Afsah Anwar
ML-based IoT Malware Detection Under Adversarial Settings: A Systematic Evaluation
Aug 30, 2021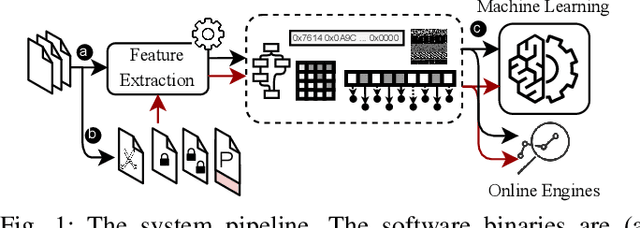
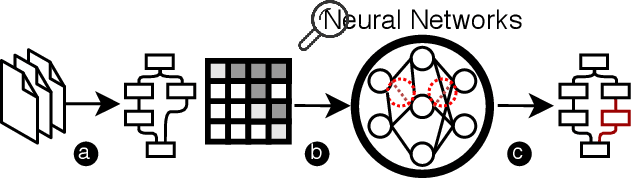
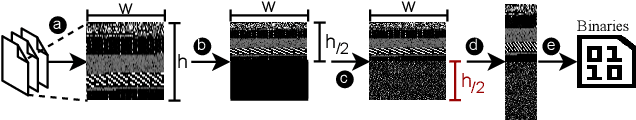
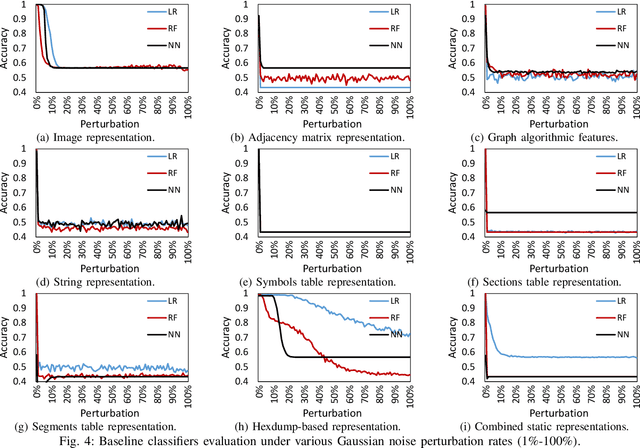
Abstract:The rapid growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices is paralleled by them being on the front-line of malicious attacks. This has led to an explosion in the number of IoT malware, with continued mutations, evolution, and sophistication. These malicious software are detected using machine learning (ML) algorithms alongside the traditional signature-based methods. Although ML-based detectors improve the detection performance, they are susceptible to malware evolution and sophistication, making them limited to the patterns that they have been trained upon. This continuous trend motivates the large body of literature on malware analysis and detection research, with many systems emerging constantly, and outperforming their predecessors. In this work, we systematically examine the state-of-the-art malware detection approaches, that utilize various representation and learning techniques, under a range of adversarial settings. Our analyses highlight the instability of the proposed detectors in learning patterns that distinguish the benign from the malicious software. The results exhibit that software mutations with functionality-preserving operations, such as stripping and padding, significantly deteriorate the accuracy of such detectors. Additionally, our analysis of the industry-standard malware detectors shows their instability to the malware mutations.
Examining Adversarial Learning against Graph-based IoT Malware Detection Systems
Feb 15, 2019
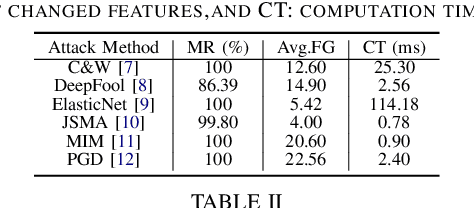

Abstract:The main goal of this study is to investigate the robustness of graph-based Deep Learning (DL) models used for Internet of Things (IoT) malware classification against Adversarial Learning (AL). We designed two approaches to craft adversarial IoT software, including Off-the-Shelf Adversarial Attack (OSAA) methods, using six different AL attack approaches, and Graph Embedding and Augmentation (GEA). The GEA approach aims to preserve the functionality and practicality of the generated adversarial sample through a careful embedding of a benign sample to a malicious one. Our evaluations demonstrate that OSAAs are able to achieve a misclassification rate (MR) of 100%. Moreover, we observed that the GEA approach is able to misclassify all IoT malware samples as benign.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge