Adrian Martin
Towards AI-Driven Policing: Interdisciplinary Knowledge Discovery from Police Body-Worn Camera Footage
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a novel interdisciplinary framework for analyzing police body-worn camera (BWC) footage from the Rochester Police Department (RPD) using advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and statistical machine learning (ML) techniques. Our goal is to detect, classify, and analyze patterns of interaction between police officers and civilians to identify key behavioral dynamics, such as respect, disrespect, escalation, and de-escalation. We apply multimodal data analysis by integrating video, audio, and natural language processing (NLP) techniques to extract meaningful insights from BWC footage. We present our methodology, computational techniques, and findings, outlining a practical approach for law enforcement while advancing the frontiers of knowledge discovery from police BWC data.
Vision-based Autonomous Disinfection of High Touch Surfaces in Indoor Environments
Aug 25, 2021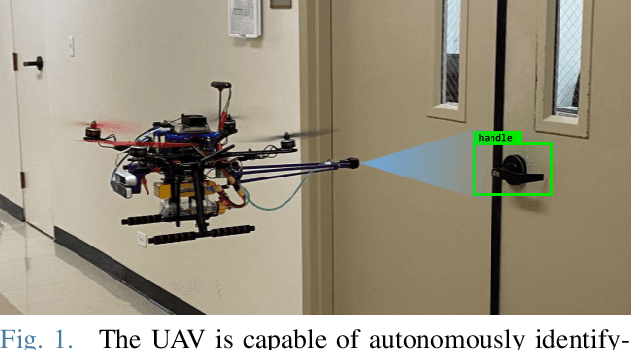
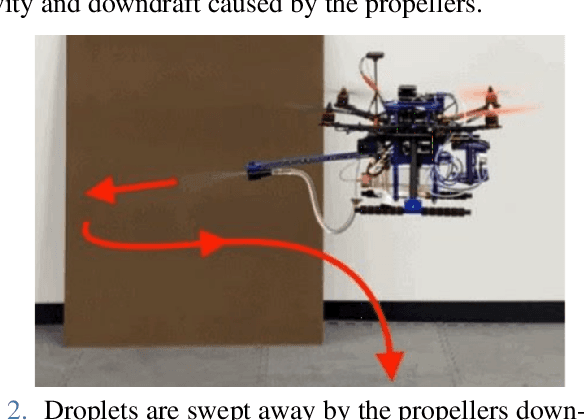
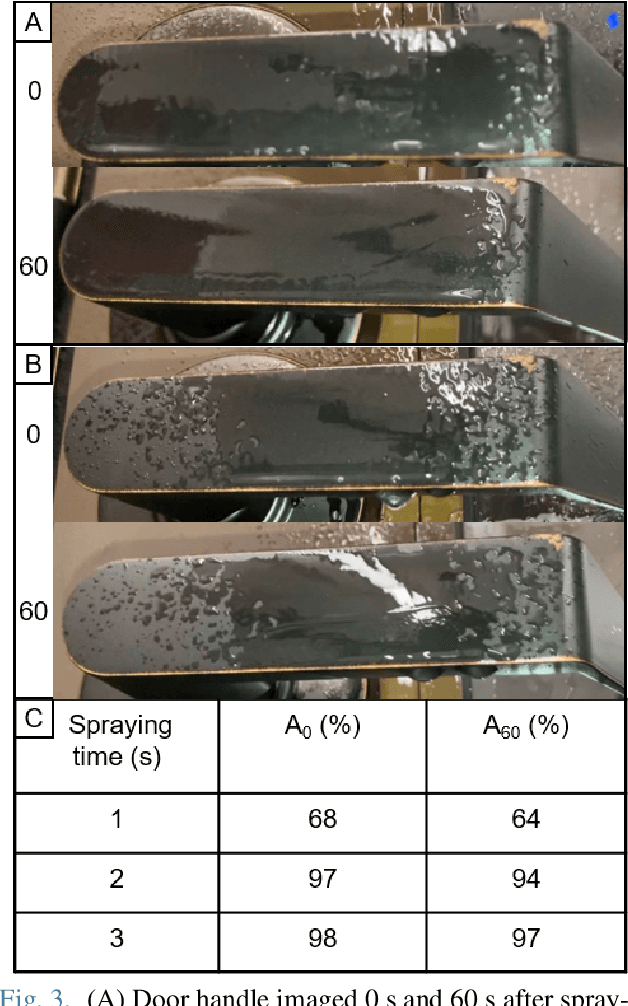
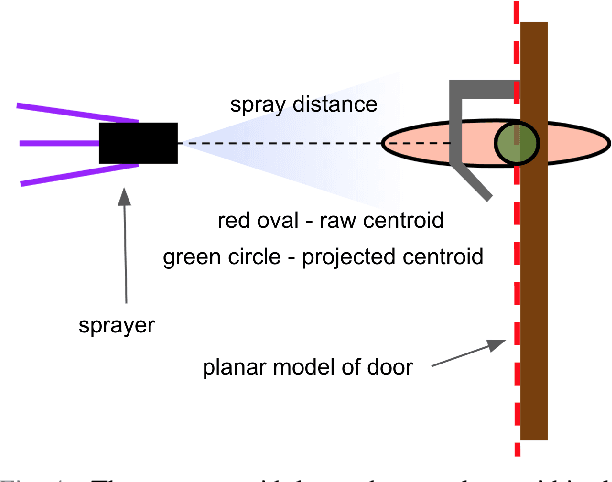
Abstract:Autonomous systems have played an important role in response to the Covid-19 pandemic. Notably, there have been multiple attempts to leverage Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to disinfect surfaces. Although recent research suggests that surface transmission has a minimal impact in the spread of Covid-19, surfaces do play a significant role in the transmission of many other viruses. Employing UAVs for mass spray disinfection offers several potential advantages including high throughput application of disinfectant, large scale deployment, and the minimization of health risks to sanitation workers. Despite these potential benefits and preliminary usage of UAVs for disinfection, there has been little research into their design and effectiveness. In this work we present an autonomous UAV capable of effectively disinfecting surfaces. We identify relevant parameters such as disinfectant concentration, amount, and application distance required of the UAV to sterilize high touch surfaces such as door handles. Finally, we develop a robotic system that enables the fully autonomous disinfection of door handles in an unstructured, previously unknown environment. To our knowledge, this is the smallest untethered UAV ever built with both full autonomy and spraying capabilities, allowing it to operate in confined indoor settings, and the first autonomous UAV to specifically target high touch surfaces on an individual basis with spray disinfectant, resulting in more efficient use of disinfectant.
On 1-Laplacian Elliptic Equations Modeling Magnetic Resonance Image Rician Denoising
Jul 12, 2016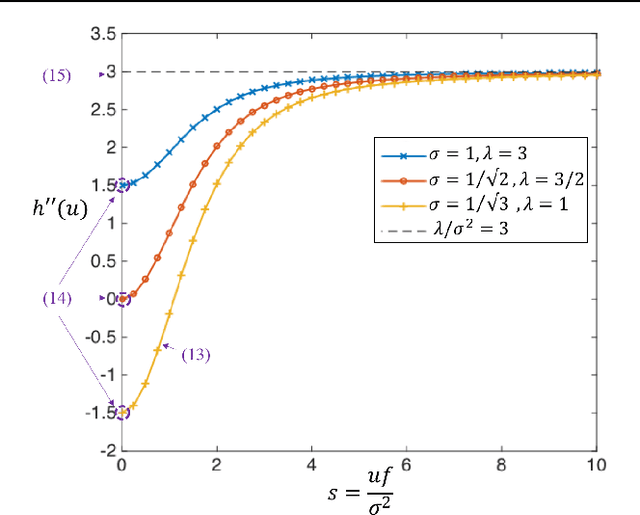
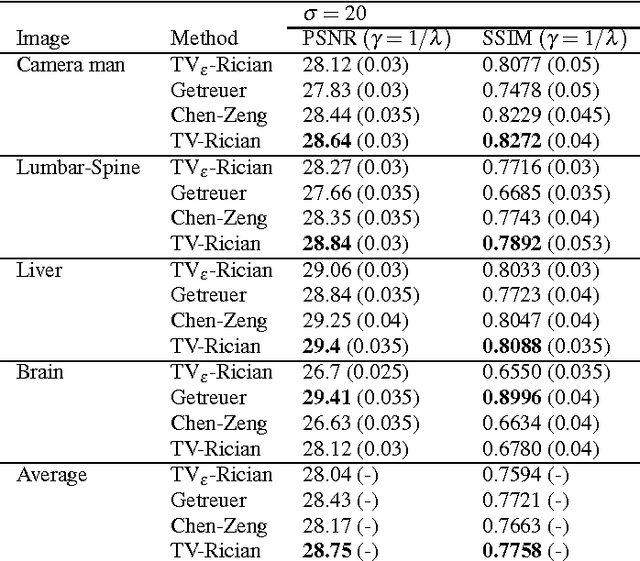
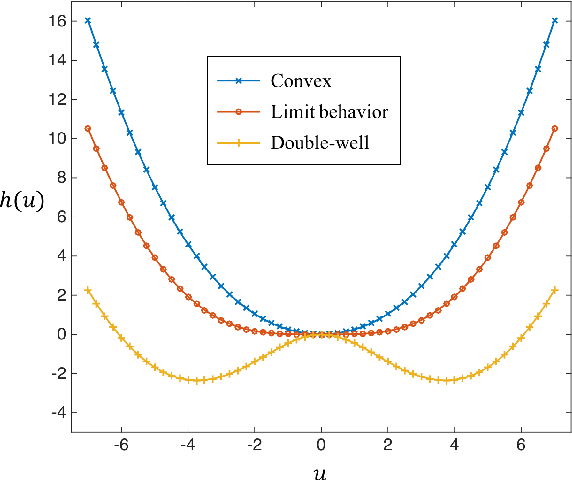
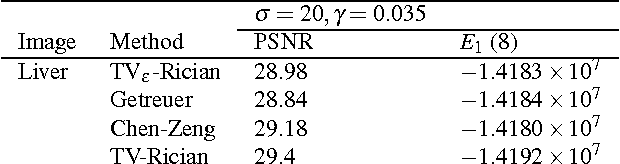
Abstract:Modeling magnitude Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI) rician denoising in a Bayesian or generalized Tikhonov framework using Total Variation (TV) leads naturally to the consideration of nonlinear elliptic equations. These involve the so called $1$-Laplacian operator and special care is needed to properly formulate the problem. The rician statistics of the data are introduced through a singular equation with a reaction term defined in terms of modified first order Bessel functions. An existence theory is provided here together with other qualitative properties of the solutions. Remarkably, each positive global minimum of the associated functional is one of such solutions. Moreover, we directly solve this non--smooth non--convex minimization problem using a convergent Proximal Point Algorithm. Numerical results based on synthetic and real MRI demonstrate a better performance of the proposed method when compared to previous TV based models for rician denoising which regularize or convexify the problem. Finally, an application on real Diffusion Tensor Images, a strongly affected by rician noise MRI modality, is presented and discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge