Saber Malekzadeh
A Combination of Deep Neural Networks and K-Nearest Neighbors for Credit Card Fraud Detection
May 27, 2022



Abstract:Detection of a Fraud transaction on credit cards became one of the major problems for financial institutions, organizations and companies. As the global financial system is highly connected to non-cash transactions and online operations fraud makers invent more effective ways to access customers' finances. The main problem in credit card fraud detection is that the number of fraud transactions is significantly lower than genuine ones. The aim of the paper is to implement new techniques, which contains of under-sampling algorithms, K-nearest Neighbor Algorithm (KNN) and Deep Neural Network (KNN) on new obtained dataset. The performance evaluation showed that DNN model gives precise high accuracy (98.12%), which shows the good ability of presented method to detect fraudulent transactions.
Hippocampus segmentation in magnetic resonance images of Alzheimer's patients using Deep machine learning
Jun 16, 2021



Abstract:Background: Alzheimers disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder and the main cause of dementia in aging. Hippocampus is prone to changes in the early stages of Alzheimers disease. Detection and observation of the hippocampus changes using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before the onset of Alzheimers disease leads to the faster preventive and therapeutic measures. Objective: The aim of this study was the segmentation of the hippocampus in magnetic resonance (MR) images of Alzheimers patients using deep machine learning method. Methods: U-Net architecture of convolutional neural network was proposed to segment the hippocampus in the real MRI data. The MR images of the 100 and 35 patients available in Alzheimers disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset, was used for the train and test of the model, respectively. The performance of the proposed method was compared with manual segmentation by measuring the similarity metrics. Results: The desired segmentation achieved after 10 iterations. A Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) = 92.3%, sensitivity = 96.5%, positive predicted value (PPV) = 90.4%, and Intersection over Union (IoU) value for the train 92.94 and test 92.93 sets were obtained which are acceptable. Conclusion: The proposed approach is promising and can be extended in the prognosis of Alzheimers disease by the prediction of the hippocampus volume changes in the early stage of the disease.
Virtual Dress Swap Using Landmark Detection
Mar 17, 2021


Abstract:Online shopping has gained popularity recently. This paper addresses one crucial problem of buying dress online, which has not been solved yet. This research tries to implement the idea of clothes swapping with the help of DeepFashion dataset where 6,223 images with eight landmarks each used. Deep Convolutional Neural Network has been built for Landmark detection.
Spell Correction for Azerbaijani Language using Deep Neural Networks
Feb 05, 2021



Abstract:Spell correction is used to detect and correct orthographic mistakes in texts. Most of the time, traditional dictionary lookup with string similarity methods is suitable for the languages that have a less complex structure such as the English language. However, the Azerbaijani language has a more complex structure and due to its morphological structure, the derivation of words is plenty that several words are derived from adding suffices, affixes to the words. Therefore, in this paper sequence to sequence model with an attention mechanism is used to develop spelling correction for Azerbaijani. Total 12000 wrong and correct sentence pairs used for training, and the model is tested on 1000 real-world misspelled words and F1-score results are 75% for distance 0, 90% for distance 1, and 96% for distance 2.
Phoneme-Based Persian Speech Recognition
Jan 15, 2019Abstract:Undoubtedly, one of the most important issues in computer science is intelligent speech recognition. In these systems, computers try to detect and respond to the speeches they are listening to, like humans. In this research, presenting of a suitable method for the diagnosis of Persian phonemes by AI using the signal processing and classification algorithms have tried. For this purpose, the STFT algorithm has been used to process the audio signals, as well as to detect and classify the signals processed by the deep artificial neural network. At first, educational samples were provided as two phonological phrases in Persian language and then signal processing operations were performed on them. Then the results for the data training have been given to the artificial deep neural network. At the final stage, the experiment was conducted on new sounds.
Classical Music Generation in Distinct Dastgahs with AlimNet ACGAN
Jan 15, 2019

Abstract:In this paper AlimNet (With respect to great musician, Alim Qasimov) an auxiliary generative adversarial deep neural network (ACGAN) for generating music categorically, is used. This proposed network is a conditional ACGAN to condition the generation process on music tracks which has a hybrid architecture, composing of different kind of layers of neural networks. The employed music dataset is MICM which contains 1137 music samples (506 violins and 631 straw) with seven types of classical music Dastgah labels. To extract both temporal and spectral features, Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) is applied to convert input audio signals from time domain to time-frequency domain. GANs are composed of a generator for generating new samples and a discriminator to help generator making better samples. Samples in time-frequency domain are used to train discriminator in fourteen classes (seven Dastgahs and two instruments). The outputs of the conditional ACGAN are also artificial music samples in those mentioned scales in time-frequency domain. Then the output of the generator is transformed by Inverse STFT (ISTFT). Finally, randomly ten generated music samples (five violin and five straw samples) are given to ten musicians to rate how exact the samples are and the overall result was 76.5%.
Instrument-Independent Dastgah Recognition of Iranian Classical Music Using AzarNet
Jan 09, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, AzarNet, a deep neural network (DNN), is proposed to recognizing seven different Dastgahs of Iranian classical music in Maryam Iranian classical music (MICM) dataset. Over the last years, there has been remarkable interest in employing feature learning and DNNs which lead to decreasing the required engineering effort. DNNs have shown better performance in many classification tasks such as audio signal classification compares to shallow processing architectures. Despite image data, audio data need some preprocessing steps to extract spectra and temporal features. Some transformations like Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) have been used in the state of art researches to transform audio signals from time-domain to time-frequency domain to extract both temporal and spectra features. In this research, the STFT output results which are extracted features are given to AzarNet for learning and classification processes. It is worth noting that, the mentioned dataset contains music tracks composed with two instruments (violin and straw). The overall f1 score of AzarNet on test set, for average of all seven classes was 86.21% which is the best result ever reported in Dastgah classification according to our best knowledge.
Fuzzy Controller of Reward of Reinforcement Learning For Handwritten Digit Recognition
Dec 17, 2018Abstract:Recognition of human environment with computer systems always was a big deal in artificial intelligence. In this area handwriting recognition and conceptualization of it to computer is an important area in it. In the past years with growth of machine learning in artificial intelligence, efforts to using this technique increased. In this paper is tried to using fuzzy controller, to optimizing amount of reward of reinforcement learning for recognition of handwritten digits. For this aim first a sample of every digit with 10 standard computer fonts, given to actor and then actor is trained. In the next level is tried to test the actor with dataset and then results show improvement of recognition when using fuzzy controller of reinforcement learning.
Persian phonemes recognition using PPNet
Dec 17, 2018



Abstract:In this paper a new approach for recognition of Persian phonemes on the PCVC speech dataset is proposed. Nowadays deep neural networks are playing main rule in classification tasks. However the best results in speech recognition are not as good as human recognition rate yet. Deep learning techniques are shown their outstanding performance over so many classification tasks like image classification, document classification, etc. Also in some tasks their performance were even better than human. So the reason why ASR (automatic speech recognition) systems are not as good as the human speech recognition system is mostly depend on features of data is fed to deep neural networks. In this research first sound samples are cut for exact extraction of phoneme sounds in 50ms samples. Then phonemes are grouped in 30 groups; Containing 23 consonants, 6 vowels and a silence phoneme. STFT (Short time Fourier transform) is applied on them and Then STFT results are given to PPNet (A new deep convolutional neural network architecture) classifier and a total average of 75.87% accuracy is reached which is the best result ever compared to other algorithms on Separated Persian phonemes (Like in PCVC speech dataset).
Persian Vowel recognition with MFCC and ANN on PCVC speech dataset
Dec 17, 2018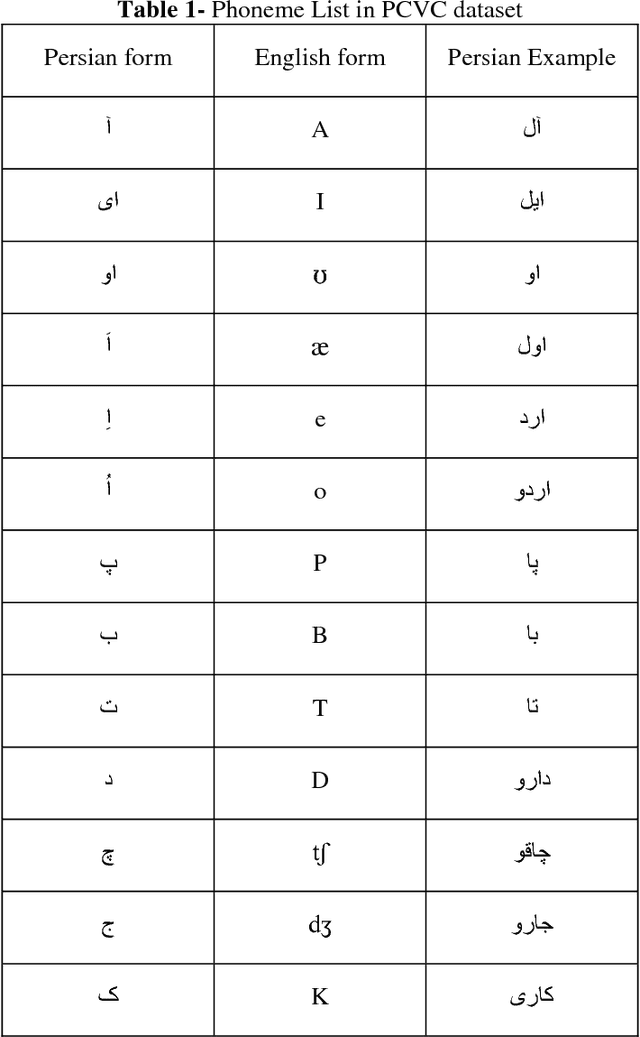
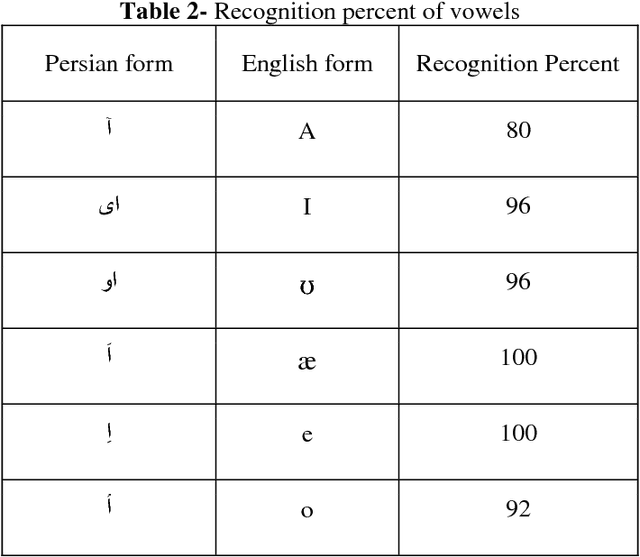
Abstract:In this paper a new method for recognition of consonant-vowel phonemes combination on a new Persian speech dataset titled as PCVC (Persian Consonant-Vowel Combination) is proposed which is used to recognize Persian phonemes. In PCVC dataset, there are 20 sets of audio samples from 10 speakers which are combinations of 23 consonant and 6 vowel phonemes of Persian language. In each sample, there is a combination of one vowel and one consonant. First, the consonant phoneme is pronounced and just after it, the vowel phoneme is pronounced. Each sound sample is a frame of 2 seconds of audio. In every 2 seconds, there is an average of 0.5 second speech and the rest is silence. In this paper, the proposed method is the implementations of the MFCC (Mel Frequency Cepstrum Coefficients) on every partitioned sound sample. Then, every train sample of MFCC vector is given to a multilayer perceptron feed-forward ANN (Artificial Neural Network) for training process. At the end, the test samples are examined on ANN model for phoneme recognition. After training and testing process, the results are presented in recognition of vowels. Then, the average percent of recognition for vowel phonemes are computed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge