Amanda Aird
Envy-Free but Still Unfair: Envy-Freeness Up To One Item (EF-1) in Personalized Recommendation
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Envy-freeness and the relaxation to Envy-freeness up to one item (EF-1) have been used as fairness concepts in the economics, game theory, and social choice literatures since the 1960s, and have recently gained popularity within the recommendation systems communities. In this short position paper we will give an overview of envy-freeness and its use in economics and recommendation systems; and illustrate why envy is not appropriate to measure fairness for use in settings where personalization plays a role.
Social Choice for Heterogeneous Fairness in Recommendation
Oct 06, 2024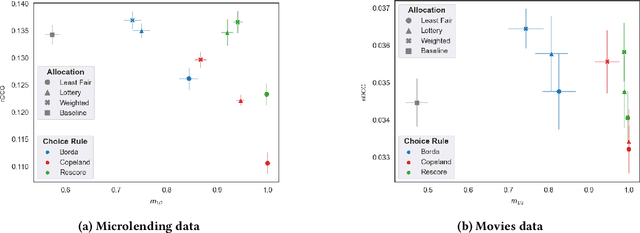
Abstract:Algorithmic fairness in recommender systems requires close attention to the needs of a diverse set of stakeholders that may have competing interests. Previous work in this area has often been limited by fixed, single-objective definitions of fairness, built into algorithms or optimization criteria that are applied to a single fairness dimension or, at most, applied identically across dimensions. These narrow conceptualizations limit the ability to adapt fairness-aware solutions to the wide range of stakeholder needs and fairness definitions that arise in practice. Our work approaches recommendation fairness from the standpoint of computational social choice, using a multi-agent framework. In this paper, we explore the properties of different social choice mechanisms and demonstrate the successful integration of multiple, heterogeneous fairness definitions across multiple data sets.
Exploring Social Choice Mechanisms for Recommendation Fairness in SCRUF
Sep 10, 2023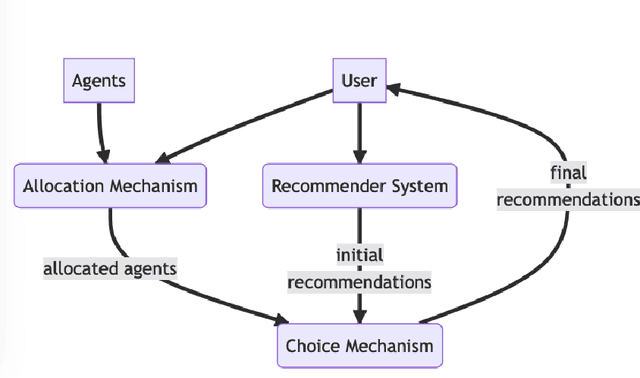
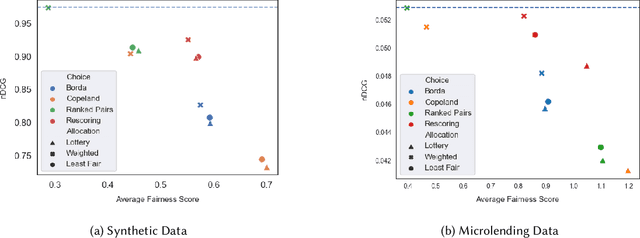
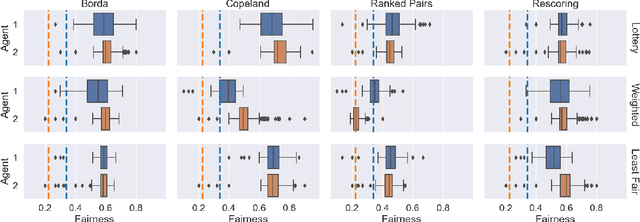
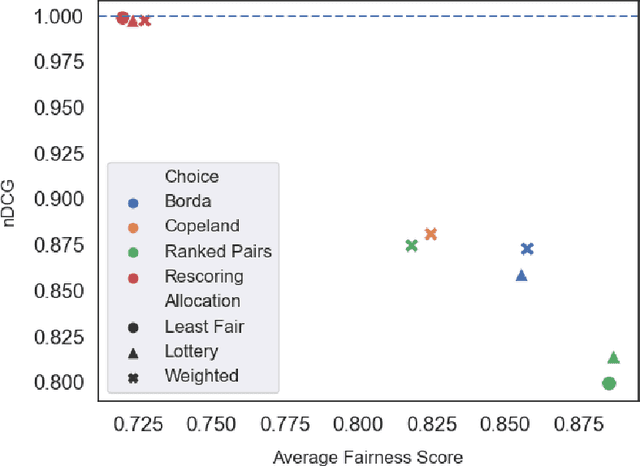
Abstract:Fairness problems in recommender systems often have a complexity in practice that is not adequately captured in simplified research formulations. A social choice formulation of the fairness problem, operating within a multi-agent architecture of fairness concerns, offers a flexible and multi-aspect alternative to fairness-aware recommendation approaches. Leveraging social choice allows for increased generality and the possibility of tapping into well-studied social choice algorithms for resolving the tension between multiple, competing fairness concerns. This paper explores a range of options for choice mechanisms in multi-aspect fairness applications using both real and synthetic data and shows that different classes of choice and allocation mechanisms yield different but consistent fairness / accuracy tradeoffs. We also show that a multi-agent formulation offers flexibility in adapting to user population dynamics.
Dynamic fairness-aware recommendation through multi-agent social choice
Mar 03, 2023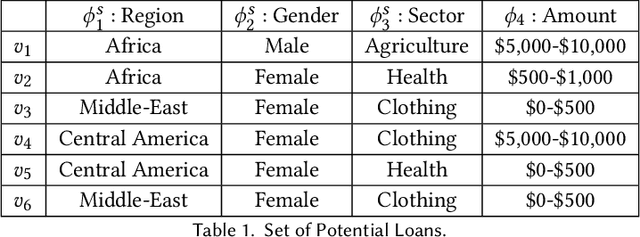


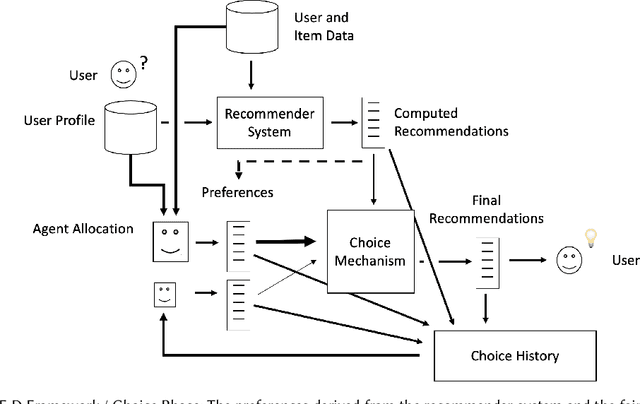
Abstract:Algorithmic fairness in the context of personalized recommendation presents significantly different challenges to those commonly encountered in classification tasks. Researchers studying classification have generally considered fairness to be a matter of achieving equality of outcomes between a protected and unprotected group, and built algorithmic interventions on this basis. We argue that fairness in real-world application settings in general, and especially in the context of personalized recommendation, is much more complex and multi-faceted, requiring a more general approach. We propose a model to formalize multistakeholder fairness in recommender systems as a two stage social choice problem. In particular, we express recommendation fairness as a novel combination of an allocation and an aggregation problem, which integrate both fairness concerns and personalized recommendation provisions, and derive new recommendation techniques based on this formulation. Simulations demonstrate the ability of the framework to integrate multiple fairness concerns in a dynamic way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge