Alexander Boden
What Matters in Explanations: Towards Explainable Fake Review Detection Focusing on Transformers
Jul 24, 2024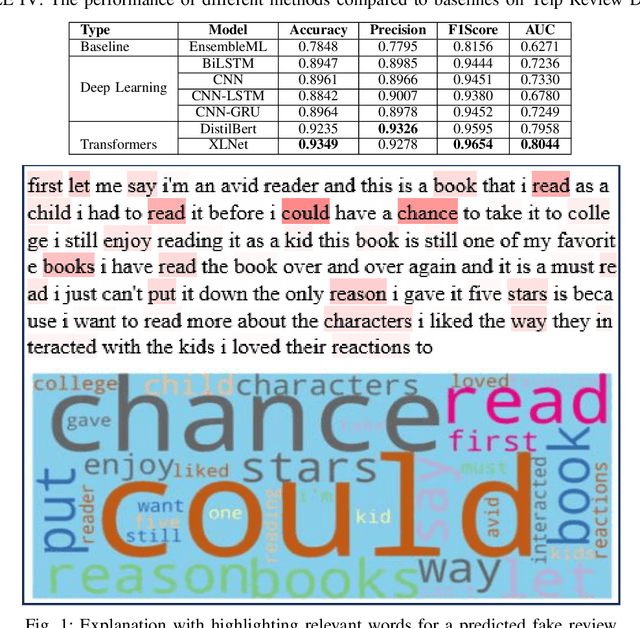

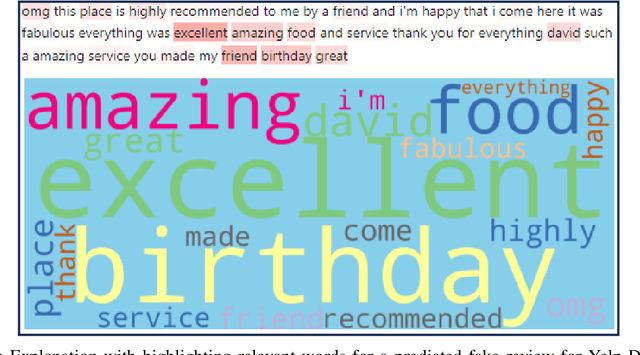

Abstract:Customers' reviews and feedback play crucial role on electronic commerce~(E-commerce) platforms like Amazon, Zalando, and eBay in influencing other customers' purchasing decisions. However, there is a prevailing concern that sellers often post fake or spam reviews to deceive potential customers and manipulate their opinions about a product. Over the past decade, there has been considerable interest in using machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models to identify such fraudulent reviews. Unfortunately, the decisions made by complex ML and DL models - which often function as \emph{black-boxes} - can be surprising and difficult for general users to comprehend. In this paper, we propose an explainable framework for detecting fake reviews with high precision in identifying fraudulent content with explanations and investigate what information matters most for explaining particular decisions by conducting empirical user evaluation. Initially, we develop fake review detection models using DL and transformer models including XLNet and DistilBERT. We then introduce layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP) technique for generating explanations that can map the contributions of words toward the predicted class. The experimental results on two benchmark fake review detection datasets demonstrate that our predictive models achieve state-of-the-art performance and outperform several existing methods. Furthermore, the empirical user evaluation of the generated explanations concludes which important information needs to be considered in generating explanations in the context of fake review identification.
Explaining AI Decisions: Towards Achieving Human-Centered Explainability in Smart Home Environments
Apr 23, 2024Abstract:Smart home systems are gaining popularity as homeowners strive to enhance their living and working environments while minimizing energy consumption. However, the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled decision-making models in smart home systems faces challenges due to the complexity and black-box nature of these systems, leading to concerns about explainability, trust, transparency, accountability, and fairness. The emerging field of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) addresses these issues by providing explanations for the models' decisions and actions. While state-of-the-art XAI methods are beneficial for AI developers and practitioners, they may not be easily understood by general users, particularly household members. This paper advocates for human-centered XAI methods, emphasizing the importance of delivering readily comprehensible explanations to enhance user satisfaction and drive the adoption of smart home systems. We review state-of-the-art XAI methods and prior studies focusing on human-centered explanations for general users in the context of smart home applications. Through experiments on two smart home application scenarios, we demonstrate that explanations generated by prominent XAI techniques might not be effective in helping users understand and make decisions. We thus argue for the necessity of a human-centric approach in representing explanations in smart home systems and highlight relevant human-computer interaction (HCI) methodologies, including user studies, prototyping, technology probes analysis, and heuristic evaluation, that can be employed to generate and present human-centered explanations to users.
Unveiling Black-boxes: Explainable Deep Learning Models for Patent Classification
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Recent technological advancements have led to a large number of patents in a diverse range of domains, making it challenging for human experts to analyze and manage. State-of-the-art methods for multi-label patent classification rely on deep neural networks (DNNs), which are complex and often considered black-boxes due to their opaque decision-making processes. In this paper, we propose a novel deep explainable patent classification framework by introducing layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP) to provide human-understandable explanations for predictions. We train several DNN models, including Bi-LSTM, CNN, and CNN-BiLSTM, and propagate the predictions backward from the output layer up to the input layer of the model to identify the relevance of words for individual predictions. Considering the relevance score, we then generate explanations by visualizing relevant words for the predicted patent class. Experimental results on two datasets comprising two-million patent texts demonstrate high performance in terms of various evaluation measures. The explanations generated for each prediction highlight important relevant words that align with the predicted class, making the prediction more understandable. Explainable systems have the potential to facilitate the adoption of complex AI-enabled methods for patent classification in real-world applications.
Arabic Sentiment Analysis with Noisy Deep Explainable Model
Sep 24, 2023Abstract:Sentiment Analysis (SA) is an indispensable task for many real-world applications. Compared to limited resourced languages (i.e., Arabic, Bengali), most of the research on SA are conducted for high resourced languages (i.e., English, Chinese). Moreover, the reasons behind any prediction of the Arabic sentiment analysis methods exploiting advanced artificial intelligence (AI)-based approaches are like black-box - quite difficult to understand. This paper proposes an explainable sentiment classification framework for the Arabic language by introducing a noise layer on Bi-Directional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)-BiLSTM models that overcome over-fitting problem. The proposed framework can explain specific predictions by training a local surrogate explainable model to understand why a particular sentiment (positive or negative) is being predicted. We carried out experiments on public benchmark Arabic SA datasets. The results concluded that adding noise layers improves the performance in sentiment analysis for the Arabic language by reducing overfitting and our method outperformed some known state-of-the-art methods. In addition, the introduced explainability with noise layer could make the model more transparent and accountable and hence help adopting AI-enabled system in practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge