Alberto Pepe
STAResNet: a Network in Spacetime Algebra to solve Maxwell's PDEs
Aug 24, 2024



Abstract:We introduce STAResNet, a ResNet architecture in Spacetime Algebra (STA) to solve Maxwell's partial differential equations (PDEs). Recently, networks in Geometric Algebra (GA) have been demonstrated to be an asset for truly geometric machine learning. In \cite{brandstetter2022clifford}, GA networks have been employed for the first time to solve partial differential equations (PDEs), demonstrating an increased accuracy over real-valued networks. In this work we solve Maxwell's PDEs both in GA and STA employing the same ResNet architecture and dataset, to discuss the impact that the choice of the right algebra has on the accuracy of GA networks. Our study on STAResNet shows how the correct geometric embedding in Clifford Networks gives a mean square error (MSE), between ground truth and estimated fields, up to 2.6 times lower than than obtained with a standard Clifford ResNet with 6 times fewer trainable parameters. STAREsNet demonstrates consistently lower MSE and higher correlation regardless of scenario. The scenarios tested are: sampling period of the dataset; presence of obstacles with either seen or unseen configurations; the number of channels in the ResNet architecture; the number of rollout steps; whether the field is in 2D or 3D space. This demonstrates how choosing the right algebra in Clifford networks is a crucial factor for more compact, accurate, descriptive and better generalising pipelines.
CGA-PoseNet: Camera Pose Regression via a 1D-Up Approach to Conformal Geometric Algebra
Feb 10, 2023Abstract:We introduce CGA-PoseNet, which uses the 1D-Up approach to Conformal Geometric Algebra (CGA) to represent rotations and translations with a single mathematical object, the motor, for camera pose regression. We do so starting from PoseNet, which successfully predicts camera poses from small datasets of RGB frames. State-of-the-art methods, however, require expensive tuning to balance the orientational and translational components of the camera pose.This is usually done through complex, ad-hoc loss function to be minimized, and in some cases also requires 3D points as well as images. Our approach has the advantage of unifying the camera position and orientation through the motor. Consequently, the network searches for a single object which lives in a well-behaved 4D space with a Euclidean signature. This means that we can address the case of image-only datasets and work efficiently with a simple loss function, namely the mean squared error (MSE) between the predicted and ground truth motors. We show that it is possible to achieve high accuracy camera pose regression with a significantly simpler problem formulation. This 1D-Up approach to CGA can be employed to overcome the dichotomy between translational and orientational components in camera pose regression in a compact and elegant way.
Do Linguistic Style and Readability of Scientific Abstracts affect their Virality?
Mar 19, 2012

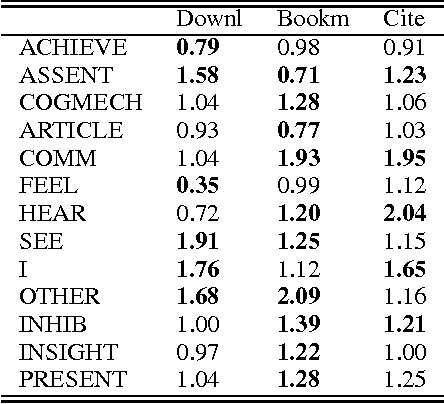
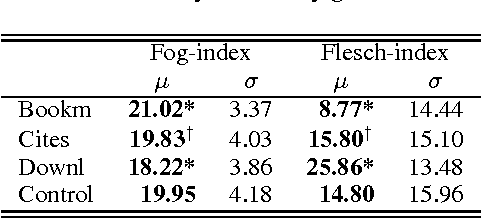
Abstract:Reactions to textual content posted in an online social network show different dynamics depending on the linguistic style and readability of the submitted content. Do similar dynamics exist for responses to scientific articles? Our intuition, supported by previous research, suggests that the success of a scientific article depends on its content, rather than on its linguistic style. In this article, we examine a corpus of scientific abstracts and three forms of associated reactions: article downloads, citations, and bookmarks. Through a class-based psycholinguistic analysis and readability indices tests, we show that certain stylistic and readability features of abstracts clearly concur in determining the success and viral capability of a scientific article.
The Dilated Triple
Jun 06, 2010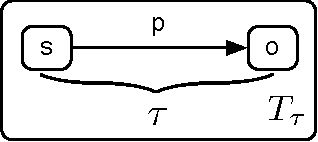

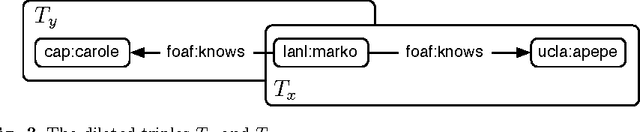
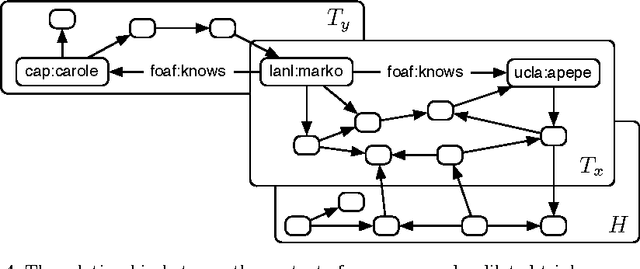
Abstract:The basic unit of meaning on the Semantic Web is the RDF statement, or triple, which combines a distinct subject, predicate and object to make a definite assertion about the world. A set of triples constitutes a graph, to which they give a collective meaning. It is upon this simple foundation that the rich, complex knowledge structures of the Semantic Web are built. Yet the very expressiveness of RDF, by inviting comparison with real-world knowledge, highlights a fundamental shortcoming, in that RDF is limited to statements of absolute fact, independent of the context in which a statement is asserted. This is in stark contrast with the thoroughly context-sensitive nature of human thought. The model presented here provides a particularly simple means of contextualizing an RDF triple by associating it with related statements in the same graph. This approach, in combination with a notion of graph similarity, is sufficient to select only those statements from an RDF graph which are subjectively most relevant to the context of the requesting process.
Faith in the Algorithm, Part 1: Beyond the Turing Test
Mar 02, 2009Abstract:Since the Turing test was first proposed by Alan Turing in 1950, the primary goal of artificial intelligence has been predicated on the ability for computers to imitate human behavior. However, the majority of uses for the computer can be said to fall outside the domain of human abilities and it is exactly outside of this domain where computers have demonstrated their greatest contribution to intelligence. Another goal for artificial intelligence is one that is not predicated on human mimicry, but instead, on human amplification. This article surveys various systems that contribute to the advancement of human and social intelligence.
Between conjecture and memento: shaping a collective emotional perception of the future
Jan 25, 2008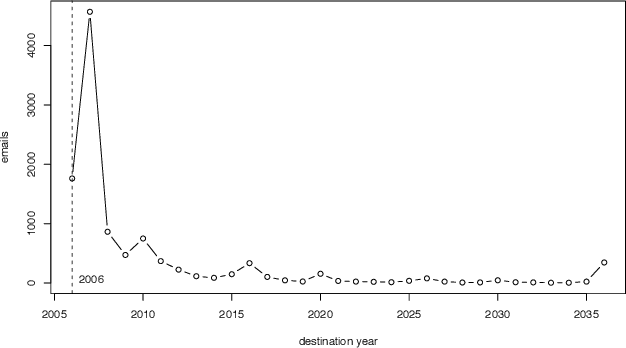
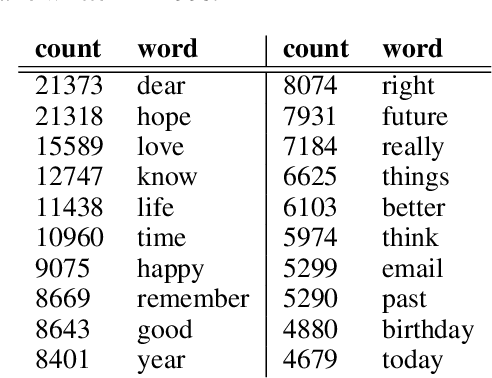
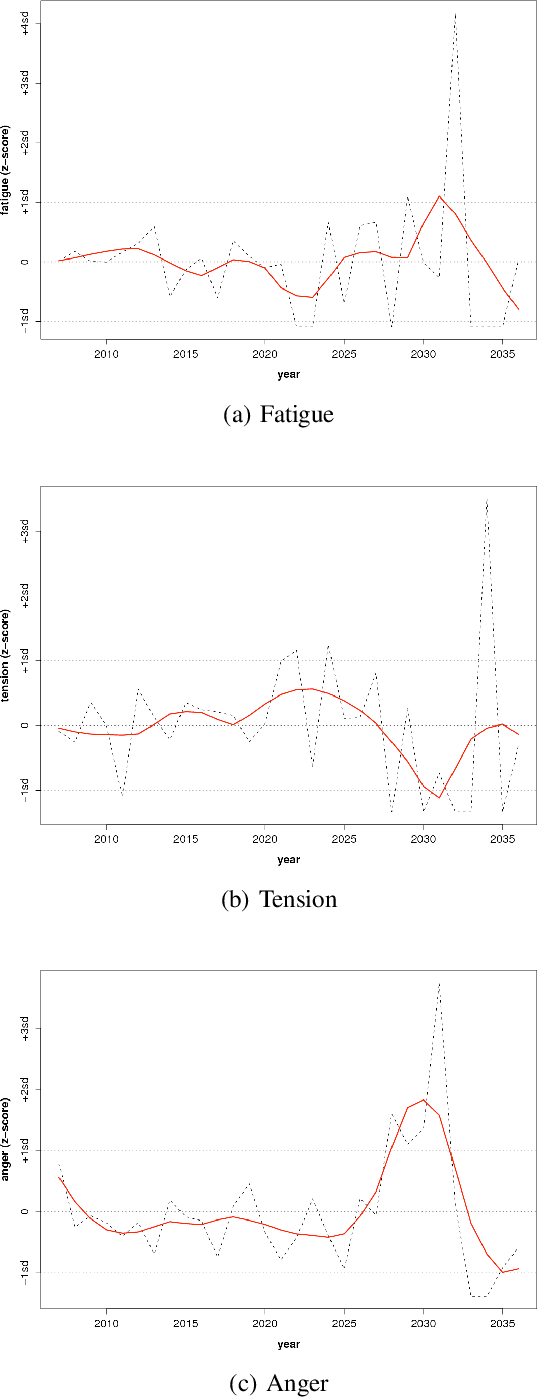
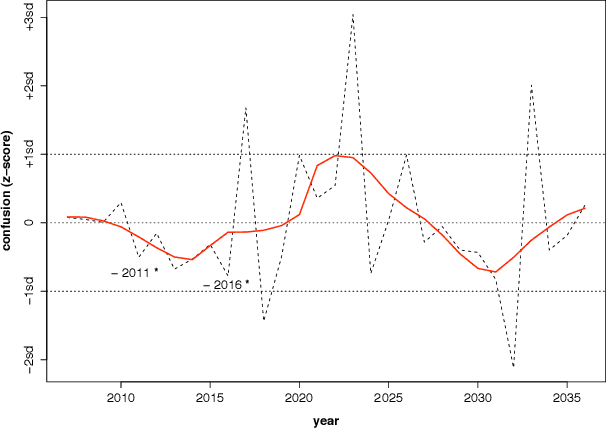
Abstract:Large scale surveys of public mood are costly and often impractical to perform. However, the web is awash with material indicative of public mood such as blogs, emails, and web queries. Inexpensive content analysis on such extensive corpora can be used to assess public mood fluctuations. The work presented here is concerned with the analysis of the public mood towards the future. Using an extension of the Profile of Mood States questionnaire, we have extracted mood indicators from 10,741 emails submitted in 2006 to futureme.org, a web service that allows its users to send themselves emails to be delivered at a later date. Our results indicate long-term optimism toward the future, but medium-term apprehension and confusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge