Ali Ahmadi
A Robust Model-Based Biped Locomotion Framework Based on Three-Mass Model: From Planning to Control
Feb 17, 2020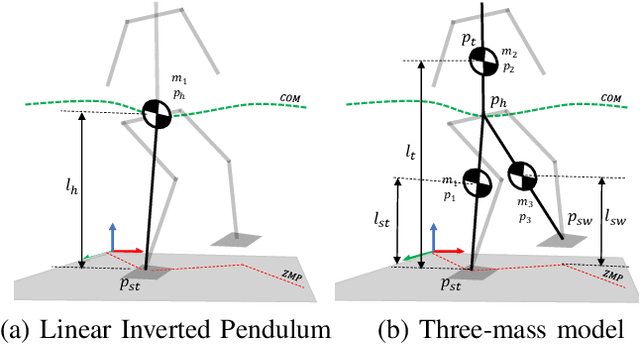
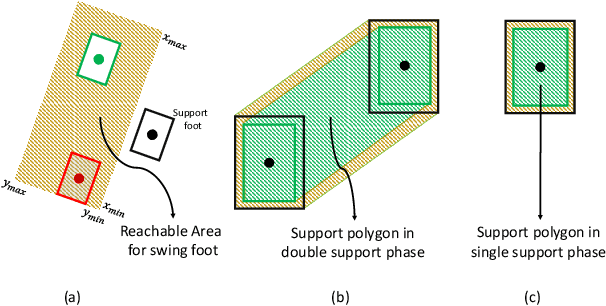
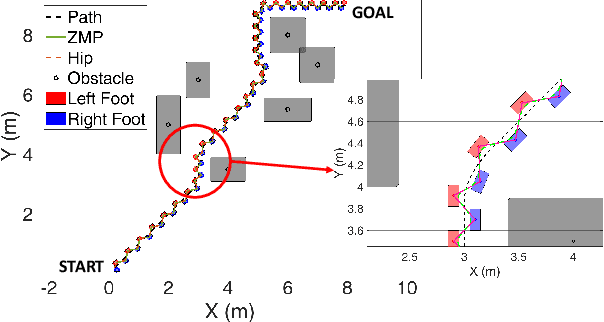

Abstract:Biped robots are inherently unstable because of their complex kinematics as well as dynamics. Despite types of research in developing biped locomotion, the performance of biped locomotion is still far from the expectations. This paper proposes a model-based framework to generate stable biped locomotion. The core of this framework is an abstract dynamics model which is composed of three masses to consider the dynamics of stance leg, torso and swing leg for minimizing the tracking problems. According to this dynamics model, we propose a modular walking reference trajectories planner which takes into account obstacles to plan all the references. Moreover, this dynamics model is used to formulate the low-level controller as a Model Predictive Control~(MPC) scheme which can consider some constraints in the states of the system, inputs, outputs and also mixed input-output. The performance and the robustness of the proposed framework are validated by performing several simulations using~\mbox{MATLAB}. The simulation results show that the proposed framework is capable of generating the biped locomotion robustly.
Content-based image retrieval using Mix histogram
Sep 20, 2019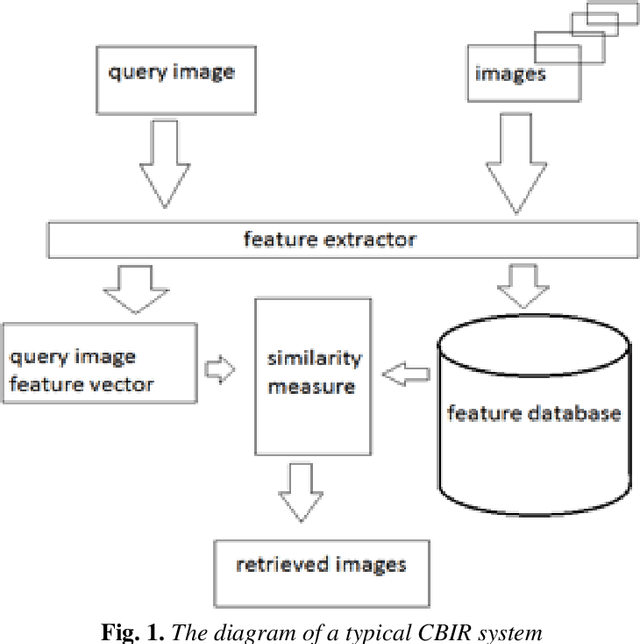
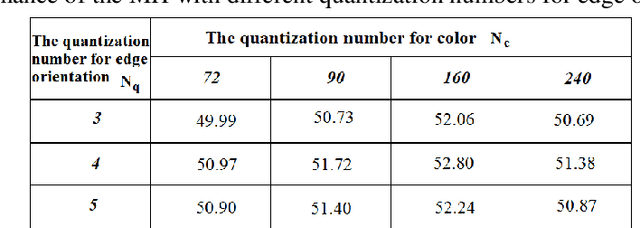
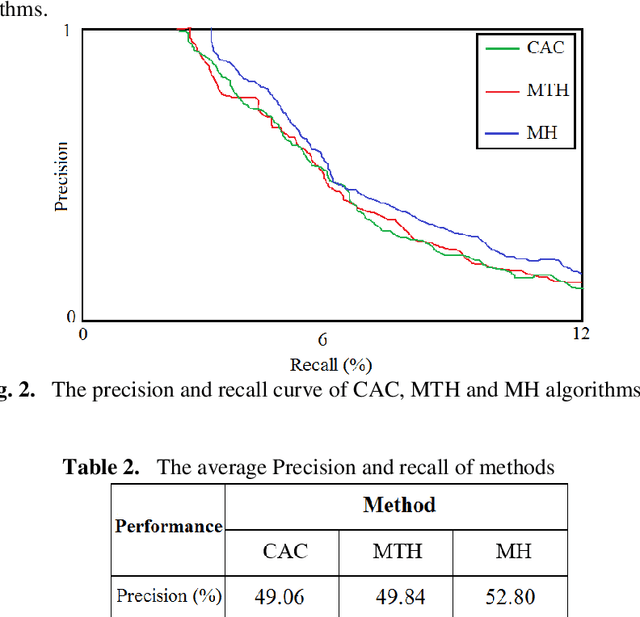

Abstract:This paper presents a new method to extract image low-level features, namely mix histogram (MH), for content-based image retrieval. Since color and edge orientation features are important visual information which help the human visual system percept and discriminate different images, this method extracts and integrates color and edge orientation information in order to measure similarity between different images. Traditional color histograms merely focus on the global distribution of color in the image and therefore fail to extract other visual features. The MH is attempting to overcome this problem by extracting edge orientations as well as color feature. The unique characteristic of the MH is that it takes into consideration both color and edge orientation information in an effective manner. Experimental results show that it outperforms many existing methods which were originally developed for image retrieval purposes.
Instrument-Independent Dastgah Recognition of Iranian Classical Music Using AzarNet
Jan 09, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, AzarNet, a deep neural network (DNN), is proposed to recognizing seven different Dastgahs of Iranian classical music in Maryam Iranian classical music (MICM) dataset. Over the last years, there has been remarkable interest in employing feature learning and DNNs which lead to decreasing the required engineering effort. DNNs have shown better performance in many classification tasks such as audio signal classification compares to shallow processing architectures. Despite image data, audio data need some preprocessing steps to extract spectra and temporal features. Some transformations like Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) have been used in the state of art researches to transform audio signals from time-domain to time-frequency domain to extract both temporal and spectra features. In this research, the STFT output results which are extracted features are given to AzarNet for learning and classification processes. It is worth noting that, the mentioned dataset contains music tracks composed with two instruments (violin and straw). The overall f1 score of AzarNet on test set, for average of all seven classes was 86.21% which is the best result ever reported in Dastgah classification according to our best knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge