Alexander Kolotov
Towards Blockchain-based Multi-Agent Robotic Systems: Analysis, Classification and Applications
Jul 17, 2019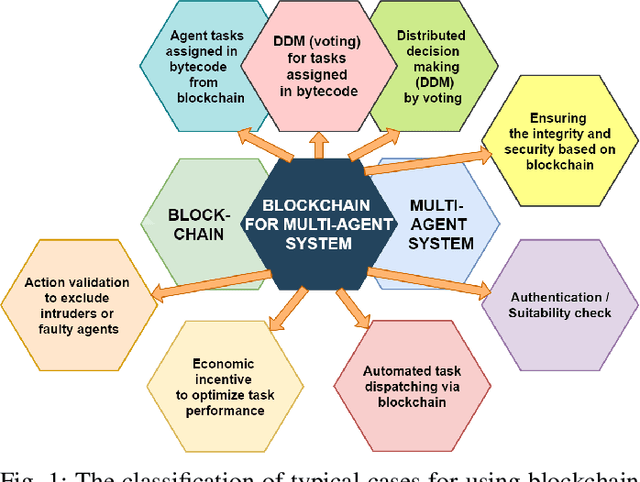
Abstract:Decentralization, immutability and transparency make of Blockchain one of the most innovative technology of recent years. This paper presents an overview of solutions based on Blockchain technology for multi-agent robotic systems, and provide an analysis and classification of this emerging field. The reasons for implementing Blockchain in a multi-robot network may be to increase the interaction efficiency between agents by providing more trusted information exchange, reaching a consensus in trustless conditions, assessing robot productivity or detecting performance problems, identifying intruders, allocating plans and tasks, deploying distributed solutions and joint missions. Blockchain-based applications are discussed to demonstrate how distributed ledger can be used to extend the number of research platforms and libraries for multi-agent robotic systems.
Blockchain Solutions for Multi-Agent Robotic Systems: Related Work and Open Questions
Mar 26, 2019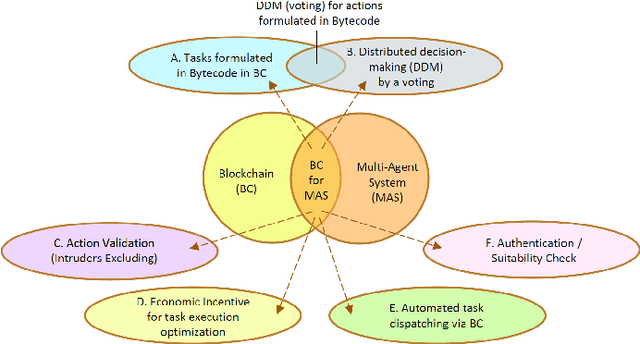
Abstract:The possibilities of decentralization and immutability make blockchain probably one of the most breakthrough and promising technological innovations in recent years. This paper presents an overview, analysis, and classification of possible blockchain solutions for practical tasks facing multi-agent robotic systems. The paper discusses blockchain-based applications that demonstrate how distributed ledger can be used to extend the existing number of research platforms and libraries for multi-agent robotic systems.
Towards blockchain-based robonomics: autonomous agents behavior validation
May 08, 2018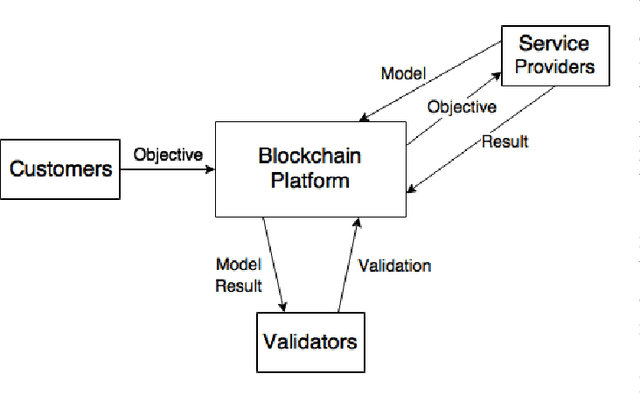
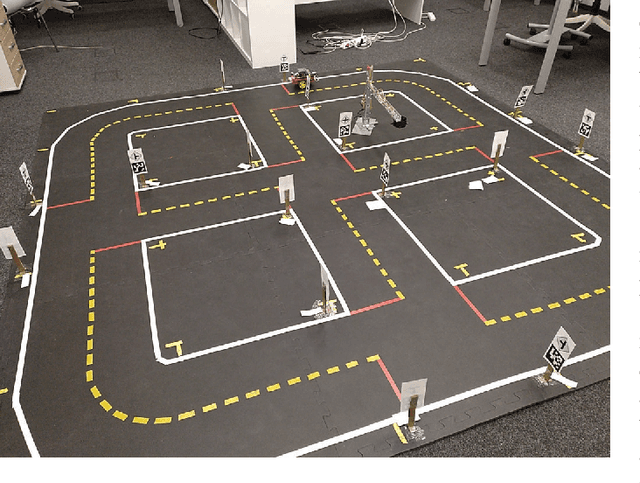
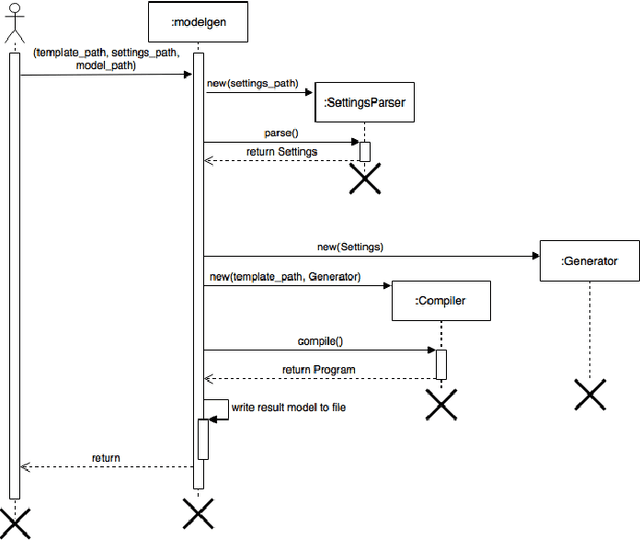
Abstract:The decentralized trading market approach, where both autonomous agents and people can consume and produce services expanding own opportunities to reach goals, looks very promising as a part of the Fourth Industrial revolution. The key component of the approach is a blockchain platform that allows an interaction between agents via liability smart contracts. Reliability of a service provider is usually determined by a reputation model. However, this solution only warns future customers about an extent of trust to the service provider in case it could not execute any previous liabilities correctly. From the other hand a blockchain consensus protocol can additionally include a validation procedure that detects incorrect liability executions in order to suspend payment transactions to questionable service providers. The paper presents the validation methodology of a liability execution for agent-based service providers in a decentralized trading market, using the Model Checking method based on the mathematical model of finite state automata and Temporal Logic properties of interest. To demonstrate this concept, we implemented the methodology in the Duckietown application, moving an autonomous mobile robot to achieve a mission goal with the following behavior validation at the end of a completed scenario.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge