Aishwarya Mandyam
PERRY: Policy Evaluation with Confidence Intervals using Auxiliary Data
Jul 26, 2025Abstract:Off-policy evaluation (OPE) methods aim to estimate the value of a new reinforcement learning (RL) policy prior to deployment. Recent advances have shown that leveraging auxiliary datasets, such as those synthesized by generative models, can improve the accuracy of these value estimates. Unfortunately, such auxiliary datasets may also be biased, and existing methods for using data augmentation for OPE in RL lack principled uncertainty quantification. In high stakes settings like healthcare, reliable uncertainty estimates are important for comparing policy value estimates. In this work, we propose two approaches to construct valid confidence intervals for OPE when using data augmentation. The first provides a confidence interval over the policy performance conditioned on a particular initial state $V^{\pi}(s_0)$-- such intervals are particularly important for human-centered applications. To do so we introduce a new conformal prediction method for high dimensional state MDPs. Second, we consider the more common task of estimating the average policy performance over many initial states; to do so we draw on ideas from doubly robust estimation and prediction powered inference. Across simulators spanning robotics, healthcare and inventory management, and a real healthcare dataset from MIMIC-IV, we find that our methods can use augmented data and still consistently produce intervals that cover the ground truth values, unlike previously proposed methods.
CANDOR: Counterfactual ANnotated DOubly Robust Off-Policy Evaluation
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Off-policy evaluation (OPE) provides safety guarantees by estimating the performance of a policy before deployment. Recent work introduced IS+, an importance sampling (IS) estimator that uses expert-annotated counterfactual samples to improve behavior dataset coverage. However, IS estimators are known to have high variance; furthermore, the performance of IS+ deteriorates when annotations are imperfect. In this work, we propose a family of OPE estimators inspired by the doubly robust (DR) principle. A DR estimator combines IS with a reward model estimate, known as the direct method (DM), and offers favorable statistical guarantees. We propose three strategies for incorporating counterfactual annotations into a DR-inspired estimator and analyze their properties under various realistic settings. We prove that using imperfect annotations in the DM part of the estimator best leverages the annotations, as opposed to using them in the IS part. To support our theoretical findings, we evaluate the proposed estimators in three contextual bandit environments. Our empirical results show that when the reward model is misspecified and the annotations are imperfect, it is most beneficial to use the annotations only in the DM portion of a DR estimator. Based on these theoretical and empirical insights, we provide a practical guide for using counterfactual annotations in different realistic settings.
Adaptive Interventions with User-Defined Goals for Health Behavior Change
Nov 16, 2023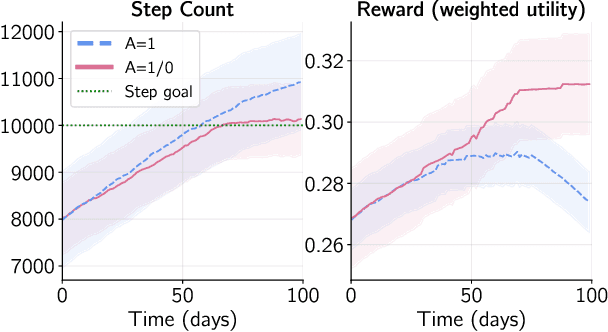
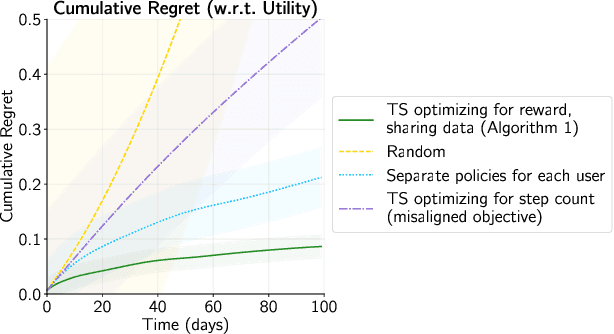
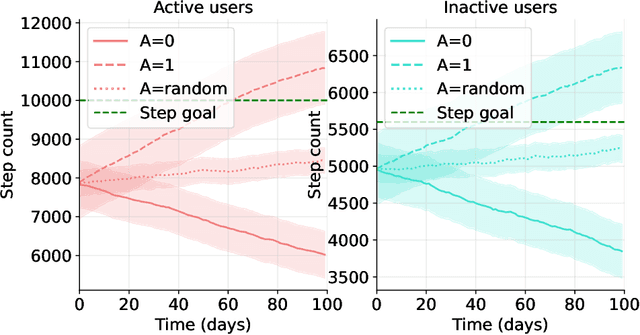
Abstract:Physical inactivity remains a major public health concern, having associations with adverse health outcomes such as cardiovascular disease and type-2 diabetes. Mobile health applications present a promising avenue for low-cost, scalable physical activity promotion, yet often suffer from small effect sizes and low adherence rates, particularly in comparison to human coaching. Goal-setting is a critical component of health coaching that has been underutilized in adaptive algorithms for mobile health interventions. This paper introduces a modification to the Thompson sampling algorithm that places emphasis on individualized goal-setting by optimizing personalized reward functions. As a step towards supporting goal-setting, this paper offers a balanced approach that can leverage shared structure while optimizing individual preferences and goals. We prove that our modification incurs only a constant penalty on the cumulative regret while preserving the sample complexity benefits of data sharing. In a physical activity simulator, we demonstrate that our algorithm achieves substantial improvements in cumulative regret compared to baselines that do not share data or do not optimize for individualized rewards.
Kernel Density Bayesian Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Mar 13, 2023Abstract:Inverse reinforcement learning~(IRL) is a powerful framework to infer an agent's reward function by observing its behavior, but IRL algorithms that learn point estimates of the reward function can be misleading because there may be several functions that describe an agent's behavior equally well. A Bayesian approach to IRL models a distribution over candidate reward functions, alleviating the shortcomings of learning a point estimate. However, several Bayesian IRL algorithms use a $Q$-value function in place of the likelihood function. The resulting posterior is computationally intensive to calculate, has few theoretical guarantees, and the $Q$-value function is often a poor approximation for the likelihood. We introduce kernel density Bayesian IRL (KD-BIRL), which uses conditional kernel density estimation to directly approximate the likelihood, providing an efficient framework that, with a modified reward function parameterization, is applicable to environments with complex and infinite state spaces. We demonstrate KD-BIRL's benefits through a series of experiments in Gridworld environments and a simulated sepsis treatment task.
Nested Policy Reinforcement Learning
Oct 06, 2021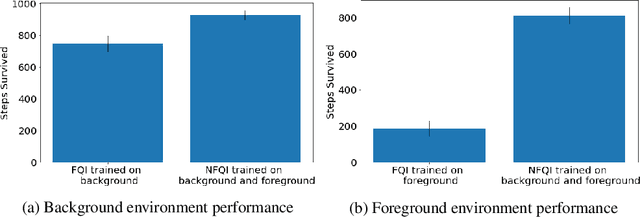

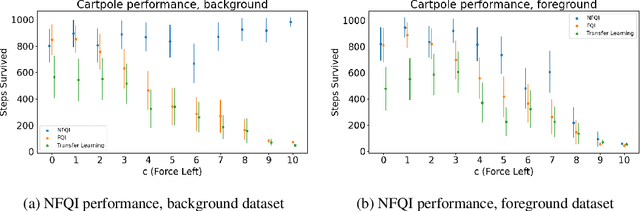

Abstract:Off-policy reinforcement learning (RL) has proven to be a powerful framework for guiding agents' actions in environments with stochastic rewards and unknown or noisy state dynamics. In many real-world settings, these agents must operate in multiple environments, each with slightly different dynamics. For example, we may be interested in developing policies to guide medical treatment for patients with and without a given disease, or policies to navigate curriculum design for students with and without a learning disability. Here, we introduce nested policy fitted Q-iteration (NFQI), an RL framework that finds optimal policies in environments that exhibit such a structure. Our approach develops a nested $Q$-value function that takes advantage of the shared structure between two groups of observations from two separate environments while allowing their policies to be distinct from one another. We find that NFQI yields policies that rely on relevant features and perform at least as well as a policy that does not consider group structure. We demonstrate NFQI's performance using an OpenAI Gym environment and a clinical decision making RL task. Our results suggest that NFQI can develop policies that are better suited to many real-world clinical environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge