Alan Salimov
Navigating the Dynamics of Financial Embeddings over Time
Jul 01, 2020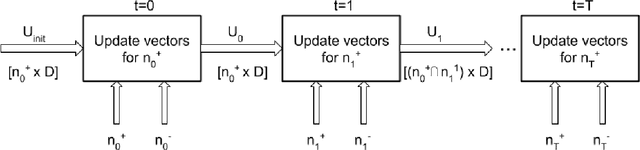
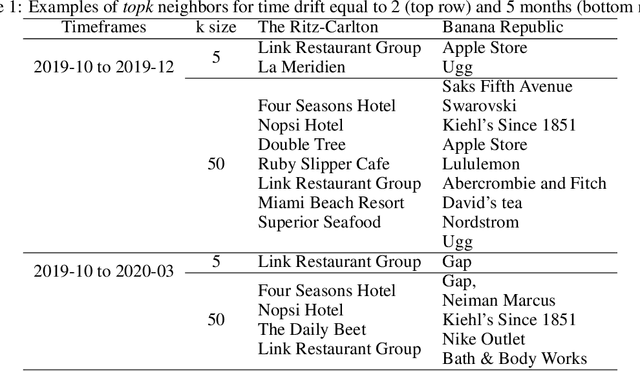
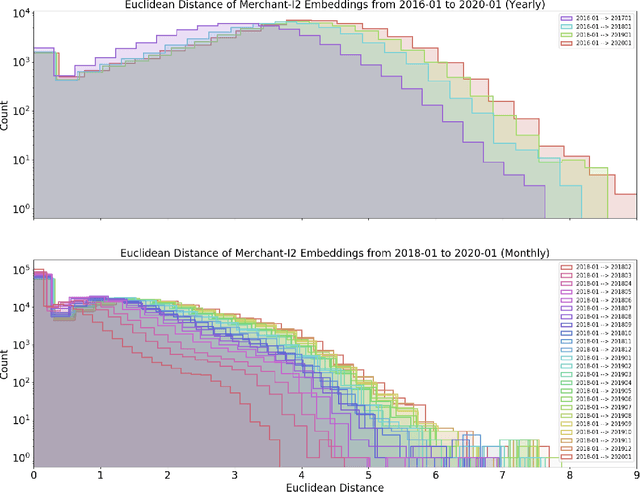
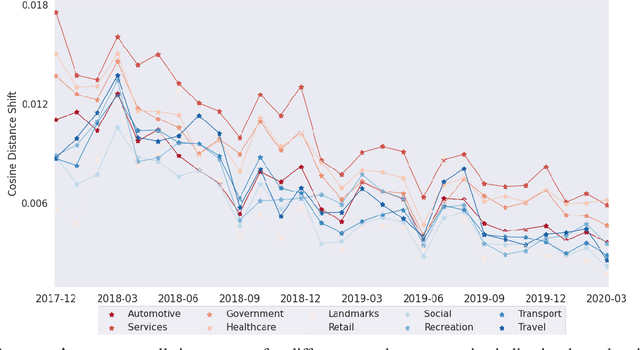
Abstract:Financial transactions constitute connections between entities and through these connections a large scale heterogeneous weighted graph is formulated. In this labyrinth of interactions that are continuously updated, there exists a variety of similarity-based patterns that can provide insights into the dynamics of the financial system. With the current work, we propose the application of Graph Representation Learning in a scalable dynamic setting as a means of capturing these patterns in a meaningful and robust way. We proceed to perform a rigorous qualitative analysis of the latent trajectories to extract real world insights from the proposed representations and their evolution over time that is to our knowledge the first of its kind in the financial sector. Shifts in the latent space are associated with known economic events and in particular the impact of the recent Covid-19 pandemic to consumer patterns. Capturing such patterns indicates the value added to financial modeling through the incorporation of latent graph representations.
An Adversarial Learning Framework For A Persona-Based Multi-Turn Dialogue Model
Apr 29, 2019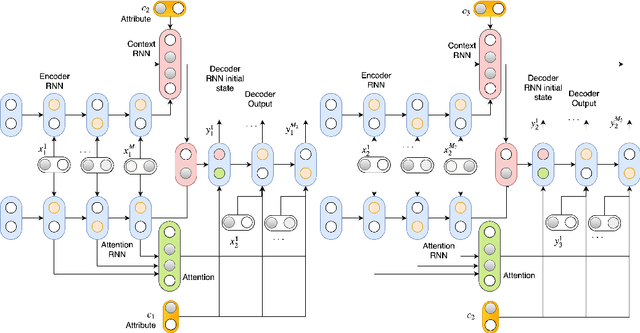
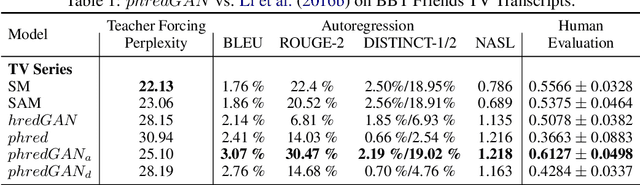
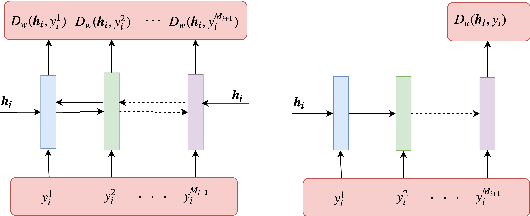
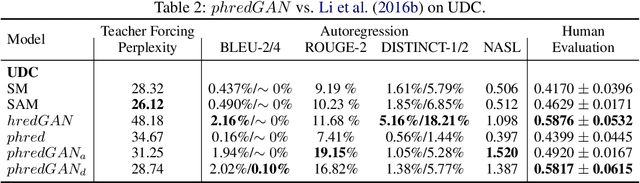
Abstract:In this paper, we extend the persona-based sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) neural network conversation model to a multi-turn dialogue scenario by modifying the state-of-the-art hredGAN architecture to simultaneously capture utterance attributes such as speaker identity, dialogue topic, speaker sentiments and so on. The proposed system, phredGAN has a persona-based HRED generator (PHRED) and a conditional discriminator. We also explore two approaches to accomplish the conditional discriminator: (1) phredGAN_a, a system that passes the attribute representation as an additional input into a traditional adversarial discriminator, and (2) phredGAN_d, a dual discriminator system which in addition to the adversarial discriminator, collaboratively predicts the attribute(s) that generated the input utterance. To demonstrate the superior performance of phredGAN over the persona Seq2Seq model, we experiment with two conversational datasets, the Ubuntu Dialogue Corpus (UDC) and TV series transcripts from the Big Bang Theory and Friends. Performance comparison is made with respect to a variety of quantitative measures as well as crowd-sourced human evaluation. We also explore the trade-offs from using either variant of phredGAN on datasets with many but weak attribute modalities (such as with Big Bang Theory and Friends) and ones with few but strong attribute modalities (customer-agent interactions in Ubuntu dataset).
Multi-turn Dialogue Response Generation in an Adversarial Learning Framework
Sep 19, 2018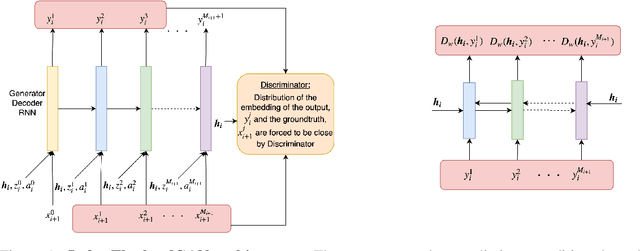
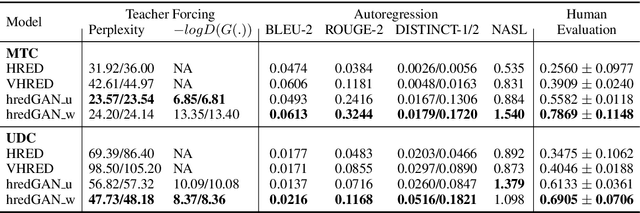
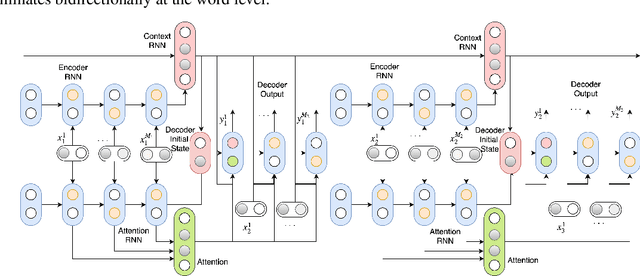
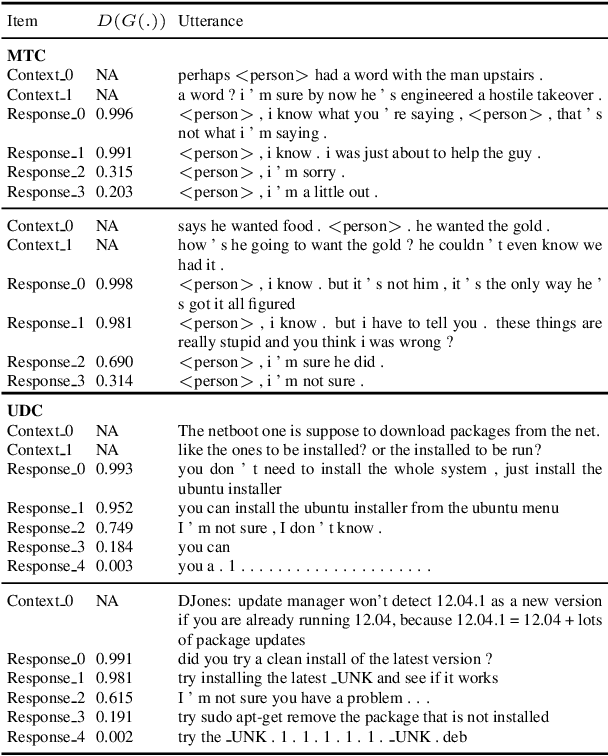
Abstract:We propose an adversarial learning approach to the generation of multi-turn dialogue responses. Our proposed framework, hredGAN, is based on conditional generative adversarial networks (GANs). The GAN's generator is a modified hierarchical recurrent encoder-decoder network (HRED) and the discriminator is a word-level bidirectional RNN that shares context and word embedding with the generator. During inference, noise samples conditioned on the dialogue history are used to perturb the generator's latent space to generate several possible responses. The final response is the one ranked best by the discriminator. The hredGAN shows major advantages over existing methods: (1) it generalizes better than networks trained using only the log-likelihood criterion, and (2) it generates longer, more informative and more diverse responses with high utterance and topic relevance even with limited training data. This superiority is demonstrated on the Movie triples and Ubuntu dialogue datasets in terms of perplexity, BLEU, ROUGE and Distinct n-gram scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge