Alexandra Vtyurina
A Search for Prompts: Generating Structured Answers from Contracts
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:In many legal processes being able to action on the concrete implication of a legal question can be valuable to automating human review or signalling certain conditions (e.g., alerts around automatic renewal). To support such tasks, we present a form of legal question answering that seeks to return one (or more) fixed answers for a question about a contract clause. After showing that unstructured generative question answering can have questionable outcomes for such a task, we discuss our exploration methodology for legal question answering prompts using OpenAI's \textit{GPT-3.5-Turbo} and provide a summary of insights. Using insights gleaned from our qualitative experiences, we compare our proposed template prompts against a common semantic matching approach and find that our prompt templates are far more accurate despite being less reliable in the exact response return. With some additional tweaks to prompts and the use of in-context learning, we are able to further improve the performance of our proposed strategy while maximizing the reliability of responses as best we can.
Shallow pooling for sparse labels
Aug 31, 2021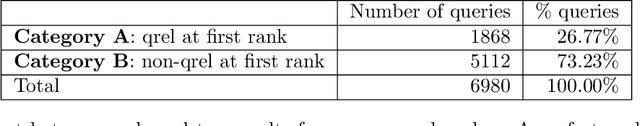
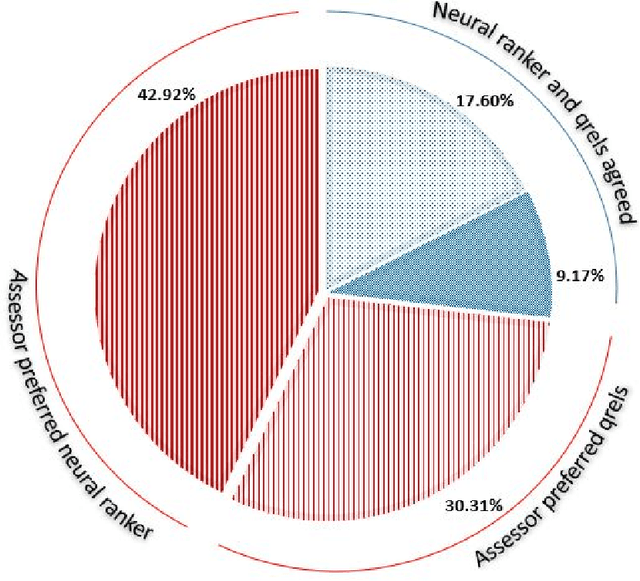
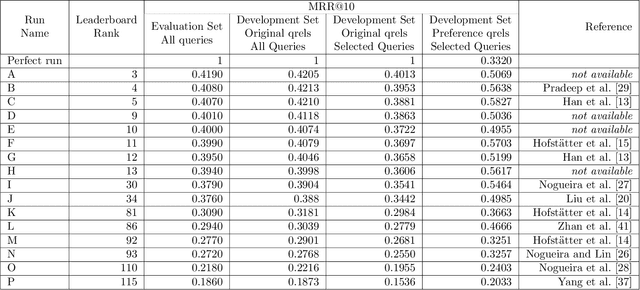
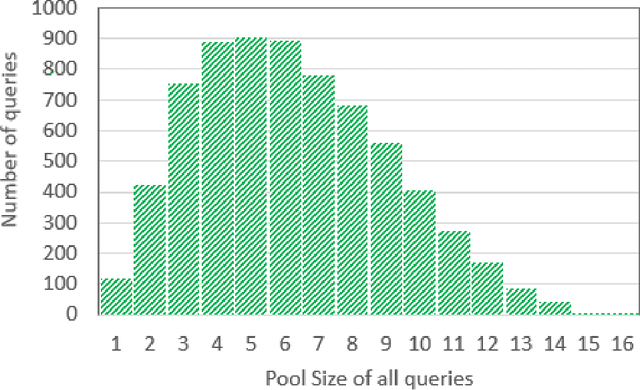
Abstract:Recent years have seen enormous gains in core IR tasks, including document and passage ranking. Datasets and leaderboards, and in particular the MS MARCO datasets, illustrate the dramatic improvements achieved by modern neural rankers. When compared with traditional test collections, the MS MARCO datasets employ substantially more queries with substantially fewer known relevant items per query. Given the sparsity of these relevance labels, the MS MARCO leaderboards track improvements with mean reciprocal rank (MRR). In essence, a relevant item is treated as the "right answer", with rankers scored on their ability to place this item high in the ranking. In working with these sparse labels, we have observed that the top items returned by a ranker often appear superior to judged relevant items. To test this observation, we employed crowdsourced workers to make preference judgments between the top item returned by a modern neural ranking stack and a judged relevant item. The results support our observation. If we imagine a perfect ranker under MRR, with a score of 1 on all queries, our preference judgments indicate that a searcher would prefer the top result from a modern neural ranking stack more frequently than the top result from the imaginary perfect ranker, making our neural ranker "better than perfect". To understand the implications for the leaderboard, we pooled the top document from available runs near the top of the passage ranking leaderboard for over 500 queries. We employed crowdsourced workers to make preference judgments over these pools and re-evaluated the runs. Our results support our concerns that current MS MARCO datasets may no longer be able to recognize genuine improvements in rankers. In future, if rankers are measured against a single "right answer", this answer should be the best answer or most preferred answer, and maintained with ongoing judgments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge