Alain Peres
Automated Algorithm Selection for Radar Network Configuration
May 07, 2022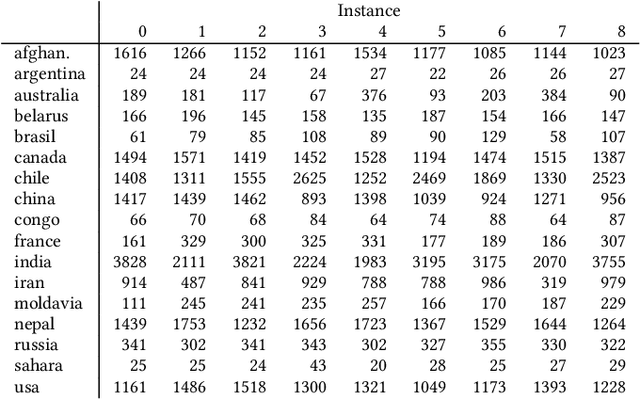
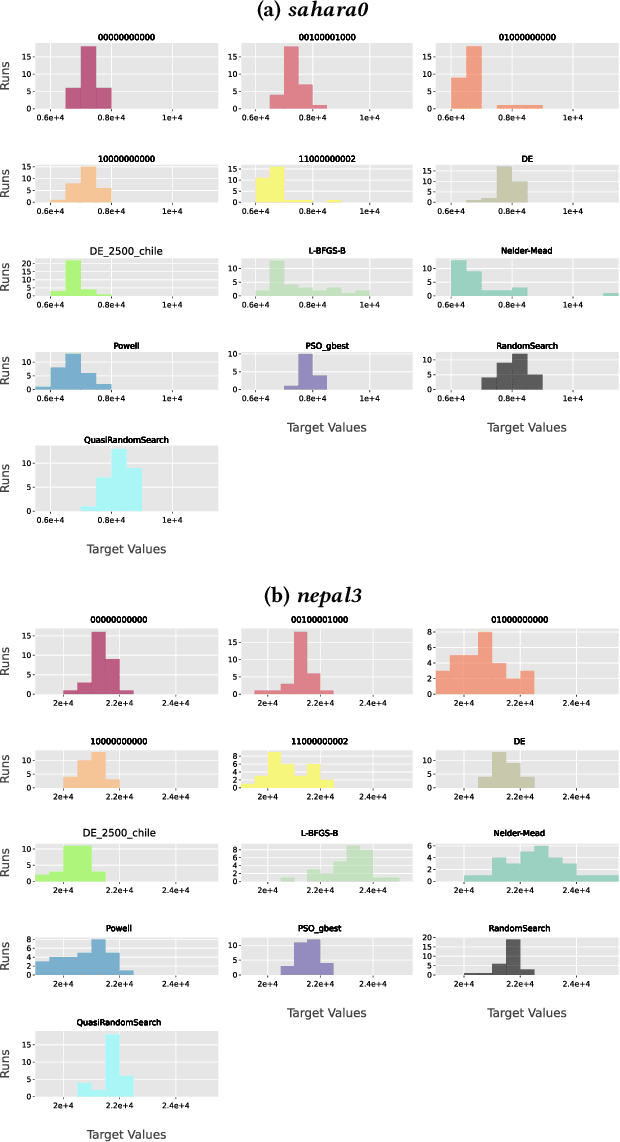

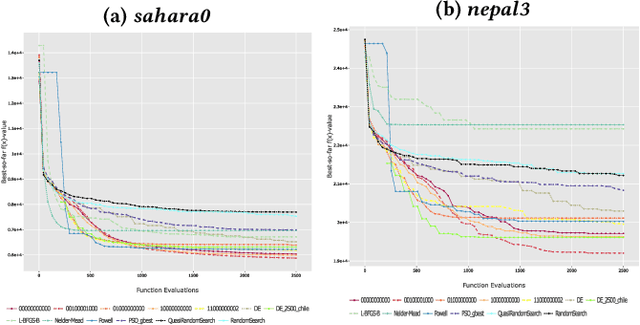
Abstract:The configuration of radar networks is a complex problem that is often performed manually by experts with the help of a simulator. Different numbers and types of radars as well as different locations that the radars shall cover give rise to different instances of the radar configuration problem. The exact modeling of these instances is complex, as the quality of the configurations depends on a large number of parameters, on internal radar processing, and on the terrains on which the radars need to be placed. Classic optimization algorithms can therefore not be applied to this problem, and we rely on "trial-and-error" black-box approaches. In this paper, we study the performances of 13~black-box optimization algorithms on 153~radar network configuration problem instances. The algorithms perform considerably better than human experts. Their ranking, however, depends on the budget of configurations that can be evaluated and on the elevation profile of the location. We therefore also investigate automated algorithm selection approaches. Our results demonstrate that a pipeline that extracts instance features from the elevation of the terrain performs on par with the classical, far more expensive approach that extracts features from the objective function.
Multi-Radar Tracking Optimization for Collaborative Combat
Oct 20, 2020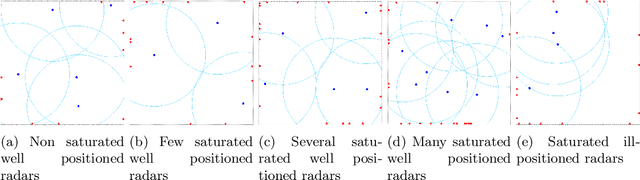
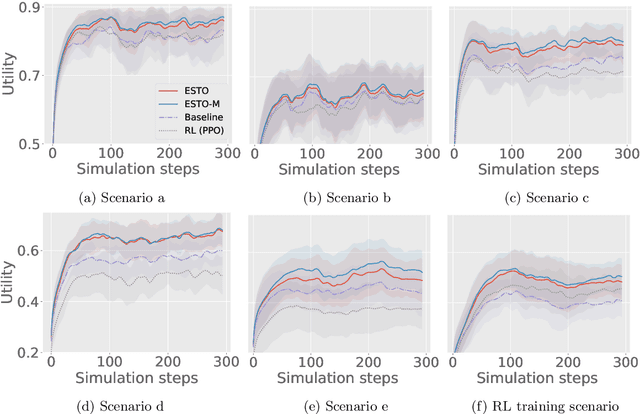
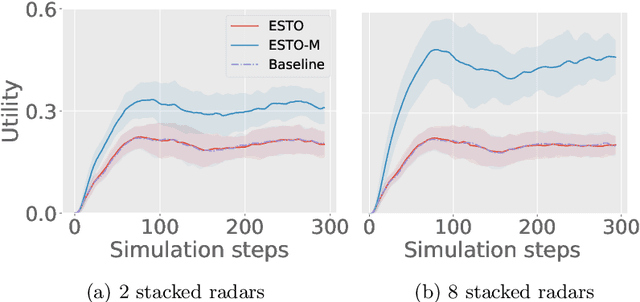
Abstract:Smart Grids of collaborative netted radars accelerate kill chains through more efficient cross-cueing over centralized command and control. In this paper, we propose two novel reward-based learning approaches to decentralized netted radar coordination based on black-box optimization and Reinforcement Learning (RL). To make the RL approach tractable, we use a simplification of the problem that we proved to be equivalent to the initial formulation. We apply these techniques on a simulation where radars can follow multiple targets at the same time and show they can learn implicit cooperation by comparing them to a greedy baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge