Ahmed A. Hassan
DRL-based Power Allocation in LiDAL-Assisted RLNC-NOMA OWC Systems
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) is a promising technique for optical wireless communication (OWC), enabling multiple users to share the optical spectrum simultaneously through the power domain. However, the imperfection of channel state information (CSI) and residual errors in decoding process deteriorate the performance of NOMA, especially when multi-parameteric and realistic dense-user indoor scenarios are considered. In this work, we model a LiDAL-assisted RLNC-NOMA OWC system, where the light detection and localization (LiDAL) technique exploits spatio-temporal information to improve user CSI, while random linear network coding (RLNC) enhances data resilience in the NOMA successive decoding process. Power allocation (PA) is a crucial issue in communication systems, particularly in the modeled system, due to the complex interactions between multiple users and the coding and detection processes. However, optimizing continuous PA dynamically requires advanced techniques to avoid excessive computational complexity. Therefore, we adopt a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework to efficiently learn near-optimal power allocation strategies, enabling enhanced system performance. In particular, a DRL-based normalized advantage function (NAF) algorithm is proposed to maximize the average sum rate of the system, and its performance is analyzed and compared to other widely used DRL-based and conventional PA schemes, such as deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG), gain ratio PA (GRPA), and exhaustive search.
Towards FAIR protocols and workflows: The OpenPREDICT case study
Nov 20, 2019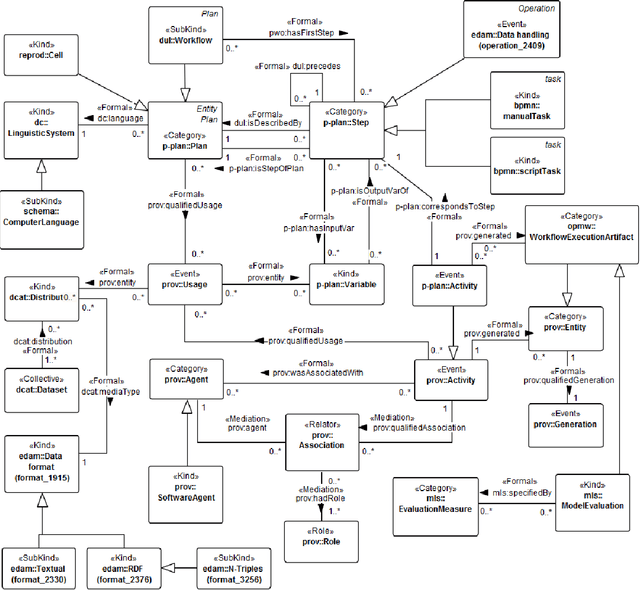
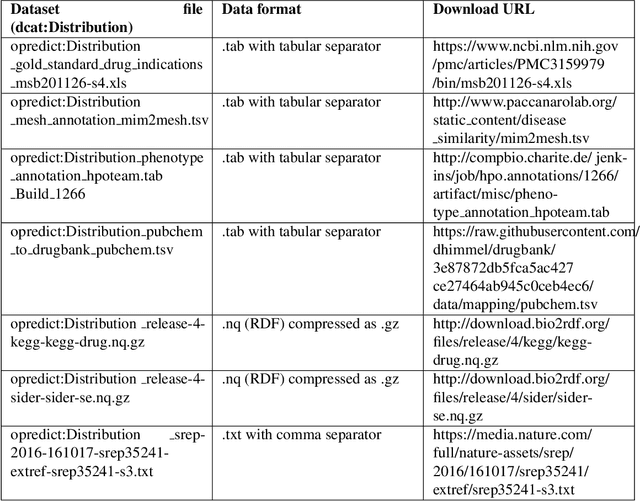
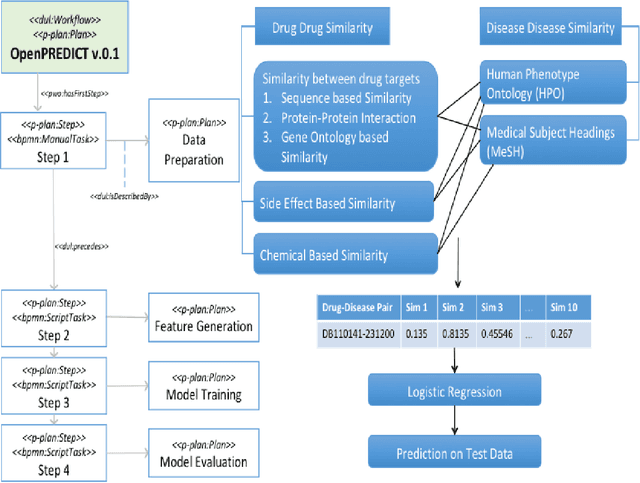
Abstract:It is essential for the advancement of science that scientists and researchers share, reuse and reproduce workflows and protocols used by others. The FAIR principles are a set of guidelines that aim to maximize the value and usefulness of research data, and emphasize a number of important points regarding the means by which digital objects are found and reused by others. The question of how to apply these principles not just to the static input and output data but also to the dynamic workflows and protocols that consume and produce them is still under debate and poses a number of challenges. In this paper we describe our inclusive and overarching approach to apply the FAIR principles to workflows and protocols and demonstrate its benefits. We apply and evaluate our approach on a case study that consists of making the PREDICT workflow, a highly cited drug repurposing workflow, open and FAIR. This includes FAIRification of the involved datasets, as well as applying semantic technologies to represent and store data about the detailed versions of the general protocol, of the concrete workflow instructions, and of their execution traces. A semantic model was proposed to better address these specific requirements and were evaluated by answering competency questions. This semantic model consists of classes and relations from a number of existing ontologies, including Workflow4ever, PROV, EDAM, and BPMN. This allowed us then to formulate and answer new kinds of competency questions. Our evaluation shows the high degree to which our FAIRified OpenPREDICT workflow now adheres to the FAIR principles and the practicality and usefulness of being able to answer our new competency questions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge