Amritanshu Pandey
PowerChain: Automating Distribution Grid Analysis with Agentic AI Workflows
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Due to the rapid pace of electrification and decarbonization, distribution grid (DG) operation and planning are becoming more complex, necessitating advanced computational analyses to ensure grid reliability and resilience. State-of-the-art DG analyses rely on disparate workflows of complex models, functions, and data pipelines, which require expert knowledge and are challenging to automate. Many small-scale utilities and cooperatives lack a large R&D workforce and therefore cannot use advanced analysis at scale. To address this gap, we develop a novel agentic AI system, PowerChain, to solve unseen DG analysis tasks via automated agentic orchestration and large language models (LLMs) function-calling. Given a natural language query, PowerChain dynamically generates and executes an ordered sequence of domain-aware functions guided by the semantics of an expert-built power systems function pool and a select reference set of known, expert-generated workflow-query pairs. Our results show that PowerChain can produce expert-level workflows with both GPT-5 and open-source Qwen models on complex, unseen DG analysis tasks operating on real utility data.
Unlearning Climate Misinformation in Large Language Models
May 29, 2024Abstract:Misinformation regarding climate change is a key roadblock in addressing one of the most serious threats to humanity. This paper investigates factual accuracy in large language models (LLMs) regarding climate information. Using true/false labeled Q&A data for fine-tuning and evaluating LLMs on climate-related claims, we compare open-source models, assessing their ability to generate truthful responses to climate change questions. We investigate the detectability of models intentionally poisoned with false climate information, finding that such poisoning may not affect the accuracy of a model's responses in other domains. Furthermore, we compare the effectiveness of unlearning algorithms, fine-tuning, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for factually grounding LLMs on climate change topics. Our evaluation reveals that unlearning algorithms can be effective for nuanced conceptual claims, despite previous findings suggesting their inefficacy in privacy contexts. These insights aim to guide the development of more factually reliable LLMs and highlight the need for additional work to secure LLMs against misinformation attacks.
Anomaly Detection in Power Grids via Context-Agnostic Learning
Apr 11, 2024Abstract:An important tool grid operators use to safeguard against failures, whether naturally occurring or malicious, involves detecting anomalies in the power system SCADA data. In this paper, we aim to solve a real-time anomaly detection problem. Given time-series measurement values coming from a fixed set of sensors on the grid, can we identify anomalies in the network topology or measurement data? Existing methods, primarily optimization-based, mostly use only a single snapshot of the measurement values and do not scale well with the network size. Recent data-driven ML techniques have shown promise by using a combination of current and historical data for anomaly detection but generally do not consider physical attributes like the impact of topology or load/generation changes on sensor measurements and thus cannot accommodate regular context-variability in the historical data. To address this gap, we propose a novel context-aware anomaly detection algorithm, GridCAL, that considers the effect of regular topology and load/generation changes. This algorithm converts the real-time power flow measurements to context-agnostic values, which allows us to analyze measurement coming from different grid contexts in an aggregate fashion, enabling us to derive a unified statistical model that becomes the basis of anomaly detection. Through numerical simulations on networks up to 2383 nodes, we show that our approach is accurate, outperforming state-of-the-art approaches, and is computationally efficient.
Towards Practical Physics-Informed ML Design and Evaluation for Power Grid
May 24, 2022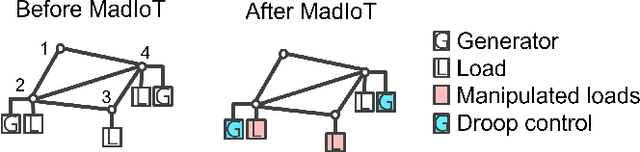

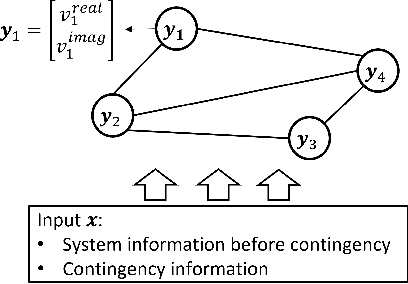
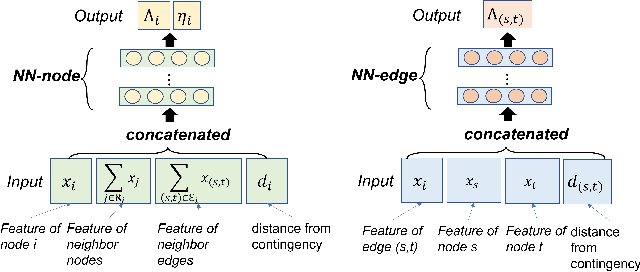
Abstract:When applied to a real-world safety critical system like the power grid, general machine learning methods suffer from expensive training, non-physical solutions, and limited interpretability. To address these challenges for power grids, many recent works have explored the inclusion of grid physics (i.e., domain expertise) into their method design, primarily through including system constraints and technical limits, reducing search space and defining meaningful features in latent space. Yet, there is no general methodology to evaluate the practicality of these approaches in power grid tasks, and limitations exist regarding scalability, generalization, interpretability, etc. This work formalizes a new concept of physical interpretability which assesses how a ML model makes predictions in a physically meaningful way and introduces an evaluation methodology that identifies a set of attributes that a practical method should satisfy. Inspired by the evaluation attributes, the paper further develops a novel contingency analysis warm starter for MadIoT cyberattack, based on a conditional Gaussian random field. This method serves as an instance of an ML model that can incorporate diverse domain knowledge and improve on these identified attributes. Experiments validate that the warm starter significantly boosts the efficiency of contingency analysis for MadIoT attack even with shallow NN architectures.
A Convex Method of Generalized State Estimation using Circuit-theoretic Node-breaker Model
Oct 07, 2021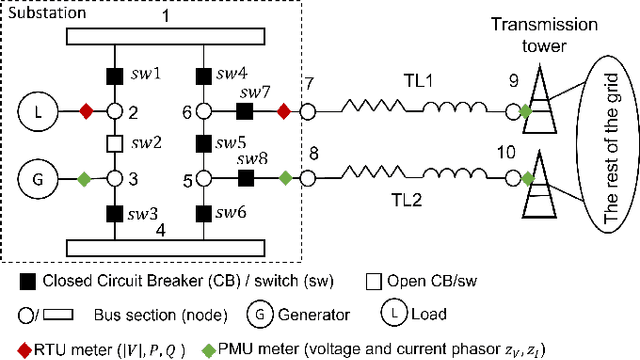
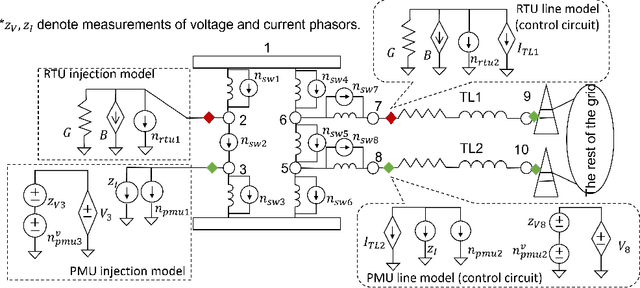
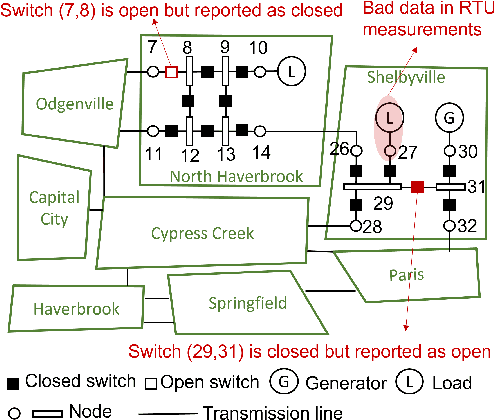
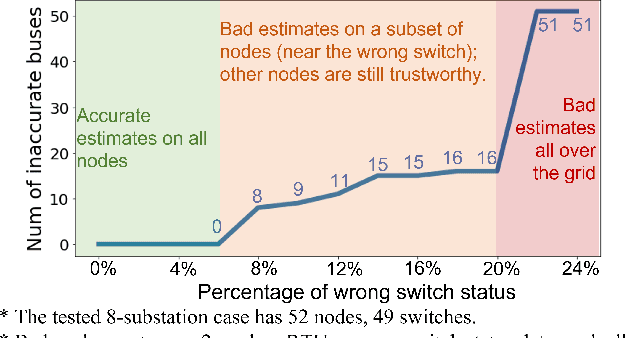
Abstract:An accurate and up-to-date grid topology is critical for situational awareness. However, it is non-trivial to obtain due to inaccurate switch status data caused by physical damage, communication error, or cyber-attack. This paper formulates a circuit-theoretic node-breaker (NB) model to create a generalized state estimation (GSE) method that is scalable and easily solvable for a practical grid with RTU and PMU measurements. We demonstrate that all switching devices (with discrete status) and meters (with continuous measurements) can be replaced with linear circuit models without relaxation so that the entire grid is mapped to an expanded linear circuit. Using this grid model, the state estimation is formulated as a Linear Programming (LP) problem whose solution includes a sparse vector of noise terms, which localizes suspicious wrong status and bad data separately. The proposed method provides the benefits of convexity and a reliable state estimation with intrinsic robustness against wrong switch status and bad measurement data.
Combined Transmission and Distribution State-Estimation for Future Electric Grids
May 14, 2021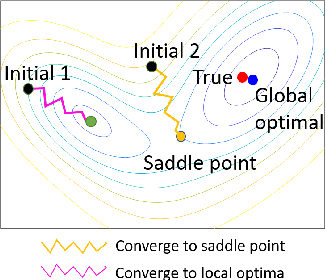
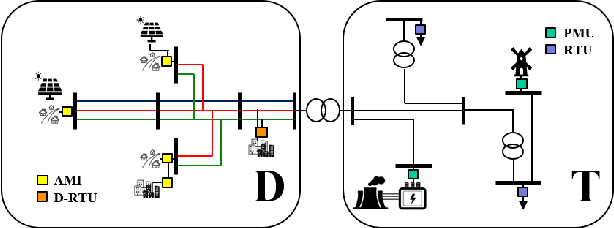
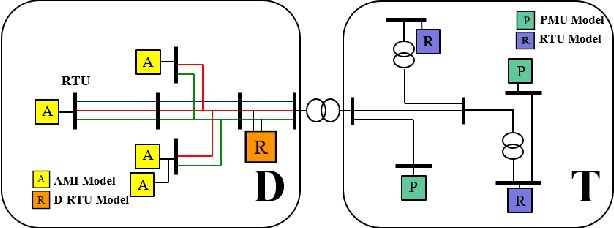
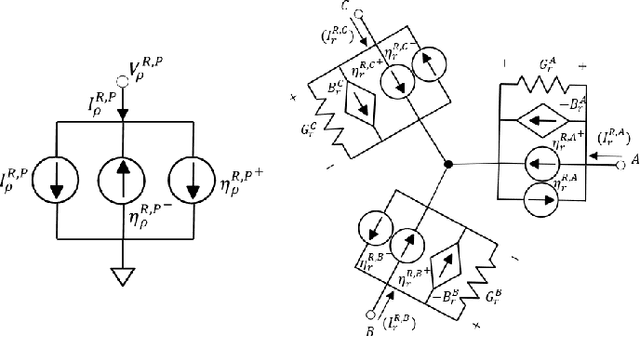
Abstract:Proliferation of grid resources on the distribution network along with the inability to forecast them accurately will render the existing methodology of grid operation and control untenable in the future. Instead, a more distributed yet coordinated approach for grid operation and control will emerge that models and analyzes the grid with a larger footprint and deeper hierarchy to unify control of disparate T&D grid resources under a common framework. Such approach will require AC state-estimation (ACSE) of joint T&D networks. Today, no practical method for realizing combined T&D ACSE exists. This paper addresses that gap from circuit-theoretic perspective through realizing a combined T&D ACSE solution methodology that is fast, convex and robust against bad-data. To address daunting challenges of problem size (million+ variables) and data-privacy, the approach is distributed both in memory and computing resources. To ensure timely convergence, the approach constructs a distributed circuit model for combined T&D networks and utilizes node-tearing techniques for efficient parallelism. To demonstrate the efficacy of the approach, combined T&D ACSE algorithm is run on large test networks that comprise of multiple T&D feeders. The results reflect the accuracy of the estimates in terms of root mean-square error and algorithm scalability in terms of wall-clock time.
Dynamic Graph-Based Anomaly Detection in the Electrical Grid
Jan 01, 2021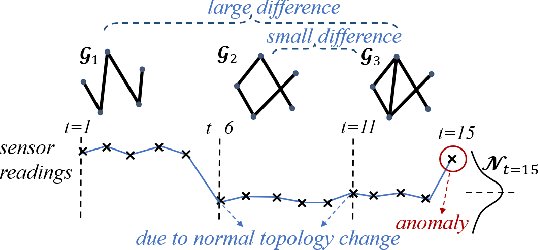
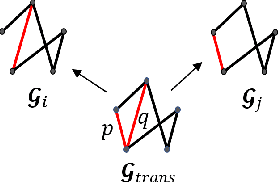
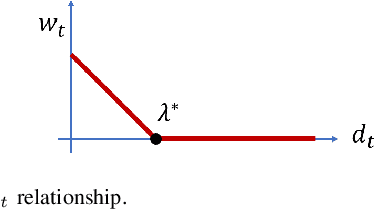
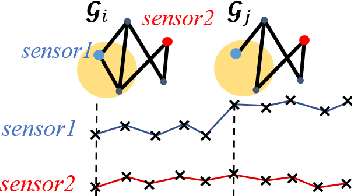
Abstract:Given sensor readings over time from a power grid, how can we accurately detect when an anomaly occurs? A key part of achieving this goal is to use the network of power grid sensors to quickly detect, in real-time, when any unusual events, whether natural faults or malicious, occur on the power grid. Existing bad-data detectors in the industry lack the sophistication to robustly detect broad types of anomalies, especially those due to emerging cyber-attacks, since they operate on a single measurement snapshot of the grid at a time. New ML methods are more widely applicable, but generally do not consider the impact of topology change on sensor measurements and thus cannot accommodate regular topology adjustments in historical data. Hence, we propose DYNWATCH, a domain knowledge based and topology-aware algorithm for anomaly detection using sensors placed on a dynamic grid. Our approach is accurate, outperforming existing approaches by 20% or more (F-measure) in experiments; and fast, running in less than 1.7ms on average per time tick per sensor on a 60K+ branch case using a laptop computer, and scaling linearly in the size of the graph.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge