Ali Bilgin
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, Department of Medical Imaging, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona
Learning to segment with limited annotations: Self-supervised pretraining with regression and contrastive loss in MRI
May 26, 2022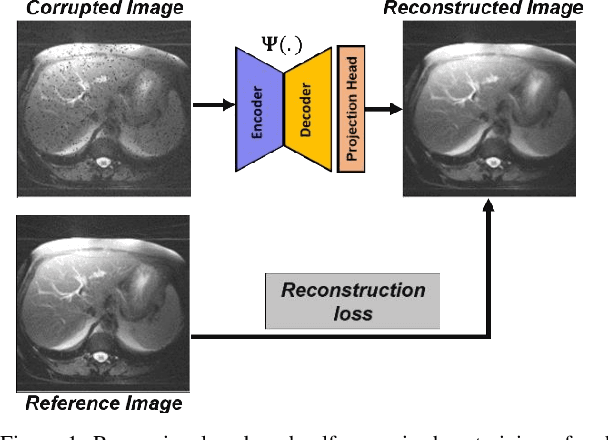
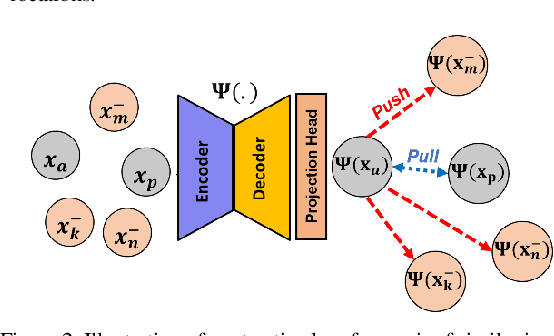
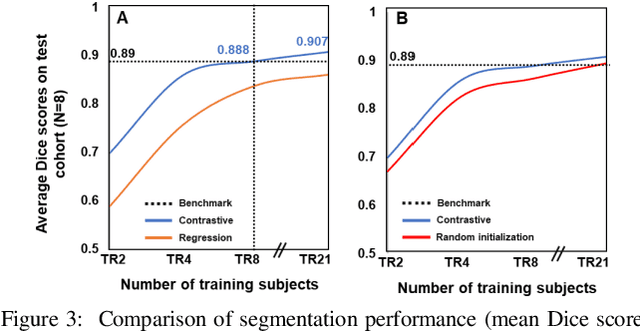
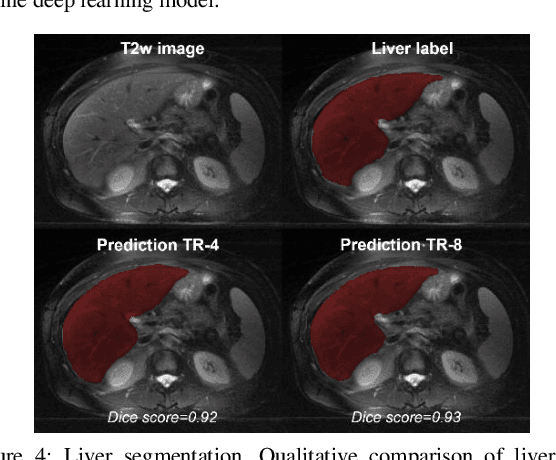
Abstract:Obtaining manual annotations for large datasets for supervised training of deep learning (DL) models is challenging. The availability of large unlabeled datasets compared to labeled ones motivate the use of self-supervised pretraining to initialize DL models for subsequent segmentation tasks. In this work, we consider two pre-training approaches for driving a DL model to learn different representations using: a) regression loss that exploits spatial dependencies within an image and b) contrastive loss that exploits semantic similarity between pairs of images. The effect of pretraining techniques is evaluated in two downstream segmentation applications using Magnetic Resonance (MR) images: a) liver segmentation in abdominal T2-weighted MR images and b) prostate segmentation in T2-weighted MR images of the prostate. We observed that DL models pretrained using self-supervision can be finetuned for comparable performance with fewer labeled datasets. Additionally, we also observed that initializing the DL model using contrastive loss based pretraining performed better than the regression loss.
A Cascaded Residual UNET for Fully Automated Segmentation of Prostate and Peripheral Zone in T2-weighted 3D Fast Spin Echo Images
Dec 25, 2020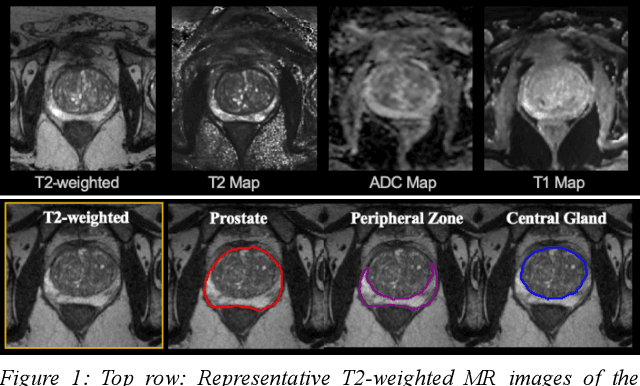
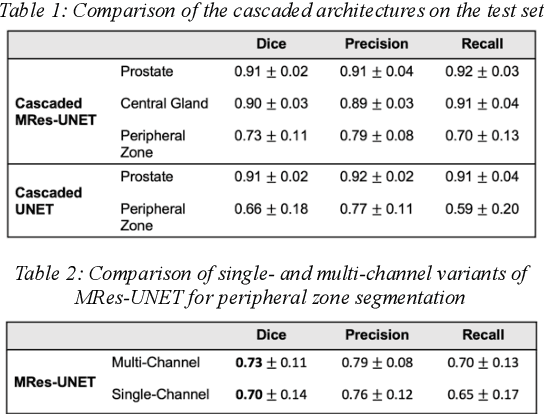
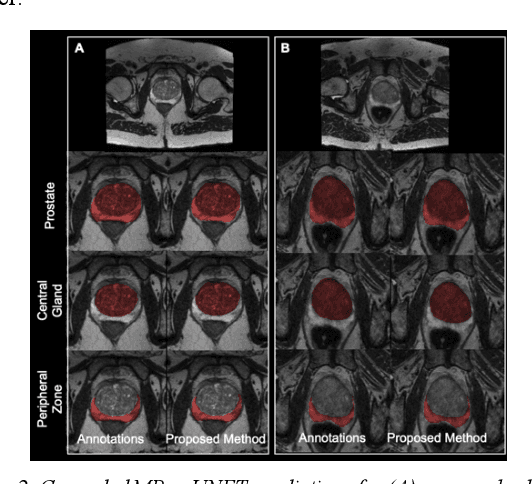
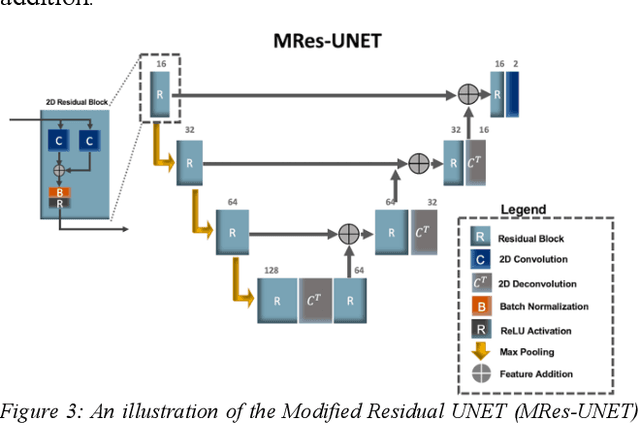
Abstract:Multi-parametric MR images have been shown to be effective in the non-invasive diagnosis of prostate cancer. Automated segmentation of the prostate eliminates the need for manual annotation by a radiologist which is time consuming. This improves efficiency in the extraction of imaging features for the characterization of prostate tissues. In this work, we propose a fully automated cascaded deep learning architecture with residual blocks, Cascaded MRes-UNET, for segmentation of the prostate gland and the peripheral zone in one pass through the network. The network yields high Dice scores ($0.91\pm.02$), precision ($0.91\pm.04$), and recall scores ($0.92\pm.03$) in prostate segmentation compared to manual annotations by an experienced radiologist. The average difference in total prostate volume estimation is less than 5%.
White matter hyperintensities volume and cognition: Assessment of a deep learning based lesion detection and quantification algorithm on the Alzheimers Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
Dec 24, 2020



Abstract:The relationship between cognition and white matter hyperintensities (WMH) volumes often depends on the accuracy of the lesion segmentation algorithm used. As such, accurate detection and quantification of WMH is of great interest. Here, we use a deep learning-based WMH segmentation algorithm, StackGen-Net, to detect and quantify WMH on 3D FLAIR volumes from ADNI. We used a subset of subjects (n=20) and obtained manual WMH segmentations by an experienced neuro-radiologist to demonstrate the accuracy of our algorithm. On a larger cohort of subjects (n=290), we observed that larger WMH volumes correlated with worse performance on executive function (P=.004), memory (P=.01), and language (P=.005).
A Contrast Synthesized Thalamic Nuclei Segmentation Scheme using Convolutional Neural Networks
Dec 17, 2020


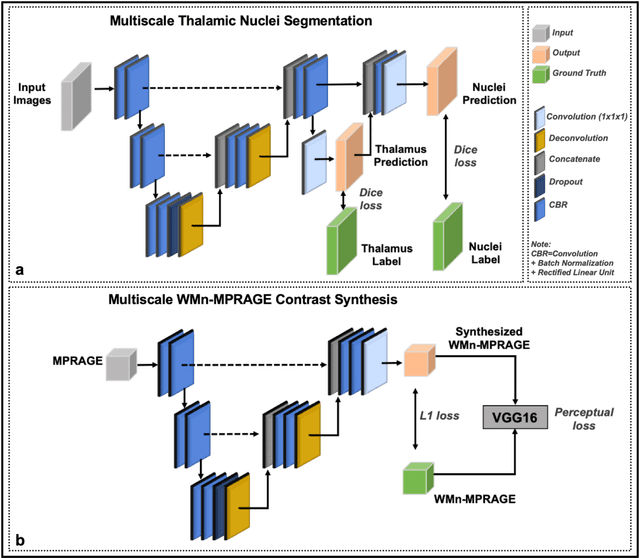
Abstract:Thalamic nuclei have been implicated in several neurological diseases. WMn-MPRAGE images have been shown to provide better intra-thalamic nuclear contrast compared to conventional MPRAGE images but the additional acquisition results in increased examination times. In this work, we investigated 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based techniques for thalamic nuclei parcellation from conventional MPRAGE images. Two 3D CNNs were developed and compared for thalamic nuclei parcellation using MPRAGE images: a) a native contrast segmentation (NCS) and b) a synthesized contrast segmentation (SCS) using WMn-MPRAGE images synthesized from MPRAGE images. We trained the two segmentation frameworks using MPRAGE images (n=35) and thalamic nuclei labels generated on WMn-MPRAGE images using a multi-atlas based parcellation technique. The segmentation accuracy and clinical utility were evaluated on a cohort comprising of healthy subjects and patients with alcohol use disorder (AUD) (n=45). The SCS network yielded higher Dice scores in the Medial geniculate nucleus (P=.003) and Centromedian nucleus (P=.01) with lower volume differences for Ventral anterior (P=.001) and Ventral posterior lateral (P=.01) nuclei when compared to the NCS network. A Bland-Altman analysis revealed tighter limits of agreement with lower coefficient of variation between true volumes and those predicted by the SCS network. The SCS network demonstrated a significant atrophy in Ventral lateral posterior nucleus in AUD patients compared to healthy age-matched controls (P=0.01), agreeing with previous studies on thalamic atrophy in alcoholism, whereas the NCS network showed spurious atrophy of the Ventral posterior lateral nucleus. CNN-based contrast synthesis prior to segmentation can provide fast and accurate thalamic nuclei segmentation from conventional MPRAGE images.
A Comparison of Deep Learning Convolution Neural Networks for Liver Segmentation in Radial Turbo Spin Echo Images
Apr 13, 2020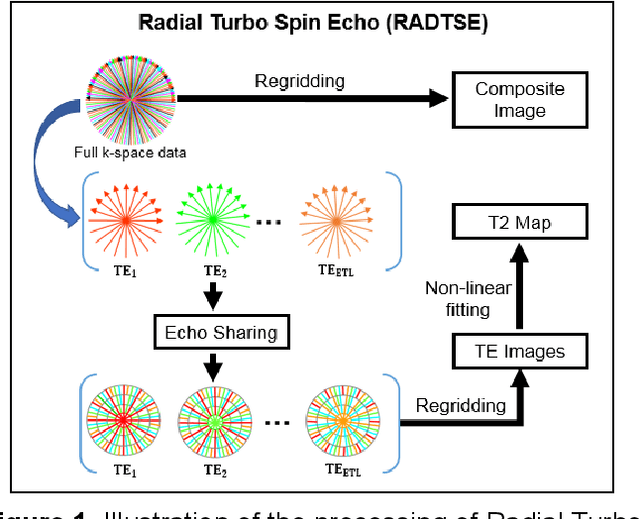
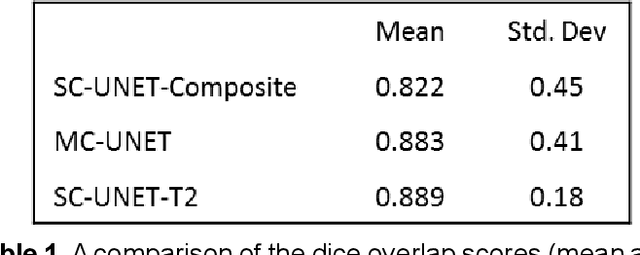
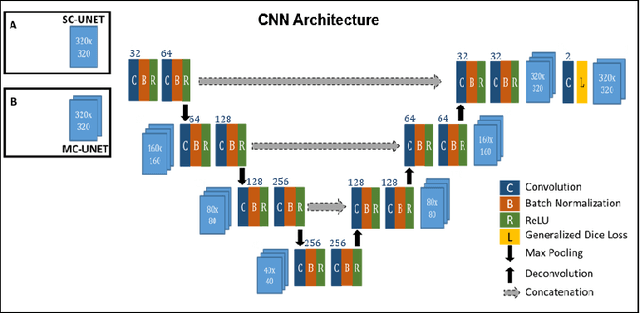
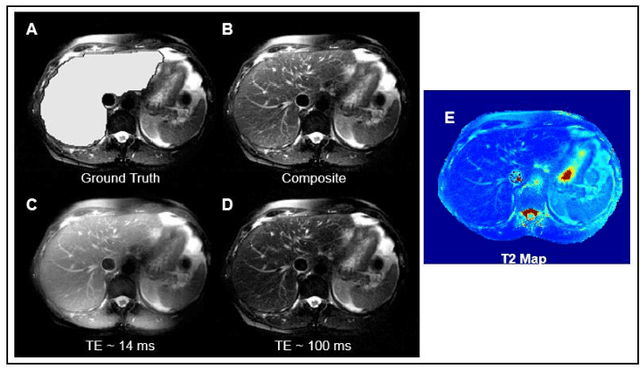
Abstract:Motion-robust 2D Radial Turbo Spin Echo (RADTSE) pulse sequence can provide a high-resolution composite image, T2-weighted images at multiple echo times (TEs), and a quantitative T2 map, all from a single k-space acquisition. In this work, we use a deep-learning convolutional neural network (CNN) for the segmentation of liver in abdominal RADTSE images. A modified UNET architecture with generalized dice loss objective function was implemented. Three 2D CNNs were trained, one for each image type obtained from the RADTSE sequence. On evaluating the performance of the CNNs on the validation set, we found that CNNs trained on TE images or the T2 maps had higher average dice scores than the composite images. This, in turn, implies that the information regarding T2 variation in tissues aids in improving the segmentation performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge