Annalena Aicher
Fostering User Engagement in the Critical Reflection of Arguments
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:A natural way to resolve different points of view and form opinions is through exchanging arguments and knowledge. Facing the vast amount of available information on the internet, people tend to focus on information consistent with their beliefs. Especially when the issue is controversial, information is often selected that does not challenge one's beliefs. To support a fair and unbiased opinion-building process, we propose a chatbot system that engages in a deliberative dialogue with a human. In contrast to persuasive systems, the envisioned chatbot aims to provide a diverse and representative overview - embedded in a conversation with the user. To account for a reflective and unbiased exploration of the topic, we enable the system to intervene if the user is too focused on their pre-existing opinion. Therefore we propose a model to estimate the users' reflective engagement (RUE), defined as their critical thinking and open-mindedness. We report on a user study with 58 participants to test our model and the effect of the intervention mechanism, discuss the implications of the results, and present perspectives for future work. The results show a significant effect on both user reflection and total user focus, proving our proposed approach's validity.
Natural Language Understanding for Argumentative Dialogue Systems in the Opinion Building Domain
Mar 03, 2021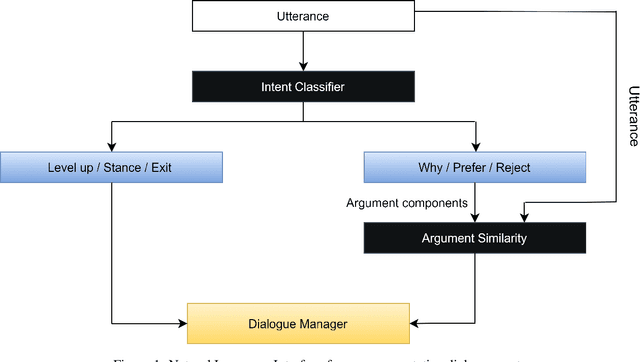
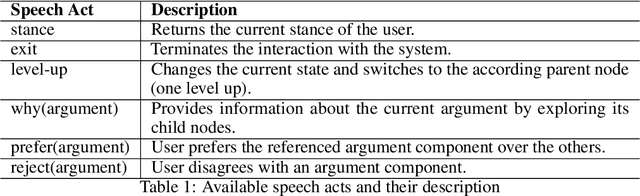
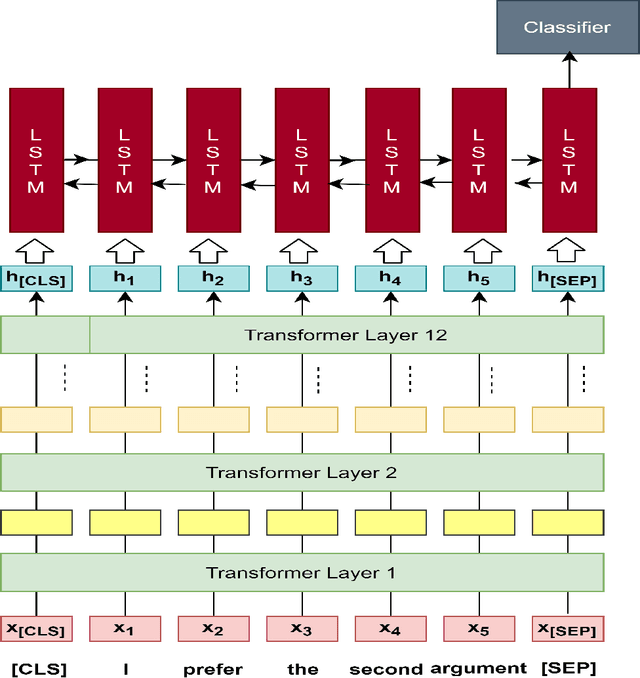

Abstract:This paper introduces a natural language understanding (NLU) framework for argumentative dialogue systems in the information-seeking and opinion building domain. Our approach distinguishes multiple user intents and identifies system arguments the user refers to in his or her natural language utterances. Our model is applicable in an argumentative dialogue system that allows the user to inform him-/herself about and build his/her opinion towards a controversial topic. In order to evaluate the proposed approach, we collect user utterances for the interaction with the respective system and labeled with intent and reference argument in an extensive online study. The data collection includes multiple topics and two different user types (native speakers from the UK and non-native speakers from China). The evaluation indicates a clear advantage of the utilized techniques over baseline approaches, as well as a robustness of the proposed approach against new topics and different language proficiency as well as cultural background of the user.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge