Anja Philippsen
The world seems different in a social context: a neural network analysis of human experimental data
Mar 03, 2022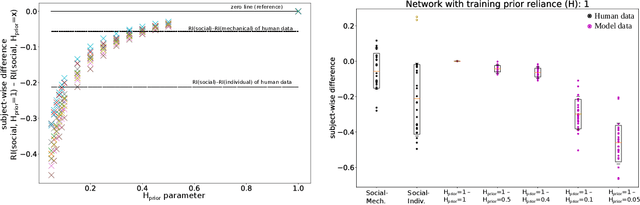
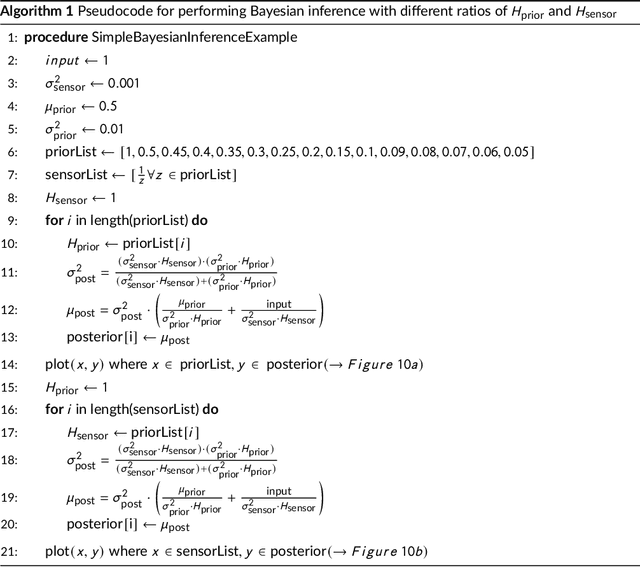
Abstract:Human perception and behavior are affected by the situational context, in particular during social interactions. A recent study demonstrated that humans perceive visual stimuli differently depending on whether they do the task by themselves or together with a robot. Specifically, it was found that the central tendency effect is stronger in social than in non-social task settings. The particular nature of such behavioral changes induced by social interaction, and their underlying cognitive processes in the human brain are, however, still not well understood. In this paper, we address this question by training an artificial neural network inspired by the predictive coding theory on the above behavioral data set. Using this computational model, we investigate whether the change in behavior that was caused by the situational context in the human experiment could be explained by continuous modifications of a parameter expressing how strongly sensory and prior information affect perception. We demonstrate that it is possible to replicate human behavioral data in both individual and social task settings by modifying the precision of prior and sensory signals, indicating that social and non-social task settings might in fact exist on a continuum. At the same time an analysis of the neural activation traces of the trained networks provides evidence that information is coded in fundamentally different ways in the network in the individual and in the social conditions. Our results emphasize the importance of computational replications of behavioral data for generating hypotheses on the underlying cognitive mechanisms of shared perception and may provide inspiration for follow-up studies in the field of neuroscience.
A Review on Neural Network Models of Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorder
Jun 24, 2019
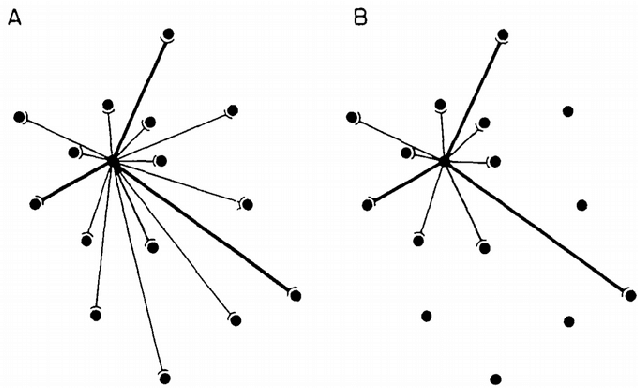
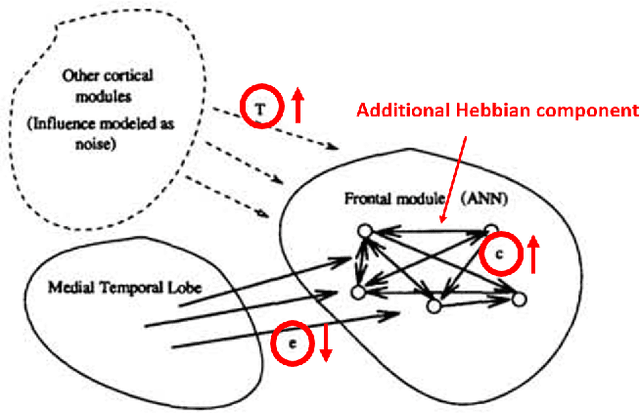
Abstract:This survey presents the most relevant neural network models of autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia, from the first connectionist models to recent deep network architectures. We analyzed and compared the most representative symptoms with its neural model counterpart, detailing the alteration introduced in the network that generates each of the symptoms, and identifying their strengths and weaknesses. For completeness we additionally cross-compared Bayesian and free-energy approaches. Models of schizophrenia mainly focused on hallucinations and delusional thoughts using neural disconnections or inhibitory imbalance as the predominating alteration. Models of autism rather focused on perceptual difficulties, mainly excessive attention to environment details, implemented as excessive inhibitory connections or increased sensory precision. We found an excessive tight view of the psychopathologies around one specific and simplified effect, usually constrained to the technical idiosyncrasy of the network used. Recent theories and evidence on sensorimotor integration and body perception combined with modern neural network architectures offer a broader and novel spectrum to approach these psychopathologies, outlining the future research on neural networks computational psychiatry, a powerful asset for understanding the inner processes of the human brain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge