Akhila Krishna
PathoGen-X: A Cross-Modal Genomic Feature Trans-Align Network for Enhanced Survival Prediction from Histopathology Images
Nov 01, 2024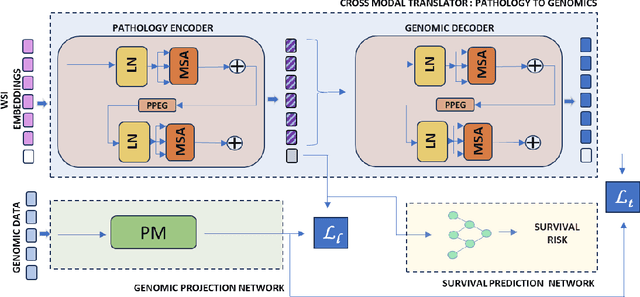
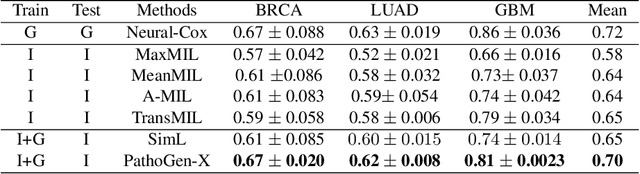
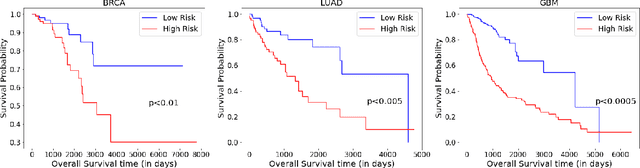
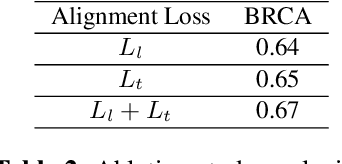
Abstract:Accurate survival prediction is essential for personalized cancer treatment. However, genomic data - often a more powerful predictor than pathology data - is costly and inaccessible. We present the cross-modal genomic feature translation and alignment network for enhanced survival prediction from histopathology images (PathoGen-X). It is a deep learning framework that leverages both genomic and imaging data during training, relying solely on imaging data at testing. PathoGen-X employs transformer-based networks to align and translate image features into the genomic feature space, enhancing weaker imaging signals with stronger genomic signals. Unlike other methods, PathoGen-X translates and aligns features without projecting them to a shared latent space and requires fewer paired samples. Evaluated on TCGA-BRCA, TCGA-LUAD, and TCGA-GBM datasets, PathoGen-X demonstrates strong survival prediction performance, emphasizing the potential of enriched imaging models for accessible cancer prognosis.
Advancing Gene Selection in Oncology: A Fusion of Deep Learning and Sparsity for Precision Gene Selection
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Gene selection plays a pivotal role in oncology research for improving outcome prediction accuracy and facilitating cost-effective genomic profiling for cancer patients. This paper introduces two gene selection strategies for deep learning-based survival prediction models. The first strategy uses a sparsity-inducing method while the second one uses importance based gene selection for identifying relevant genes. Our overall approach leverages the power of deep learning to model complex biological data structures, while sparsity-inducing methods ensure the selection process focuses on the most informative genes, minimizing noise and redundancy. Through comprehensive experimentation on diverse genomic and survival datasets, we demonstrate that our strategy not only identifies gene signatures with high predictive power for survival outcomes but can also streamlines the process for low-cost genomic profiling. The implications of this research are profound as it offers a scalable and effective tool for advancing personalized medicine and targeted cancer therapies. By pushing the boundaries of gene selection methodologies, our work contributes significantly to the ongoing efforts in cancer genomics, promising improved diagnostic and prognostic capabilities in clinical settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge