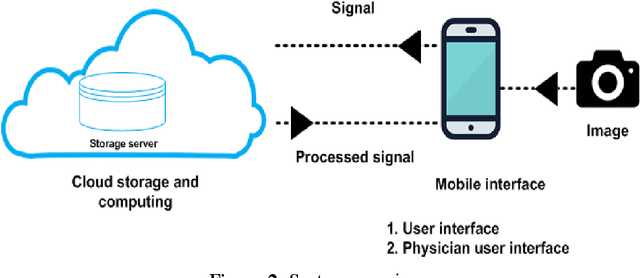
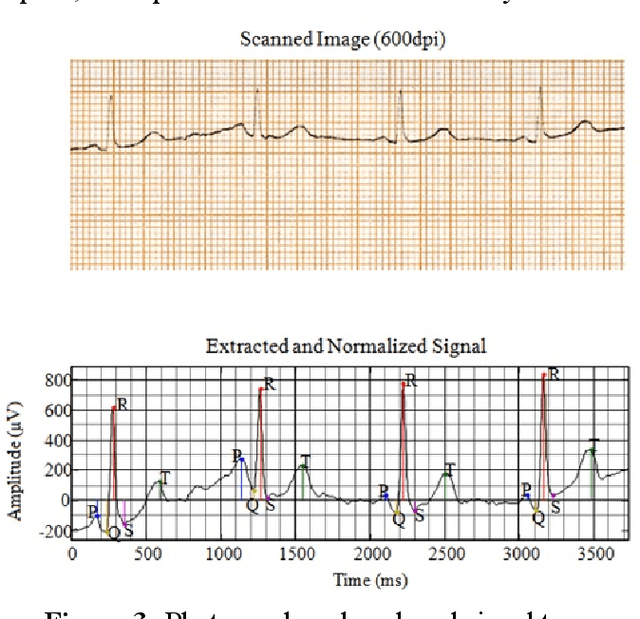
Abstract:Mobile cloud computing is an emerging field that is gaining popularity across borders at a rapid pace. Similarly, the field of health informatics is also considered as an extremely important field. This work observes the collaboration between these two fields to solve the traditional problem of extracting Electrocardiogram signals from trace reports and then performing analysis. The developed system has two front ends, the first dedicated for the user to perform the photographing of the trace report. Once the photographing is complete, mobile computing is used to extract the signal. Once the signal is extracted, it is uploaded into the server and further analysis is performed on the signal in the cloud. Once this is done, the second interface, intended for the use of the physician, can download and view the trace from the cloud. The data is securely held using a password-based authentication method. The system presented here is one of the first attempts at delivering the total solution, and after further upgrades, it will be possible to deploy the system in a commercial setting.
Resource-Aware Network Topology Management Framework
Feb 26, 2020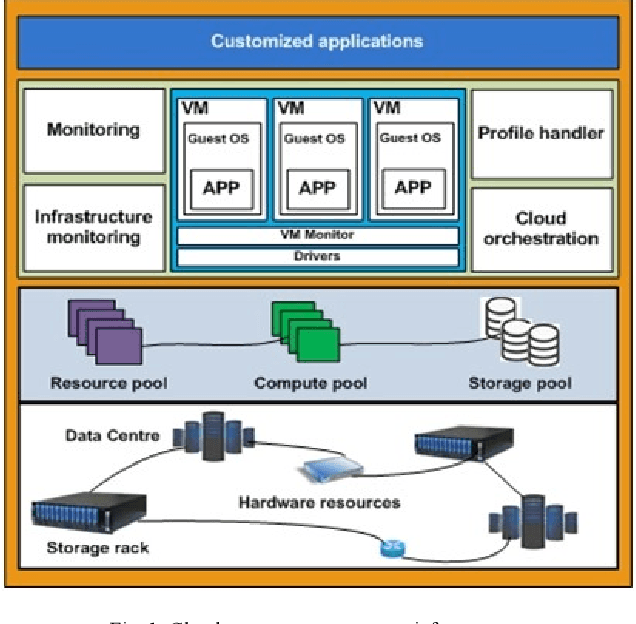
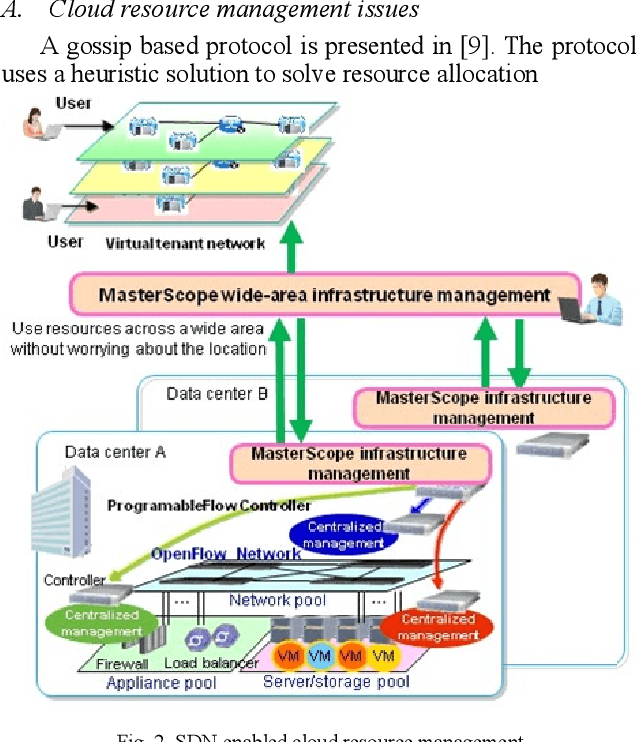
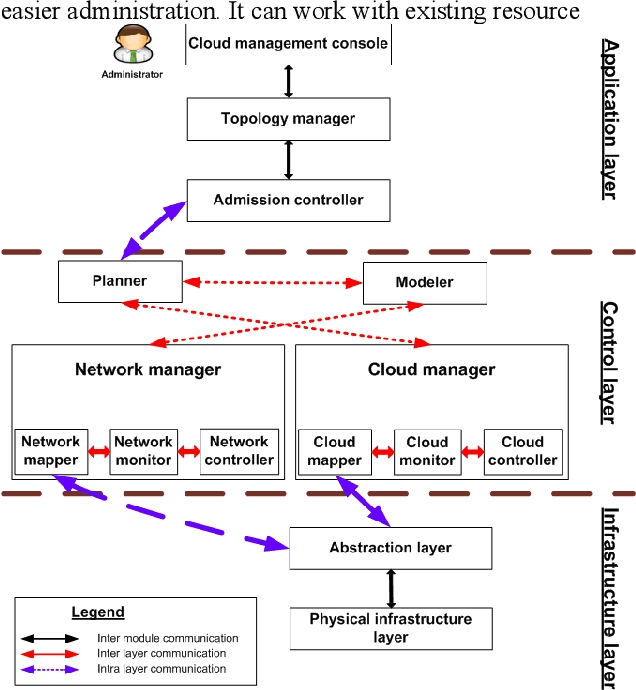
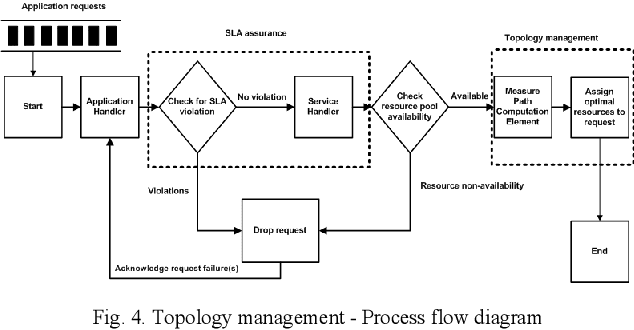
Abstract:Cloud infrastructure provides computing services where computing resources can be adjusted on-demand. However, the adoption of cloud infrastructures brings concerns like reliance on the service provider network, reliability, compliance for service level agreements. Software-defined networking (SDN) is a networking concept that suggests the segregation of a network data plane from the control plane. This concept improves networking behavior. In this paper, we present an SDN-enabled resource-aware topology framework. The proposed framework employs SLA compliance, Path Computation Element (PCE) and shares fair loading to achieve better topology features. We also present an evaluation, showcasing the potential of our framework.
Application of ERA5 and MENA simulations to predict offshore wind energy potential
Feb 24, 2020



Abstract:This study explores wind energy resources in different locations through the Gulf of Oman and also their future variability due climate change impacts. In this regard, EC-EARTH near surface wind outputs obtained from CORDEX-MENA simulations are used for historical and future projection of the energy. The ERA5 wind data are employed to assess suitability of the climate model. Moreover, the ERA5 wave data over the study area are applied to compute sea surface roughness as an important variable for converting near surface wind speeds to those of wind speed at turbine hub-height. Considering the power distribution, bathymetry and distance from the coats, some spots as tentative energy hotspots to provide detailed assessment of directional and temporal variability and also to investigate climate change impact studies. RCP8.5 as a common climatic scenario is used to project and extract future variation of the energy in the selected sites. The results of this study demonstrate that the selected locations have a suitable potential for wind power turbine plan and constructions.
Prediction of flow characteristics in the bubble column reactor by the artificial pheromone-based communication of biological ants
Jan 09, 2020



Abstract:In order to perceive the behavior presented by the multiphase chemical reactors, the ant colony optimization algorithm was combined with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) data. This intelligent algorithm creates a probabilistic technique for computing flow and it can predict various levels of three-dimensional bubble column reactor (BCR). This artificial ant algorithm is mimicking real ant behavior. This method can anticipate the flow characteristics in the reactor using almost 30 % of the whole data in the domain. Following discovering the suitable parameters, the method is used for predicting the points not being simulated with CFD, which represent mesh refinement of Ant colony method. In addition, it is possible to anticipate the bubble-column reactors in the absence of numerical results or training of exact values of evaluated data. The major benefits include reduced computational costs and time savings. The results show a great agreement between ant colony prediction and CFD outputs in different sections of the BCR. The combination of ant colony system and neural network framework can provide the smart structure to estimate biological and nature physics base phenomena. The ant colony optimization algorithm (ACO) framework based on ant behavior can solve all local mathematical answers throughout 3D bubble column reactor. The integration of all local answers can provide the overall solution in the reactor for different characteristics. This new overview of modelling can illustrate new sight into biological behavior in nature.
Modeling Climate Change Impact on Wind Power Resources Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
Jan 09, 2020



Abstract:Climate change impacts and adaptations are the subjects to ongoing issues that attract the attention of many researchers. Insight into the wind power potential in an area and its probable variation due to climate change impacts can provide useful information for energy policymakers and strategists for sustainable development and management of the energy. In this study, spatial variation of wind power density at the turbine hub-height and its variability under future climatic scenarios are taken under consideration. An ANFIS based post-processing technique was employed to match the power outputs of the regional climate model with those obtained from the reference data. The near-surface wind data obtained from a regional climate model are employed to investigate climate change impacts on the wind power resources in the Caspian Sea. Subsequent to converting near-surface wind speed to turbine hub-height speed and computation of wind power density, the results have been investigated to reveal mean annual power, seasonal, and monthly variability for a 20-year period in the present (1981-2000) and in the future (2081-2100). The findings of this study indicated that the middle and northern parts of the Caspian Sea are placed with the highest values of wind power. However, the results of the post-processing technique using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) model showed that the real potential of the wind power in the area is lower than those of projected from the regional climate model.
Modeling Daily Pan Evaporation in Humid Climates Using Gaussian Process Regression
Aug 01, 2019



Abstract:Evaporation is one of the main processes in the hydrological cycle, and it is one of the most critical factors in agricultural, hydrological, and meteorological studies. Due to the interactions of multiple climatic factors, the evaporation is a complex and nonlinear phenomenon; therefore, the data-based methods can be used to have precise estimations of it. In this regard, in the present study, Gaussian Process Regression, Nearest-Neighbor, Random Forest and Support Vector Regression were used to estimate the pan evaporation in the meteorological stations of Golestan Province, Iran. For this purpose, meteorological data including PE, temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and sunny hours collected from the Gonbad-e Kavus, Gorgan and Bandar Torkman stations from 2011 through 2017. The accuracy of the studied methods was determined using the statistical indices of Root Mean Squared Error, correlation coefficient and Mean Absolute Error. Furthermore, the Taylor charts utilized for evaluating the accuracy of the mentioned models. We report that GPR for Gonbad-e Kavus Station with input parameters of T, W and S and GPR for Gorgan and Bandar Torkmen stations with input parameters of T, RH, W, and S had the most accurate performances and proposed for precise estimation of PE. Due to the high rate of evaporation in Iran and the lack of measurement instruments, the findings of the current study indicated that the PE values might be estimated with few easily measured meteorological parameters accurately.
A New Malware Detection System Using a High Performance-ELM method
Jun 27, 2019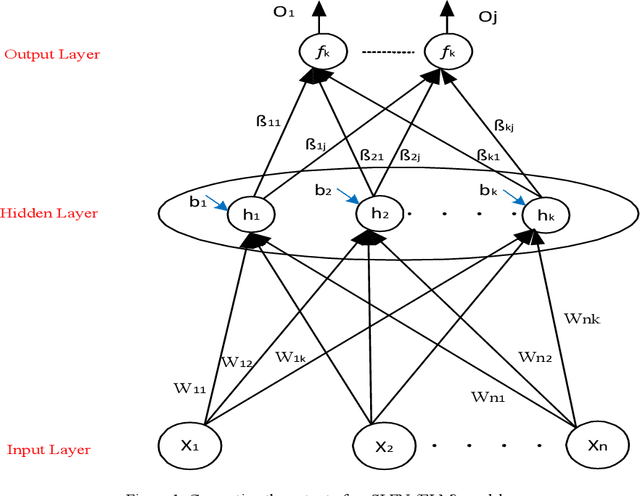
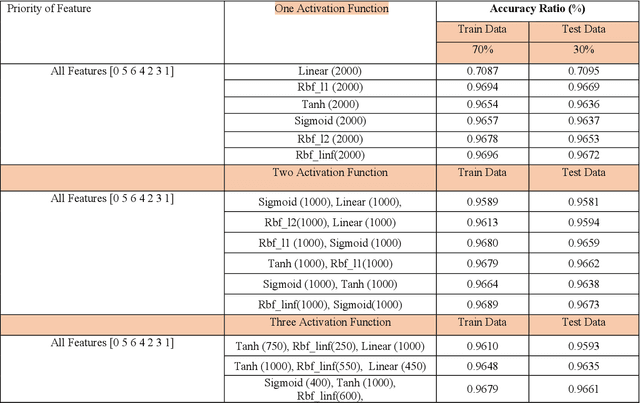
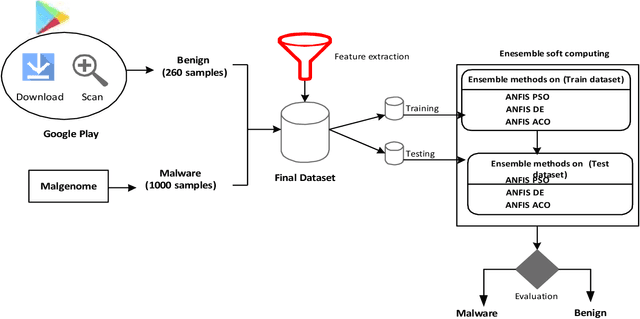
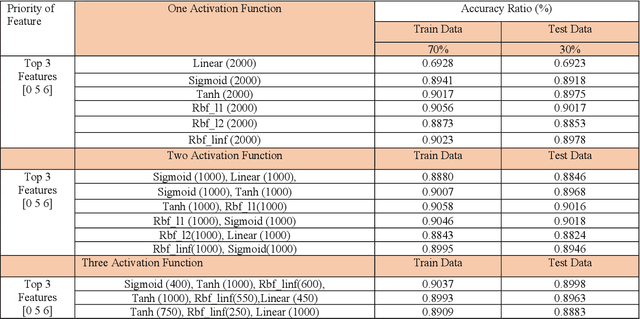
Abstract:A vital element of a cyberspace infrastructure is cybersecurity. Many protocols proposed for security issues, which leads to anomalies that affect the related infrastructure of cyberspace. Machine learning (ML) methods used to mitigate anomalies behavior in mobile devices. This paper aims to apply a High Performance Extreme Learning Machine (HP-ELM) to detect possible anomalies in two malware datasets. Two widely used datasets (the CTU-13 and Malware) are used to test the effectiveness of HP-ELM. Extensive comparisons are carried out in order to validate the effectiveness of the HP-ELM learning method. The experiment results demonstrate that the HP-ELM was the highest accuracy of performance of 0.9592 for the top 3 features with one activation function.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge