Md Atabuzzaman
What Matters in Explanations: Towards Explainable Fake Review Detection Focusing on Transformers
Jul 24, 2024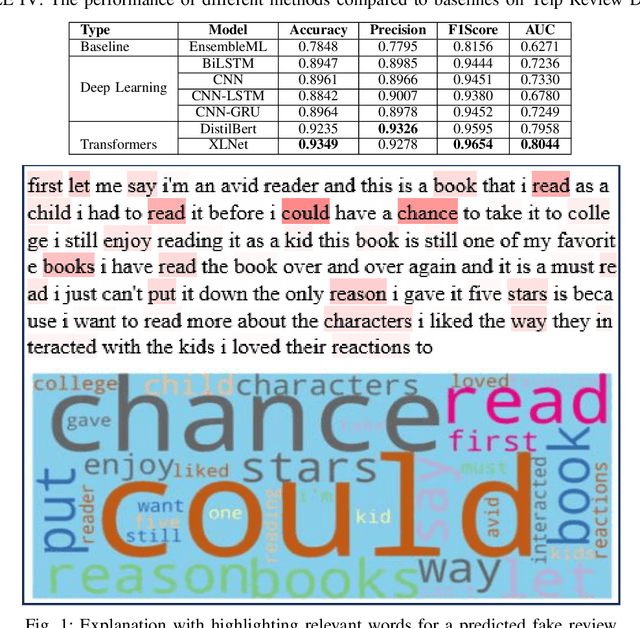

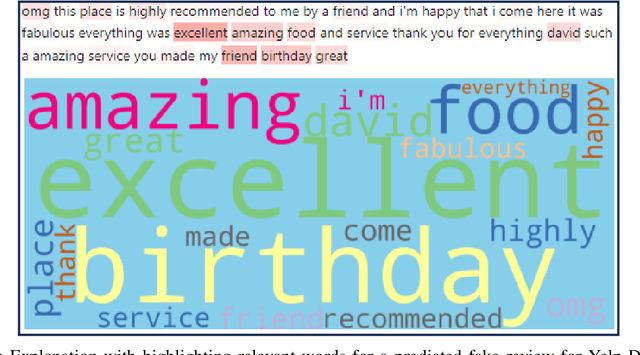

Abstract:Customers' reviews and feedback play crucial role on electronic commerce~(E-commerce) platforms like Amazon, Zalando, and eBay in influencing other customers' purchasing decisions. However, there is a prevailing concern that sellers often post fake or spam reviews to deceive potential customers and manipulate their opinions about a product. Over the past decade, there has been considerable interest in using machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models to identify such fraudulent reviews. Unfortunately, the decisions made by complex ML and DL models - which often function as \emph{black-boxes} - can be surprising and difficult for general users to comprehend. In this paper, we propose an explainable framework for detecting fake reviews with high precision in identifying fraudulent content with explanations and investigate what information matters most for explaining particular decisions by conducting empirical user evaluation. Initially, we develop fake review detection models using DL and transformer models including XLNet and DistilBERT. We then introduce layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP) technique for generating explanations that can map the contributions of words toward the predicted class. The experimental results on two benchmark fake review detection datasets demonstrate that our predictive models achieve state-of-the-art performance and outperform several existing methods. Furthermore, the empirical user evaluation of the generated explanations concludes which important information needs to be considered in generating explanations in the context of fake review identification.
Textual Entailment Recognition with Semantic Features from Empirical Text Representation
Oct 18, 2022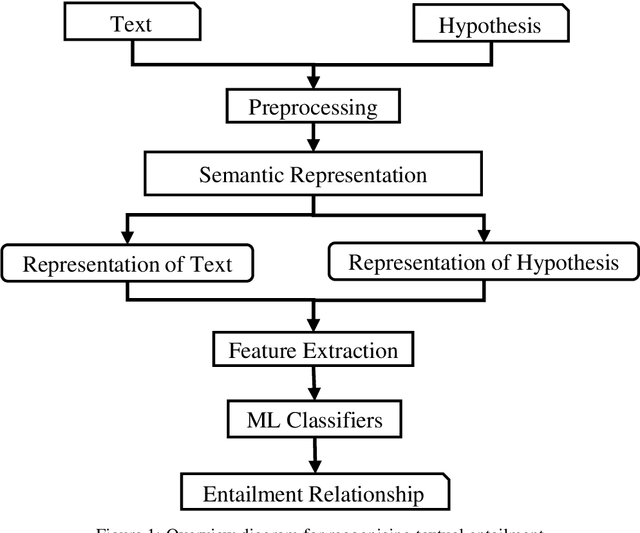
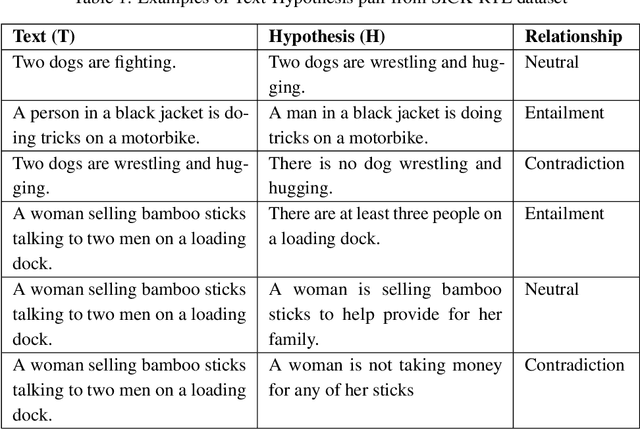
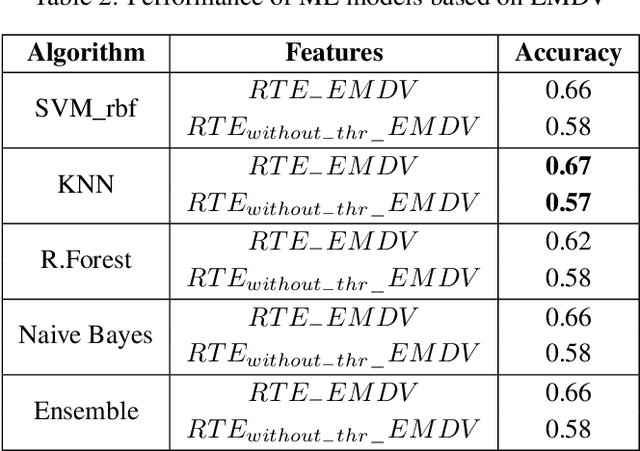
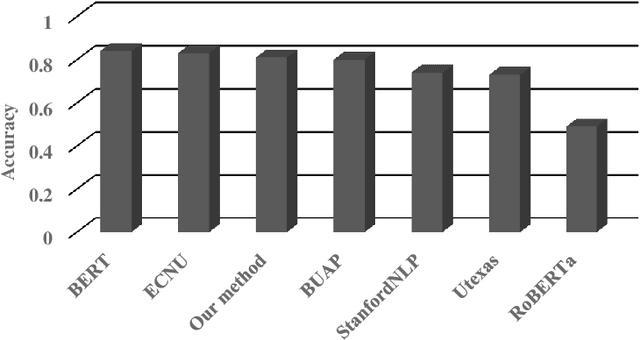
Abstract:Textual entailment recognition is one of the basic natural language understanding(NLU) tasks. Understanding the meaning of sentences is a prerequisite before applying any natural language processing(NLP) techniques to automatically recognize the textual entailment. A text entails a hypothesis if and only if the true value of the hypothesis follows the text. Classical approaches generally utilize the feature value of each word from word embedding to represent the sentences. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to identifying the textual entailment relationship between text and hypothesis, thereby introducing a new semantic feature focusing on empirical threshold-based semantic text representation. We employ an element-wise Manhattan distance vector-based feature that can identify the semantic entailment relationship between the text-hypothesis pair. We carried out several experiments on a benchmark entailment classification(SICK-RTE) dataset. We train several machine learning(ML) algorithms applying both semantic and lexical features to classify the text-hypothesis pair as entailment, neutral, or contradiction. Our empirical sentence representation technique enriches the semantic information of the texts and hypotheses found to be more efficient than the classical ones. In the end, our approach significantly outperforms known methods in understanding the meaning of the sentences for the textual entailment classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge