Abder-Rahman Ali
Prompt-driven Universal Model for View-Agnostic Echocardiography Analysis
Apr 09, 2024Abstract:Echocardiography segmentation for cardiac analysis is time-consuming and resource-intensive due to the variability in image quality and the necessity to process scans from various standard views. While current automated segmentation methods in echocardiography show promising performance, they are trained on specific scan views to analyze corresponding data. However, this solution has a limitation as the number of required models increases with the number of standard views. To address this, in this paper, we present a prompt-driven universal method for view-agnostic echocardiography analysis. Considering the domain shift between standard views, we first introduce a method called prompt matching, aimed at learning prompts specific to different views by matching prompts and querying input embeddings using a pre-trained vision model. Then, we utilized a pre-trained medical language model to align textual information with pixel data for accurate segmentation. Extensive experiments on three standard views showed that our approach significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art universal methods and achieves comparable or even better performances over the segmentation model trained and tested on same views.
Skin cancer detection based on deep learning and entropy to detect outlier samples
Sep 10, 2019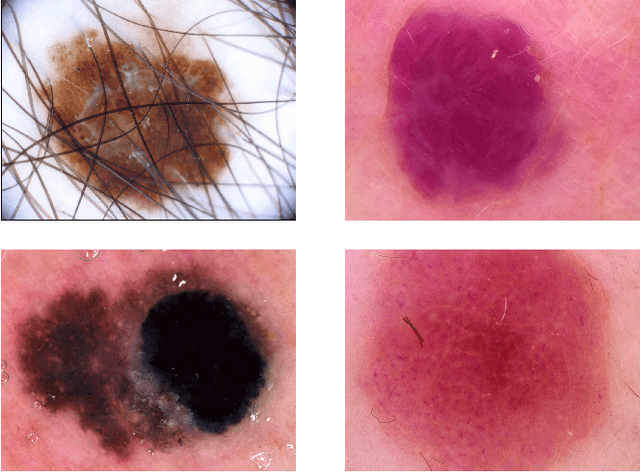
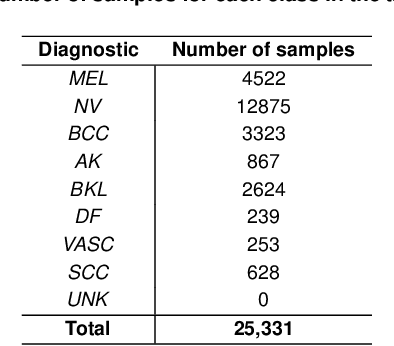
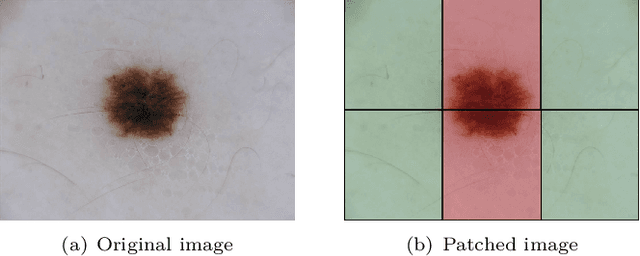
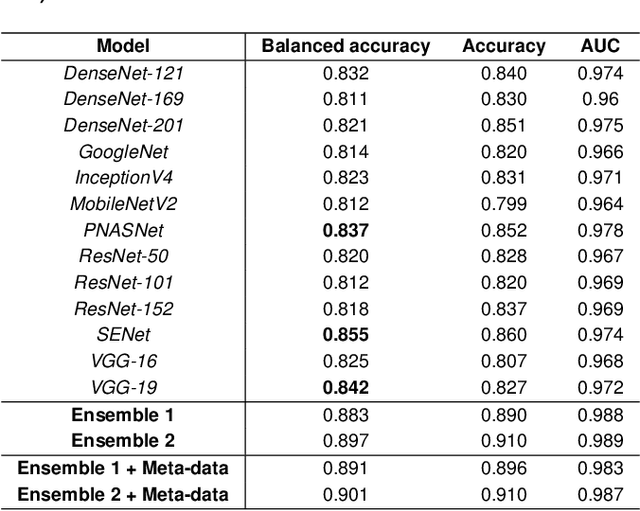
Abstract:We describe our methods to address both tasks of the ISIC 2019 challenge. The goal of this challenge is to provide the diagnostic for skin cancer using images and meta-data. There are nine classes in the dataset, nonetheless, one of them is an outlier and is not present on it. To tackle the challenge, we apply an ensemble of classifiers, which has 13 convolutional neural networks (CNN), we develop two approaches to handle the outlier class and we propose a straightforward method to use the meta-data along with the images. Throughout this report, we detail each methodology and parameters to make it easy to replicate our work. The results obtained are in accordance with the previous challenges and the approaches to detect the outlier class and to address the meta-data seem to be work properly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge