Md Rezaul Karim
Child Mortality Prediction in Bangladesh: A Decade-Long Validation Study
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The predictive machine learning models for child mortality tend to be inaccurate when applied to future populations, since they suffer from look-ahead bias due to the randomization used in cross-validation. The Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) data from Bangladesh for 2011-2022, with n = 33,962, are used in this paper. We trained the model on (2011-2014) data, validated it on 2017 data, and tested it on 2022 data. Eight years after the initial test of the model, a genetic algorithm-based Neural Architecture Search found a single-layer neural architecture (with 64 units) to be superior to XGBoost (AUROC = 0.76 vs. 0.73; p < 0.01). Additionally, through a detailed fairness audit, we identified an overall "Socioeconomic Predictive Gradient," with a positive correlation between regional poverty level (r = -0.62) and the algorithm's AUC. In addition, we found that the model performed at its highest levels in the least affluent divisions (AUC 0.74) and decreased dramatically in the wealthiest divisions (AUC 0.66). These findings suggest that the model is identifying areas with the greatest need for intervention. Our model would identify approximately 1300 additional at-risk children annually than a Gradient Boosting model when screened at the 10% level and validated using SHAP values and Platt Calibration, and therefore provide a robust, production-ready computational phenotype for targeted maternal and child health interventions.
Pre-trained Encoders for Global Child Development: Transfer Learning Enables Deployment in Data-Scarce Settings
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:A large number of children experience preventable developmental delays each year, yet the deployment of machine learning in new countries has been stymied by a data bottleneck: reliable models require thousands of samples, while new programs begin with fewer than 100. We introduce the first pre-trained encoder for global child development, trained on 357,709 children across 44 countries using UNICEF survey data. With only 50 training samples, the pre-trained encoder achieves an average AUC of 0.65 (95% CI: 0.56-0.72), outperforming cold-start gradient boosting at 0.61 by 8-12% across regions. At N=500, the encoder achieves an AUC of 0.73. Zero-shot deployment to unseen countries achieves AUCs up to 0.84. We apply a transfer learning bound to explain why pre-training diversity enables few-shot generalization. These results establish that pre-trained encoders can transform the feasibility of ML for SDG 4.2.1 monitoring in resource-constrained settings.
The Depth Delusion: Why Transformers Should Be Wider, Not Deeper
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Neural scaling laws describe how language model loss decreases with parameters and data, but treat architecture as interchangeable--a billion parameters could arise from a shallow-wide model (10 layers & 8,192 hidden dimension) or a deep-narrow one (80 layers & 2,048 hidden dimension). We propose architecture-conditioned scaling laws decomposing this dependence, finding that optimal depth scales as D* ~ C^0.12 while optimal width scales as W* ~ C^0.34, meaning width should grow 2.8x faster than depth. We discover a critical depth phenomenon: beyond D_crit ~ W^0.44 (sublinear in W), adding layers increases loss despite adding parameters--the Depth Delusion. Empirically, we validate these findings across 30 transformer architectures spanning 17M to 7B parameters, each trained on representative high-compute samples, achieving R^2 = 0.922. Our central finding: at 7B scale, a 64-layer model (6.38B params) underperforms a 32-layer model (6.86B params) by 0.12 nats, despite being significantly deeper. This demonstrates that optimal depth-width tradeoffs persist at the production scale.
Distributed Causality in the SDG Network: Evidence from Panel VAR and Conditional Independence Analysis
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:The achievement of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is dependent upon strategic resource distribution. We propose a causal discovery framework using Panel Vector Autoregression, along with both country-specific fixed effects and PCMCI+ conditional independence testing on 168 countries (2000-2025) to develop the first complete causal architecture of SDG dependencies. Utilizing 8 strategically chosen SDGs, we identify a distributed causal network (i.e., no single 'hub' SDG), with 10 statistically significant Granger-causal relationships identified as 11 unique direct effects. Education to Inequality is identified as the most statistically significant direct relationship (r = -0.599; p < 0.05), while effect magnitude significantly varies depending on income levels (e.g., high-income: r = -0.65; lower-middle-income: r = -0.06; non-significant). We also reject the idea that there exists a single 'keystone' SDG. Additionally, we offer a proposed tiered priority framework for the SDGs namely, identifying upstream drivers (Education, Growth), enabling goals (Institutions, Energy), and downstream outcomes (Poverty, Health). Therefore, we conclude that effective SDG acceleration can be accomplished through coordinated multi-dimensional intervention(s), and that single-goal sequential strategies are insufficient.
The Dependency Divide: An Interpretable Machine Learning Framework for Profiling Student Digital Satisfaction in the Bangladesh Context
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Background: While digital access has expanded rapidly in resource-constrained contexts, satisfaction with digital learning platforms varies significantly among students with seemingly equal connectivity. Traditional digital divide frameworks fail to explain these variations. Purpose: This study introduces the "Dependency Divide", a novel framework proposing that highly engaged students become conditionally vulnerable to infrastructure failures, challenging assumptions that engagement uniformly benefits learners in post-access environments. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 396 university students in Bangladesh using a three-stage analytical approach: (1) stability-validated K-prototypes clustering to identify student profiles, (2) profile-specific Random Forest models with SHAP and ALE analysis to determine satisfaction drivers, and (3) formal interaction analysis with propensity score matching to test the Dependency Divide hypothesis. Results: Three distinct profiles emerged: Casually Engaged (58%), Efficient Learners (35%), and Hyper-Engaged (7%). A significant interaction between educational device time and internet reliability (\b{eta} = 0.033, p = 0.028) confirmed the Dependency Divide: engagement increased satisfaction only when infrastructure remained reliable. Hyper-Engaged students showed greatest vulnerability despite or because of their sophisticated digital workflows. Policy simulations demonstrated that targeted reliability improvements for high-dependency users yielded 2.06 times greater returns than uniform interventions. Conclusions: In fragile infrastructure contexts, capability can become liability. Digital transformation policies must prioritize reliability for dependency-prone users, establish contingency systems, and educate students about dependency risks rather than uniformly promoting engagement.
Textual Entailment Recognition with Semantic Features from Empirical Text Representation
Oct 18, 2022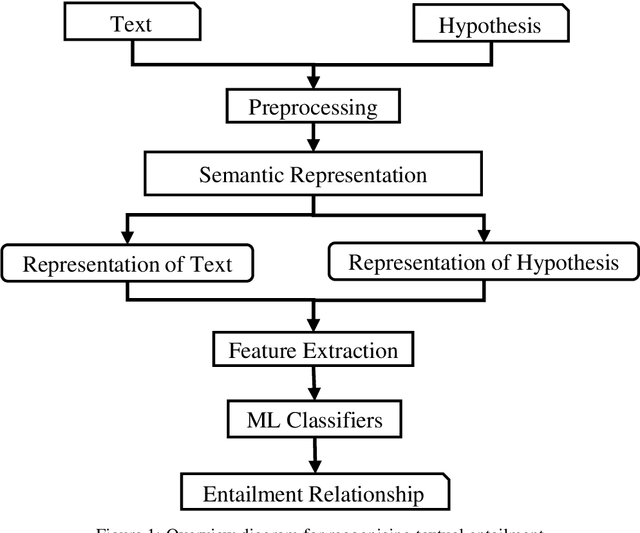
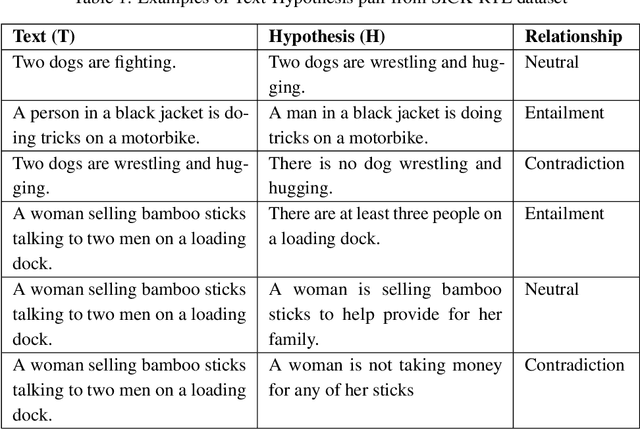
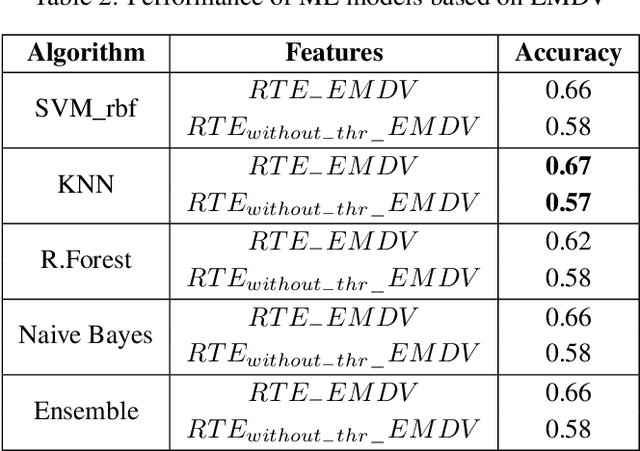
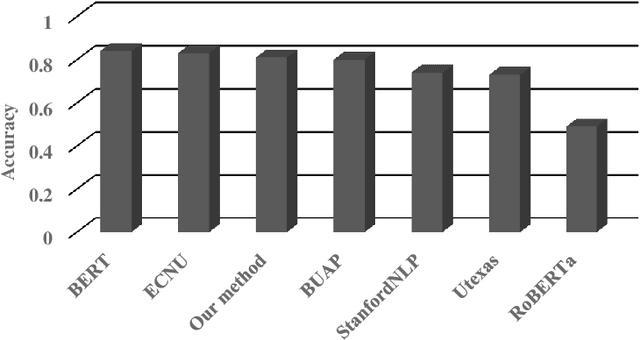
Abstract:Textual entailment recognition is one of the basic natural language understanding(NLU) tasks. Understanding the meaning of sentences is a prerequisite before applying any natural language processing(NLP) techniques to automatically recognize the textual entailment. A text entails a hypothesis if and only if the true value of the hypothesis follows the text. Classical approaches generally utilize the feature value of each word from word embedding to represent the sentences. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to identifying the textual entailment relationship between text and hypothesis, thereby introducing a new semantic feature focusing on empirical threshold-based semantic text representation. We employ an element-wise Manhattan distance vector-based feature that can identify the semantic entailment relationship between the text-hypothesis pair. We carried out several experiments on a benchmark entailment classification(SICK-RTE) dataset. We train several machine learning(ML) algorithms applying both semantic and lexical features to classify the text-hypothesis pair as entailment, neutral, or contradiction. Our empirical sentence representation technique enriches the semantic information of the texts and hypotheses found to be more efficient than the classical ones. In the end, our approach significantly outperforms known methods in understanding the meaning of the sentences for the textual entailment classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge