Alireza Baghban
Comparative analysis of machine learning models for Ammonia Capture of Ionic Liquids
Feb 19, 2020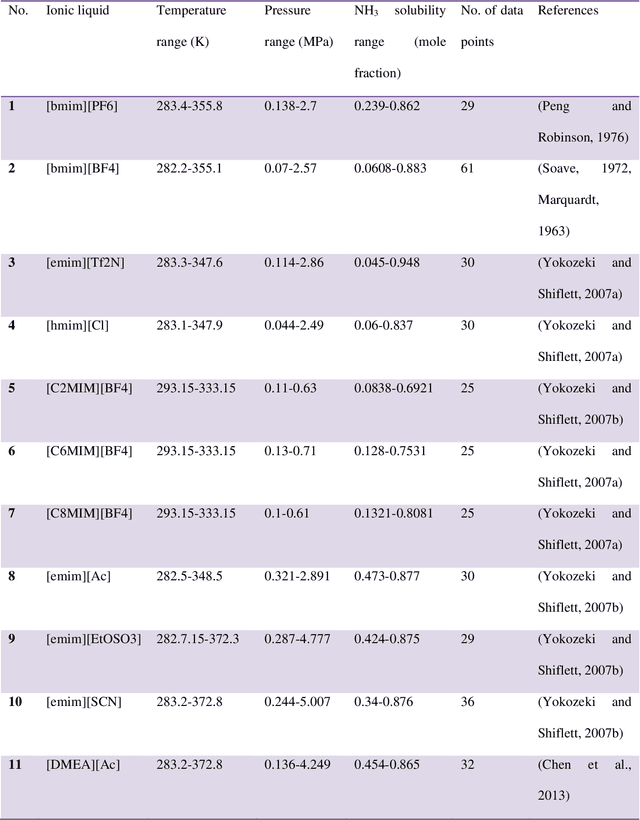
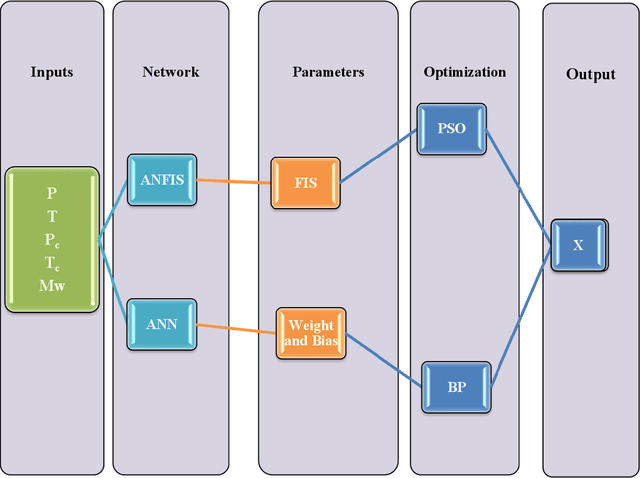
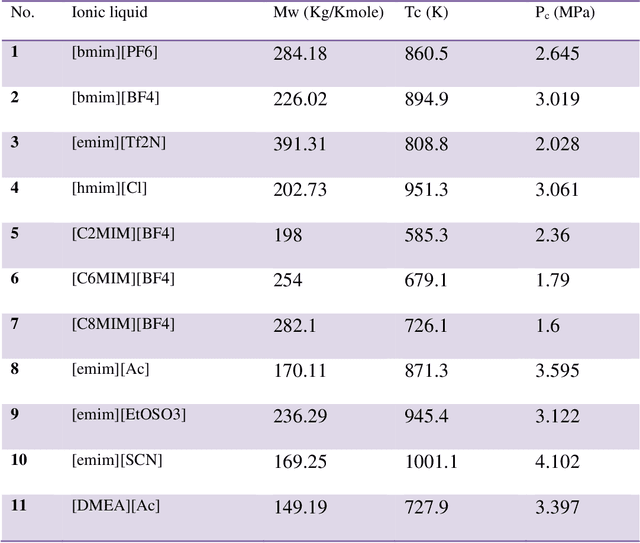
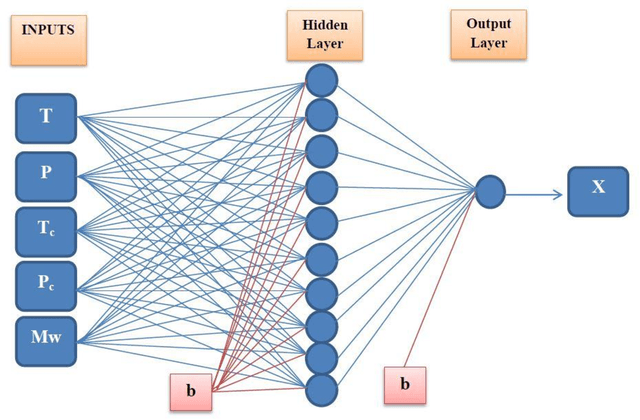
Abstract:Industry uses various solvents in the processes of refrigeration and ventilation. Among them, the Ionic liquids (ILs) as the relatively new solvents, are known for their proven eco-friendly characteristics. In this research, a comprehensive literature review was carried out to deliver an insight into the ILs and the prediction models used for estimating the ammonia solubility in ILs. Furthermore, a number of advanced machine learning methods, i.e. multilayer perceptron (MLP) and a combination of particle swarm optimization (PSO) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) models are used to estimate the solubility of ammonia in various ionic liquids. Affecting parameters were molecular weight, critical temperature and pressure of ILs. Furthermore, the salability is also predicted using the two-equation of states. Down the line, some comparisons were drawn between experimental and modeling results which is rarely done. The study shows that the equations of states are not able estimate the solubility of ammonia accurately, by contrast, artificial intelligence methods have produced promising results.
Evaluation of electrical efficiency of photovoltaic thermal solar collector
Feb 11, 2020



Abstract:Solar energy is a renewable resource of energy that is broadly utilized and has the least emissions among renewable energies. In this study, machine learning methods of artificial neural networks (ANNs), least squares support vector machines (LSSVM), and neuro-fuzzy are used for advancing prediction models for the thermal performance of a photovoltaic-thermal solar collector (PV/T). In the proposed models, the inlet temperature, flow rate, heat, solar radiation, and the sun heat have been considered as the inputs variables. Data set has been extracted through experimental measurements from a novel solar collector system. Different analyses are performed to examine the credibility of the introduced approaches and evaluate their performance. The proposed LSSVM model outperformed ANFIS and ANNs models. LSSVM model is reported suitable when the laboratory measurements are costly and time-consuming, or achieving such values requires sophisticated interpretations.
Applying ANN, ANFIS, and LSSVM Models for Estimation of Acid Solvent Solubility in Supercritical CO$_2$
Nov 21, 2019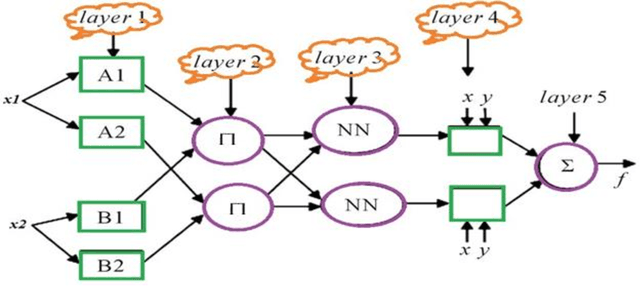
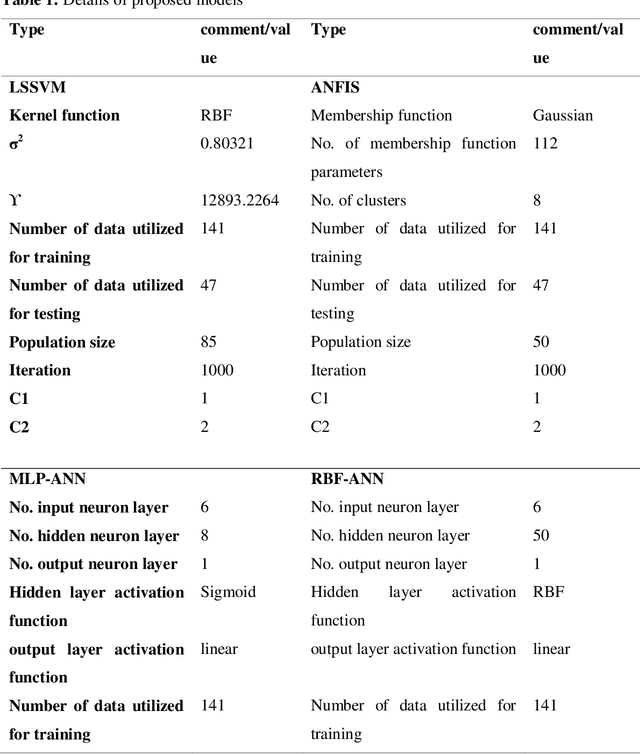
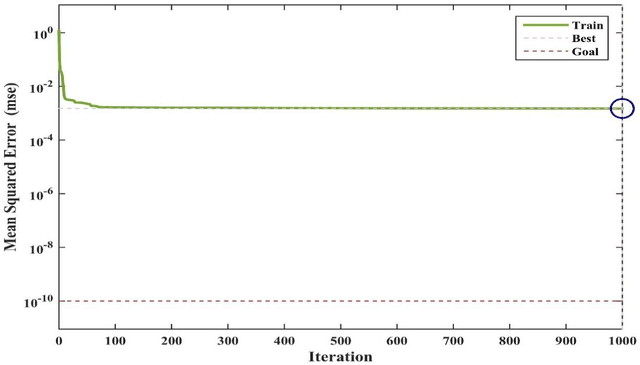
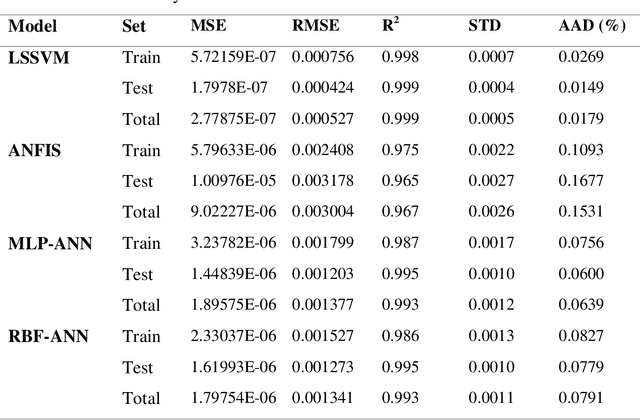
Abstract:In the present work, a novel and the robust computational investigation is carried out to estimate solubility of different acids in supercritical carbon dioxide. Four different algorithms such as radial basis function artificial neural network, Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network (ANN), Least squares support vector machine (LSSVM) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) are developed to predict the solubility of different acids in carbon dioxide based on the temperature, pressure, hydrogen number, carbon number, molecular weight, and acid dissociation constant of acid. In the purpose of best evaluation of proposed models, different graphical and statistical analyses and also a novel sensitivity analysis are carried out. The present study proposed the great manners for best acid solubility estimation in supercritical carbon dioxide, which can be helpful for engineers and chemists to predict operational conditions in industries.
Developing an ANFIS PSO Model to Estimate Mercury Emission in Combustion Flue Gases
Sep 16, 2019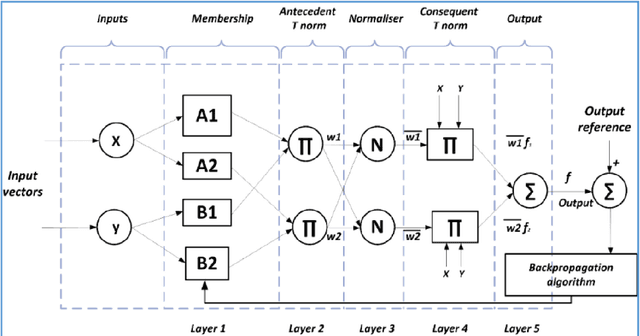

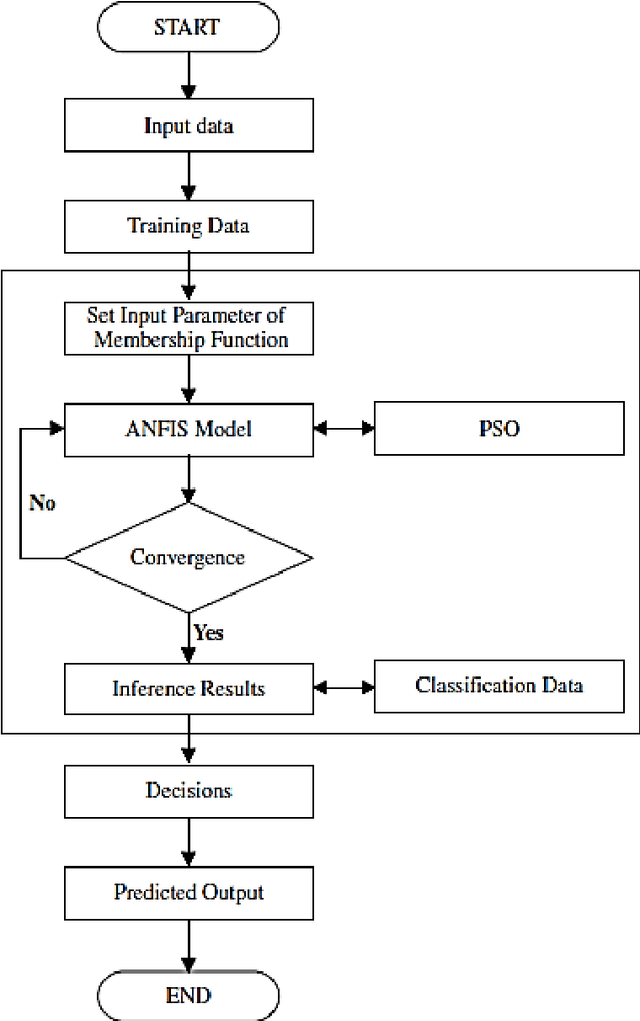
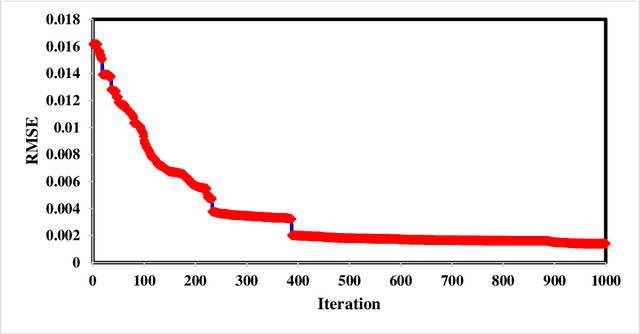
Abstract:Accurate prediction of mercury content emitted from fossil fueled power stations is of utmost important for environmental pollution assessment and hazard mitigation. In this paper, mercury content in the output gas of power stations boilers was predicted using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system method integrated with particle swarm optimization. The input parameters of the model include coal characteristics and the operational parameters of the boilers. The dataset has been collected from a number of power plants and employed to educate and examine the proposed model. To evaluate the performance of the proposed ANFIS PSO model the statistical meter of MARE was implemented. Furthermore, relative errors between acquired data and predicted values presented, which confirm the accuracy of the model to deal nonlinearity and representing the dependency of flue gas mercury content into the specifications of coal and the boiler type.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge