Andre C. P. L. F. de Carvalho
Model interpretation using improved local regression with variable importance
Sep 12, 2022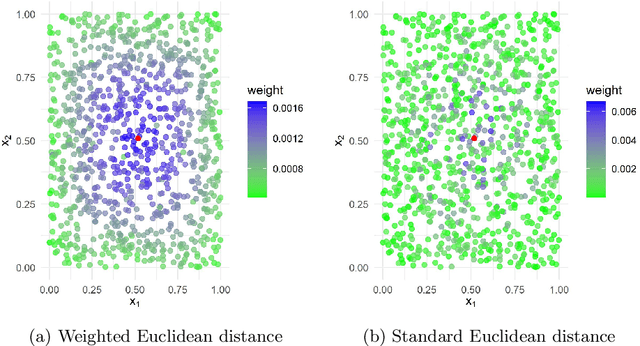
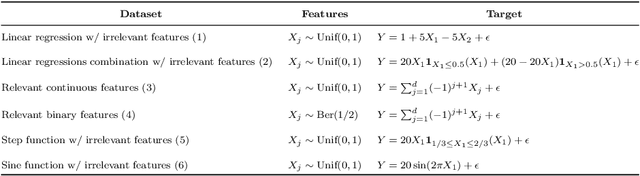
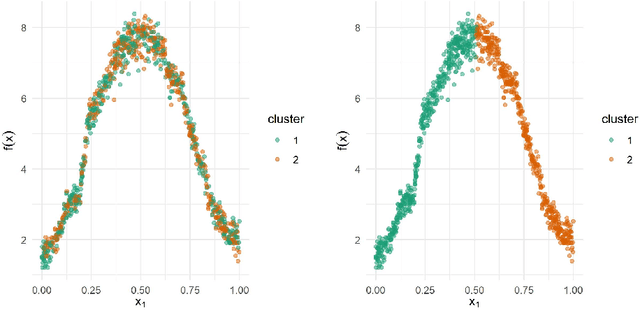
Abstract:A fundamental question on the use of ML models concerns the explanation of their predictions for increasing transparency in decision-making. Although several interpretability methods have emerged, some gaps regarding the reliability of their explanations have been identified. For instance, most methods are unstable (meaning that they give very different explanations with small changes in the data), and do not cope well with irrelevant features (that is, features not related to the label). This article introduces two new interpretability methods, namely VarImp and SupClus, that overcome these issues by using local regressions fits with a weighted distance that takes into account variable importance. Whereas VarImp generates explanations for each instance and can be applied to datasets with more complex relationships, SupClus interprets clusters of instances with similar explanations and can be applied to simpler datasets where clusters can be found. We compare our methods with state-of-the art approaches and show that it yields better explanations according to several metrics, particularly in high-dimensional problems with irrelevant features, as well as when the relationship between features and target is non-linear.
MeLIME: Meaningful Local Explanation for Machine Learning Models
Sep 12, 2020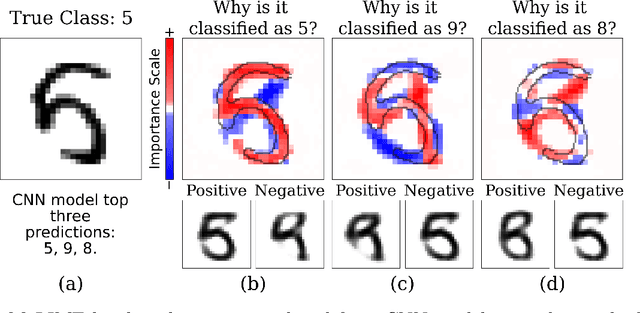
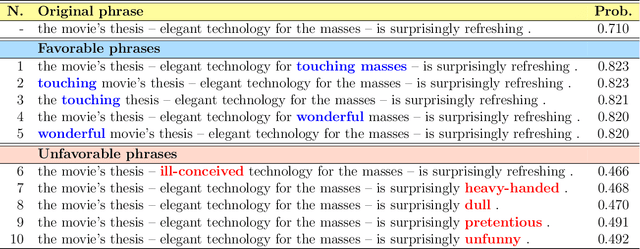
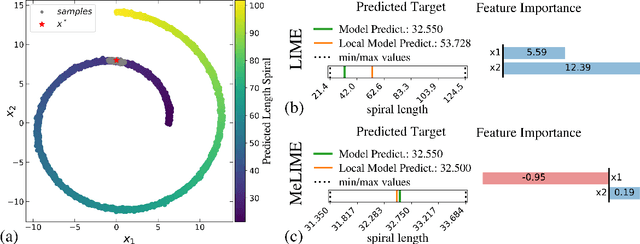
Abstract:Most state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms induce black-box models, preventing their application in many sensitive domains. Hence, many methodologies for explaining machine learning models have been proposed to address this problem. In this work, we introduce strategies to improve local explanations taking into account the distribution of the data used to train the black-box models. We show that our approach, MeLIME, produces more meaningful explanations compared to other techniques over different ML models, operating on various types of data. MeLIME generalizes the LIME method, allowing more flexible perturbation sampling and the use of different local interpretable models. Additionally, we introduce modifications to standard training algorithms of local interpretable models fostering more robust explanations, even allowing the production of counterfactual examples. To show the strengths of the proposed approach, we include experiments on tabular data, images, and text; all showing improved explanations. In particular, MeLIME generated more meaningful explanations on the MNIST dataset than methods such as GuidedBackprop, SmoothGrad, and Layer-wise Relevance Propagation. MeLIME is available on https://github.com/tiagobotari/melime.
Reconstructing commuters network using machine learning and urban indicators
Aug 09, 2019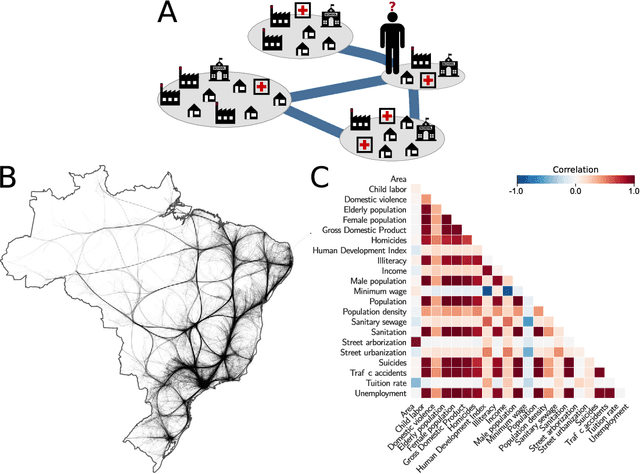
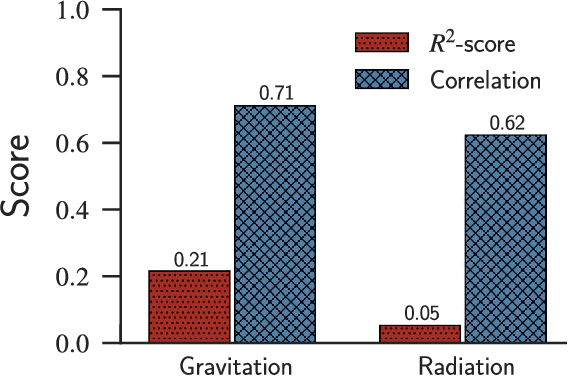
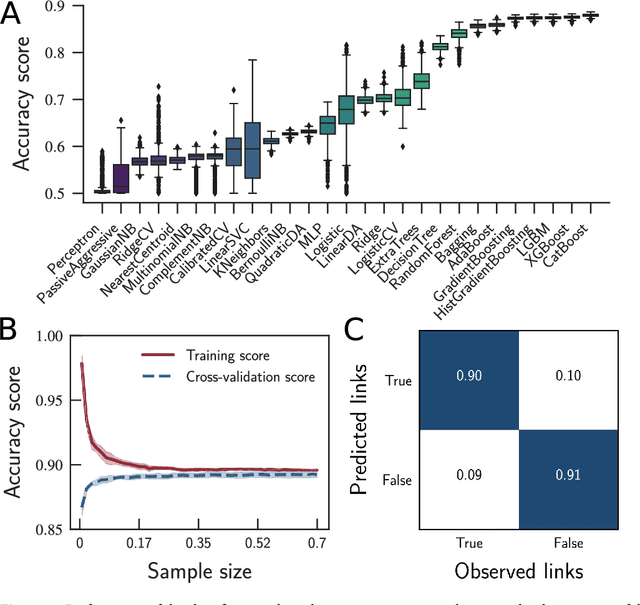
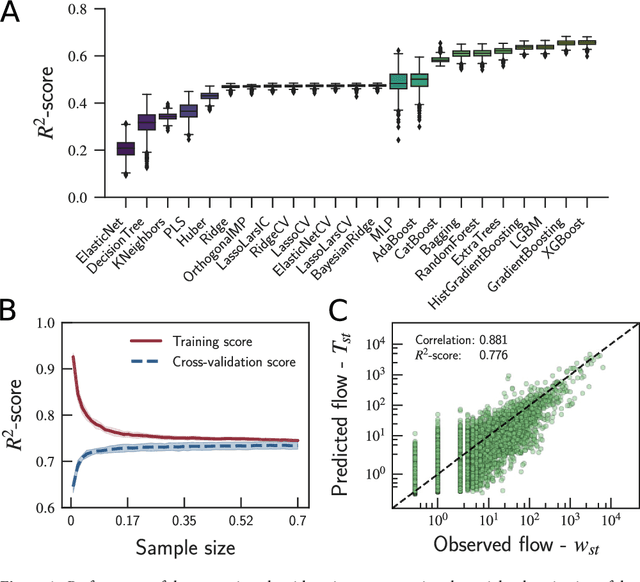
Abstract:Human mobility has a significant impact on several layers of society, from infrastructural planning and economics to the spread of diseases and crime. Representing the system as a complex network, in which nodes are assigned to regions (e.g., a city) and links indicate the flow of people between two of them, physics-inspired models have been proposed to quantify the number of people migrating from one city to the other. Despite the advances made by these models, our ability to predict the number of commuters and reconstruct mobility networks remains limited. Here, we propose an alternative approach using machine learning and 22 urban indicators to predict the flow of people and reconstruct the intercity commuters network. Our results reveal that predictions based on machine learning algorithms and urban indicators can reconstruct the commuters network with 90.4% of accuracy and describe 77.6% of the variance observed in the flow of people between cities. We also identify essential features to recover the network structure and the urban indicators mostly related to commuting patterns. As previously reported, distance plays a significant role in commuting, but other indicators, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and unemployment rate, are also driven-forces for people to commute. We believe that our results shed new lights on the modeling of migration and reinforce the role of urban indicators on commuting patterns. Also, because link-prediction and network reconstruction are still open challenges in network science, our results have implications in other areas, like economics, social sciences, and biology, where node attributes can give us information about the existence of links connecting entities in the network.
* 28 pages, 5 figures
Local Interpretation Methods to Machine Learning Using the Domain of the Feature Space
Jul 31, 2019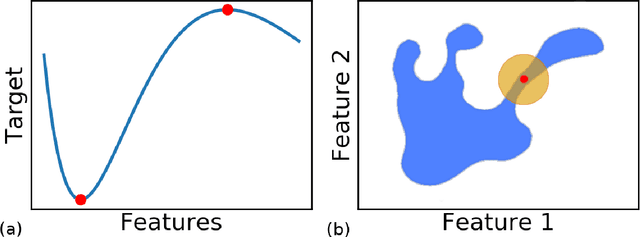
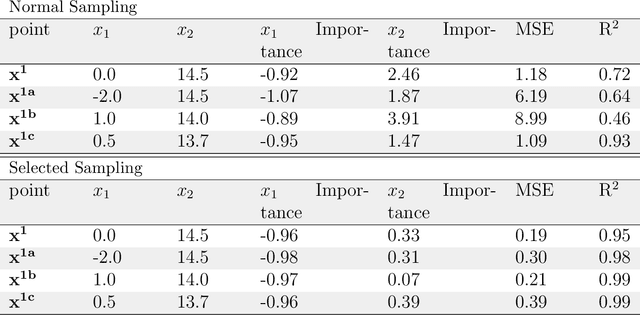
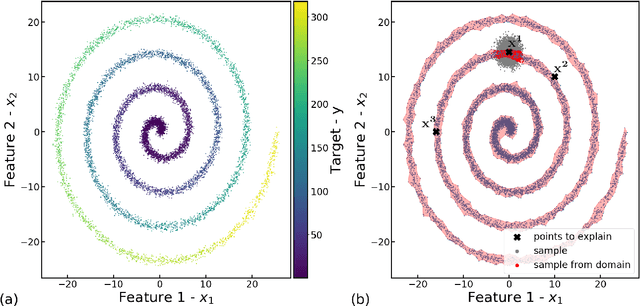
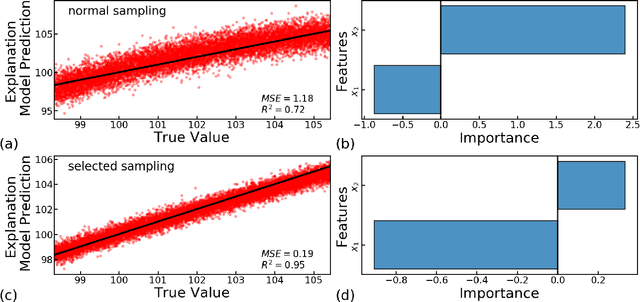
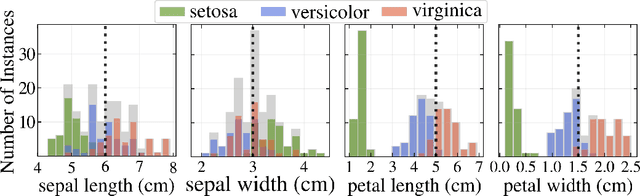
Abstract:As machine learning becomes an important part of many real world applications affecting human lives, new requirements, besides high predictive accuracy, become important. One important requirement is transparency, which has been associated with model interpretability. Many machine learning algorithms induce models difficult to interpret, named black box. Moreover, people have difficulty to trust models that cannot be explained. In particular for machine learning, many groups are investigating new methods able to explain black box models. These methods usually look inside the black models to explain their inner work. By doing so, they allow the interpretation of the decision making process used by black box models. Among the recently proposed model interpretation methods, there is a group, named local estimators, which are designed to explain how the label of particular instance is predicted. For such, they induce interpretable models on the neighborhood of the instance to be explained. Local estimators have been successfully used to explain specific predictions. Although they provide some degree of model interpretability, it is still not clear what is the best way to implement and apply them. Open questions include: how to best define the neighborhood of an instance? How to control the trade-off between the accuracy of the interpretation method and its interpretability? How to make the obtained solution robust to small variations on the instance to be explained? To answer to these questions, we propose and investigate two strategies: (i) using data instance properties to provide improved explanations, and (ii) making sure that the neighborhood of an instance is properly defined by taking the geometry of the domain of the feature space into account. We evaluate these strategies in a regression task and present experimental results that show that they can improve local explanations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge