Alain Berthoz
CdF
On the mechanical contribution of head stabilization to passive dynamics of anthropometric walkers
Oct 29, 2020



Abstract:During the steady gait, humans stabilize their head around the vertical orientation. While there are sensori-cognitive explanations for this phenomenon, its mechanical e fect on the body dynamics remains un-explored. In this study, we take profit from the similarities that human steady gait share with the locomotion of passive dynamics robots. We introduce a simplified anthropometric D model to reproduce a broad walking dynamics. In a previous study, we showed heuristically that the presence of a stabilized head-neck system significantly influences the dynamics of walking. This paper gives new insights that lead to understanding this mechanical e fect. In particular, we introduce an original cart upper-body model that allows to better understand the mechanical interest of head stabilization when walking, and we study how this e fect is sensitive to the choice of control parameters.
Integration of navigation and action selection functionalities in a computational model of cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loops
Jan 03, 2006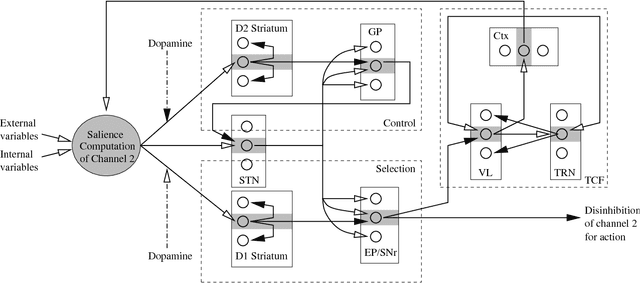
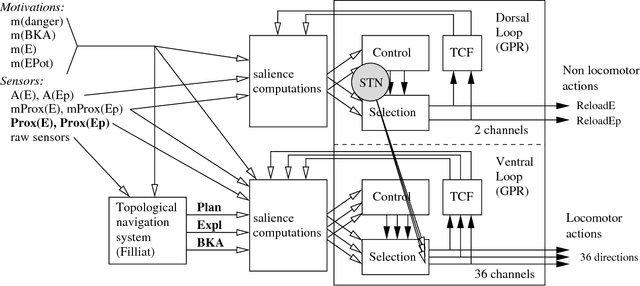
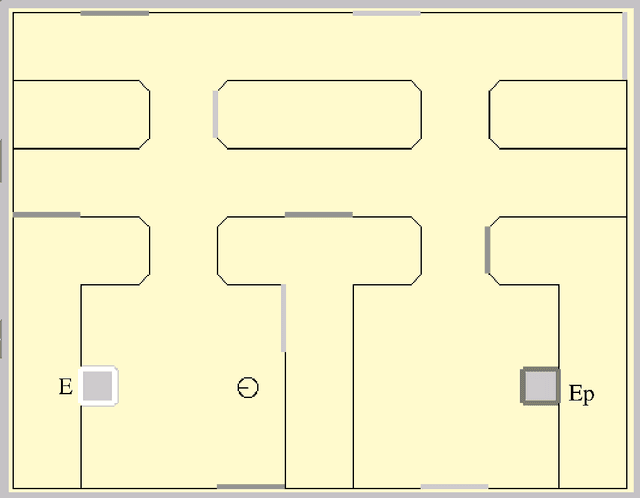
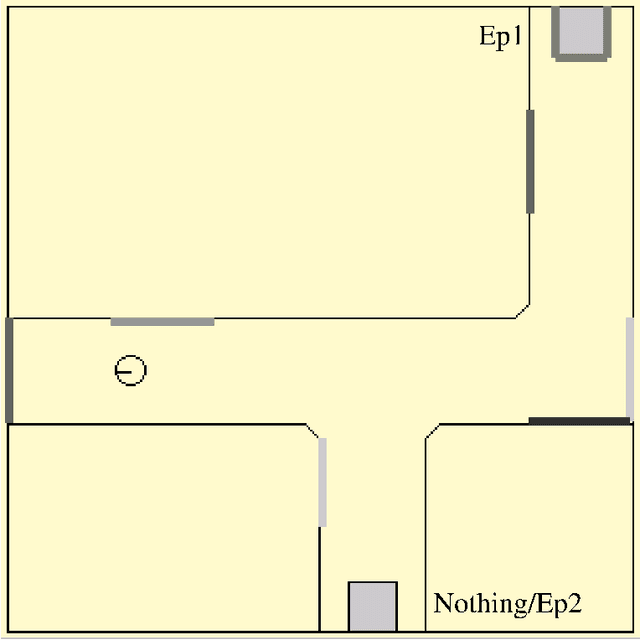
Abstract:This article describes a biomimetic control architecture affording an animat both action selection and navigation functionalities. It satisfies the survival constraint of an artificial metabolism and supports several complementary navigation strategies. It builds upon an action selection model based on the basal ganglia of the vertebrate brain, using two interconnected cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loops: a ventral one concerned with appetitive actions and a dorsal one dedicated to consummatory actions. The performances of the resulting model are evaluated in simulation. The experiments assess the prolonged survival permitted by the use of high level navigation strategies and the complementarity of navigation strategies in dynamic environments. The correctness of the behavioral choices in situations of antagonistic or synergetic internal states are also tested. Finally, the modelling choices are discussed with regard to their biomimetic plausibility, while the experimental results are estimated in terms of animat adaptivity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge