Ahmed K. Kadhim
Omni TM-AE: A Scalable and Interpretable Embedding Model Using the Full Tsetlin Machine State Space
May 22, 2025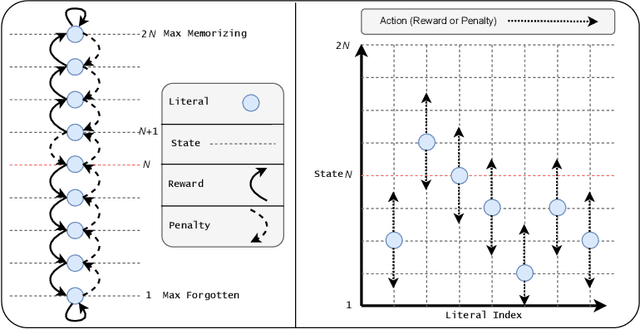
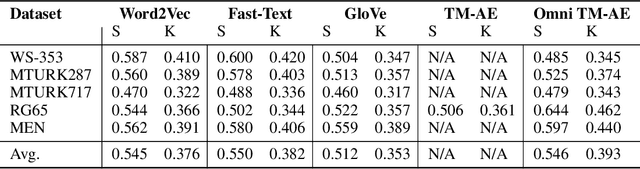
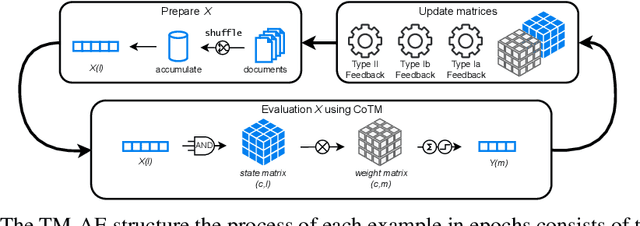
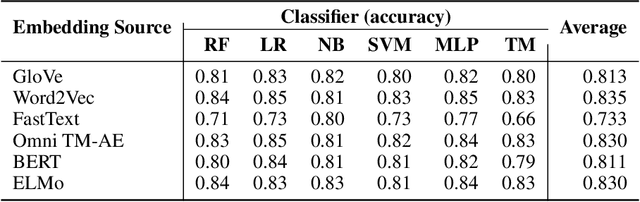
Abstract:The increasing complexity of large-scale language models has amplified concerns regarding their interpretability and reusability. While traditional embedding models like Word2Vec and GloVe offer scalability, they lack transparency and often behave as black boxes. Conversely, interpretable models such as the Tsetlin Machine (TM) have shown promise in constructing explainable learning systems, though they previously faced limitations in scalability and reusability. In this paper, we introduce Omni Tsetlin Machine AutoEncoder (Omni TM-AE), a novel embedding model that fully exploits the information contained in the TM's state matrix, including literals previously excluded from clause formation. This method enables the construction of reusable, interpretable embeddings through a single training phase. Extensive experiments across semantic similarity, sentiment classification, and document clustering tasks show that Omni TM-AE performs competitively with and often surpasses mainstream embedding models. These results demonstrate that it is possible to balance performance, scalability, and interpretability in modern Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems without resorting to opaque architectures.
Adversarial Attacks on AI-Generated Text Detection Models: A Token Probability-Based Approach Using Embeddings
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, text generation tools utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) have occasionally been misused across various domains, such as generating student reports or creative writings. This issue prompts plagiarism detection services to enhance their capabilities in identifying AI-generated content. Adversarial attacks are often used to test the robustness of AI-text generated detectors. This work proposes a novel textual adversarial attack on the detection models such as Fast-DetectGPT. The method employs embedding models for data perturbation, aiming at reconstructing the AI generated texts to reduce the likelihood of detection of the true origin of the texts. Specifically, we employ different embedding techniques, including the Tsetlin Machine (TM), an interpretable approach in machine learning for this purpose. By combining synonyms and embedding similarity vectors, we demonstrates the state-of-the-art reduction in detection scores against Fast-DetectGPT. Particularly, in the XSum dataset, the detection score decreased from 0.4431 to 0.2744 AUROC, and in the SQuAD dataset, it dropped from 0.5068 to 0.3532 AUROC.
Scalable Multi-phase Word Embedding Using Conjunctive Propositional Clauses
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:The Tsetlin Machine (TM) architecture has recently demonstrated effectiveness in Machine Learning (ML), particularly within Natural Language Processing (NLP). It has been utilized to construct word embedding using conjunctive propositional clauses, thereby significantly enhancing our understanding and interpretation of machine-derived decisions. The previous approach performed the word embedding over a sequence of input words to consolidate the information into a cohesive and unified representation. However, that approach encounters scalability challenges as the input size increases. In this study, we introduce a novel approach incorporating two-phase training to discover contextual embeddings of input sequences. Specifically, this method encapsulates the knowledge for each input word within the dataset's vocabulary, subsequently constructing embeddings for a sequence of input words utilizing the extracted knowledge. This technique not only facilitates the design of a scalable model but also preserves interpretability. Our experimental findings revealed that the proposed method yields competitive performance compared to the previous approaches, demonstrating promising results in contrast to human-generated benchmarks. Furthermore, we applied the proposed approach to sentiment analysis on the IMDB dataset, where the TM embedding and the TM classifier, along with other interpretable classifiers, offered a transparent end-to-end solution with competitive performance.
Exploring State Space and Reasoning by Elimination in Tsetlin Machine
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:The Tsetlin Machine (TM) has gained significant attention in Machine Learning (ML). By employing logical fundamentals, it facilitates pattern learning and representation, offering an alternative approach for developing comprehensible Artificial Intelligence (AI) with a specific focus on pattern classification in the form of conjunctive clauses. In the domain of Natural Language Processing (NLP), TM is utilised to construct word embedding and describe target words using clauses. To enhance the descriptive capacity of these clauses, we study the concept of Reasoning by Elimination (RbE) in clauses' formulation, which involves incorporating feature negations to provide a more comprehensive representation. In more detail, this paper employs the Tsetlin Machine Auto-Encoder (TM-AE) architecture to generate dense word vectors, aiming at capturing contextual information by extracting feature-dense vectors for a given vocabulary. Thereafter, the principle of RbE is explored to improve descriptivity and optimise the performance of the TM. Specifically, the specificity parameter s and the voting margin parameter T are leveraged to regulate feature distribution in the state space, resulting in a dense representation of information for each clause. In addition, we investigate the state spaces of TM-AE, especially for the forgotten/excluded features. Empirical investigations on artificially generated data, the IMDB dataset, and the 20 Newsgroups dataset showcase the robustness of the TM, with accuracy reaching 90.62\% for the IMDB.
Exploring Effects of Hyperdimensional Vectors for Tsetlin Machines
Jun 04, 2024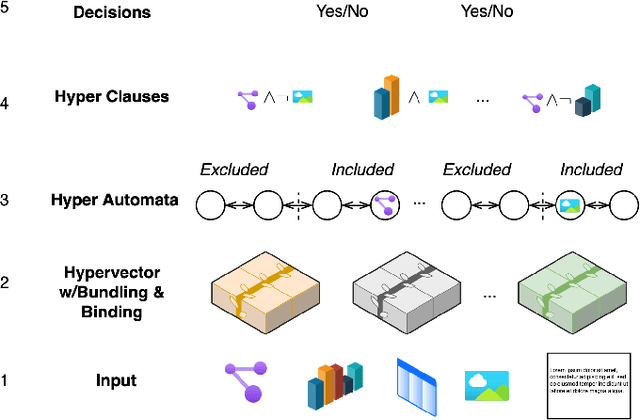
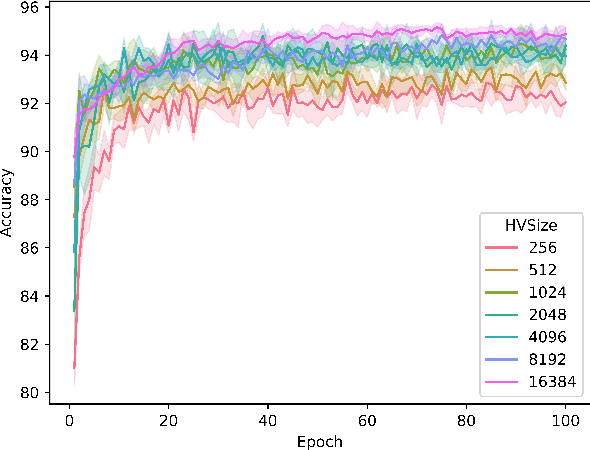
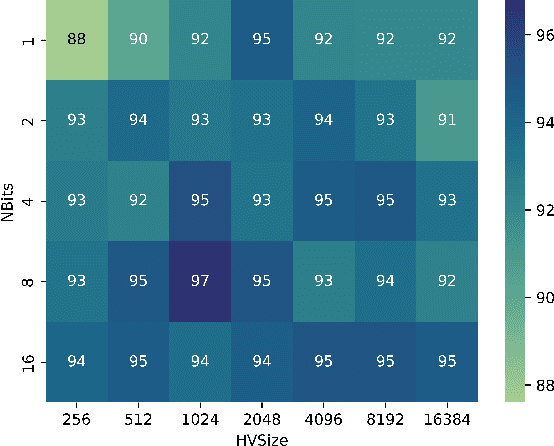
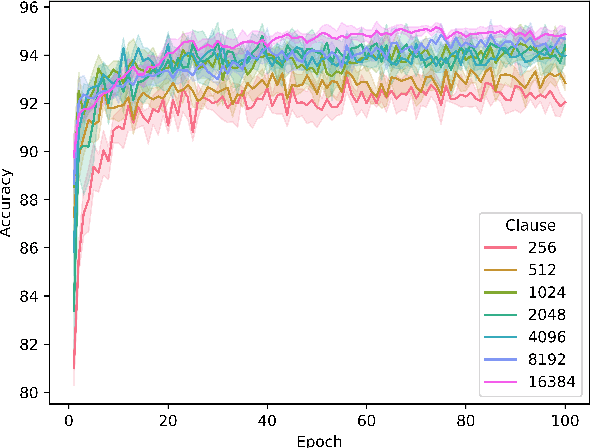
Abstract:Tsetlin machines (TMs) have been successful in several application domains, operating with high efficiency on Boolean representations of the input data. However, Booleanizing complex data structures such as sequences, graphs, images, signal spectra, chemical compounds, and natural language is not trivial. In this paper, we propose a hypervector (HV) based method for expressing arbitrarily large sets of concepts associated with any input data. Using a hyperdimensional space to build vectors drastically expands the capacity and flexibility of the TM. We demonstrate how images, chemical compounds, and natural language text are encoded according to the proposed method, and how the resulting HV-powered TM can achieve significantly higher accuracy and faster learning on well-known benchmarks. Our results open up a new research direction for TMs, namely how to expand and exploit the benefits of operating in hyperspace, including new booleanization strategies, optimization of TM inference and learning, as well as new TM applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge