Abhishek Pandala
Representation-Free Model Predictive Control for Dynamic Motions in Quadrupeds
Dec 18, 2020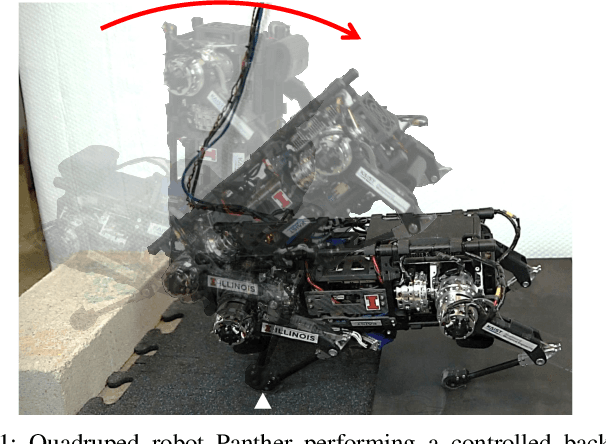
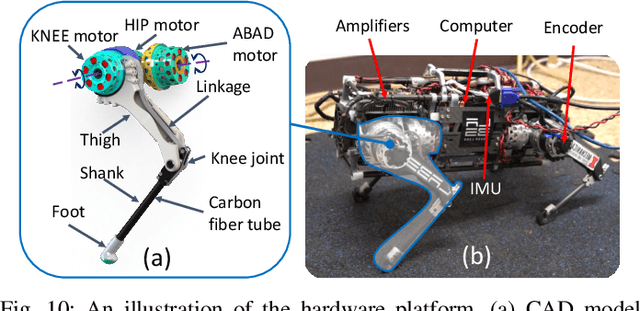
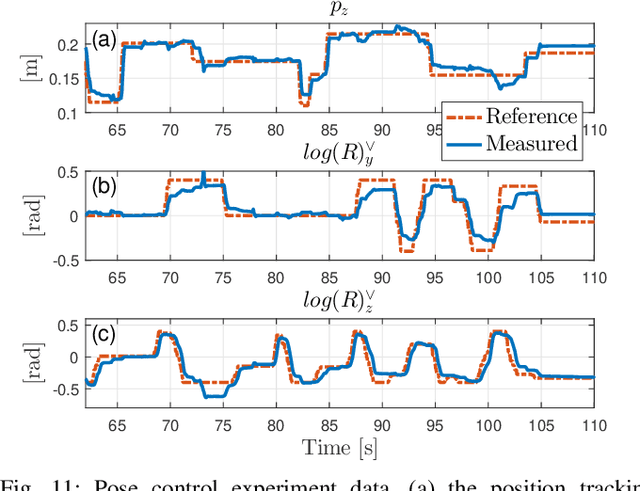
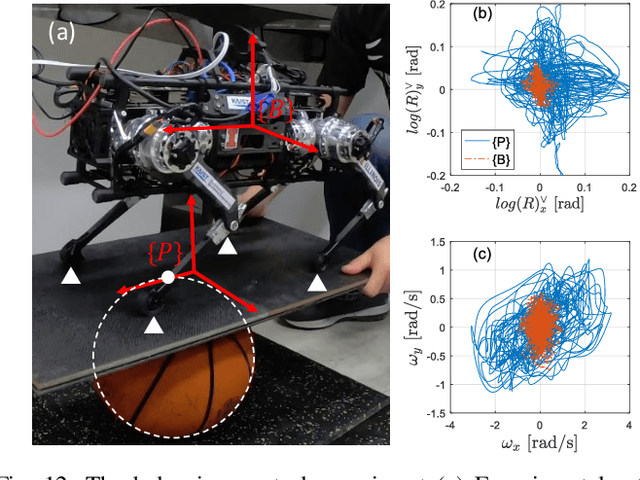
Abstract:This paper presents a novel Representation-Free Model Predictive Control (RF-MPC) framework for controlling various dynamic motions of a quadrupedal robot in three dimensional (3D) space. Our formulation directly represents the rotational dynamics using the rotation matrix, which liberates us from the issues associated with the use of Euler angles and quaternion as the orientation representations. With a variation-based linearization scheme and a carefully constructed cost function, the MPC control law is transcribed to the standard Quadratic Program (QP) form. The MPC controller can operate at real-time rates of 250 Hz on a quadruped robot. Experimental results including periodic quadrupedal gaits and a controlled backflip validate that our control strategy could stabilize dynamic motions that involve singularity in 3D maneuvers.
Quadrupedal Locomotion via Event-Based Predictive Control and QP-Based Virtual Constraints
Apr 15, 2020



Abstract:This paper aims to develop a hierarchical nonlinear control algorithm, based on model predictive control (MPC), quadratic programming (QP), and virtual constraints, to generate and stabilize locomotion patterns in a real-time manner for dynamical models of quadrupedal robots. The higher level of the proposed control scheme is developed based on an event-based MPC that computes the optimal center of mass (COM) trajectories for a reduced-order linear inverted pendulum (LIP) model subject to the feasibility of the net ground reaction force (GRF). The asymptotic stability of the desired target point for the reduced-order model under the event-based MPC approach is investigated. It is shown that the event-based nature of the proposed MPC approach can significantly reduce the computational burden associated with the real-time implementation of MPC techniques. To bridge the gap between reduced- and full-order models, QP-based virtual constraint controllers are developed at the lower level of the proposed control scheme to impose the full-order dynamics to track the optimal trajectories while having all individual GRFs in the friction cone. The analytical results of the paper are numerically confirmed on full-order simulation models of a 22 degree of freedom quadrupedal robot, Vision 60, that is augmented by a robotic manipulator. The paper numerically investigates the robustness of the proposed control algorithm against different contact models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge