A Arunkumar
The Tag-Team Approach: Leveraging CLS and Language Tagging for Enhancing Multilingual ASR
May 31, 2023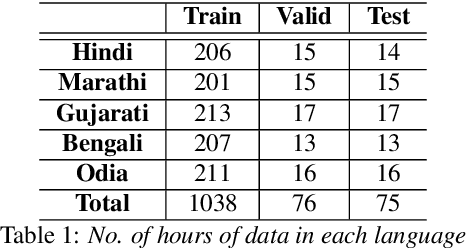
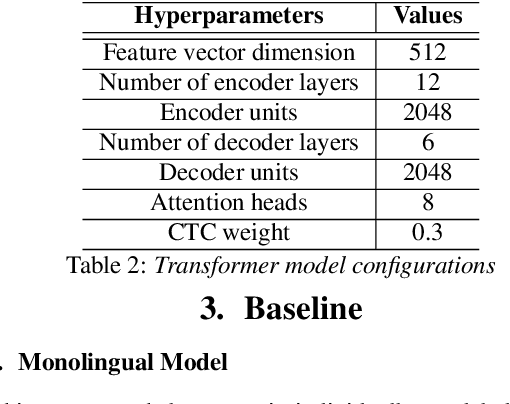
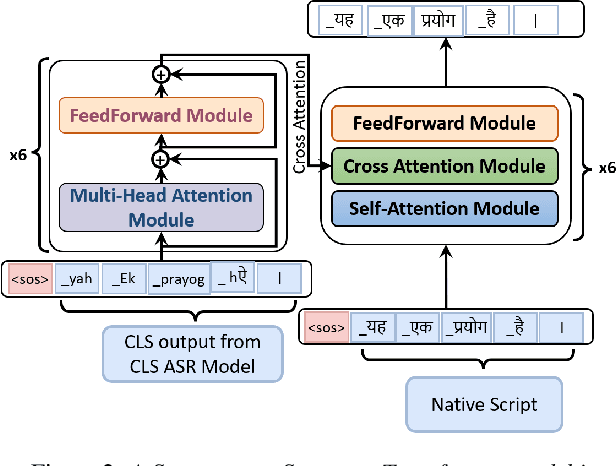
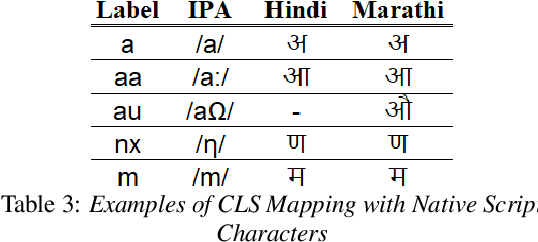
Abstract:Building a multilingual Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) system in a linguistically diverse country like India can be a challenging task due to the differences in scripts and the limited availability of speech data. This problem can be solved by exploiting the fact that many of these languages are phonetically similar. These languages can be converted into a Common Label Set (CLS) by mapping similar sounds to common labels. In this paper, new approaches are explored and compared to improve the performance of CLS based multilingual ASR model. Specific language information is infused in the ASR model by giving Language ID or using CLS to Native script converter on top of the CLS Multilingual model. These methods give a significant improvement in Word Error Rate (WER) compared to the CLS baseline. These methods are further tried on out-of-distribution data to check their robustness.
Investigation of Ensemble features of Self-Supervised Pretrained Models for Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 11, 2022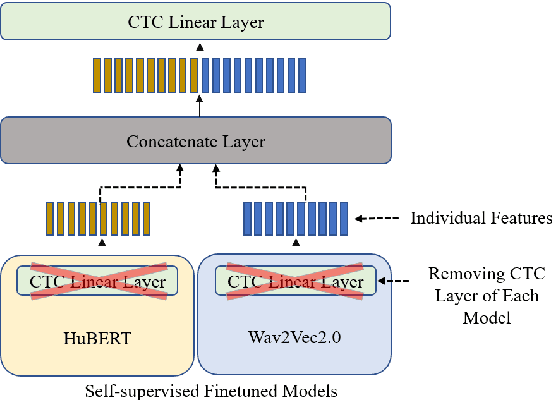
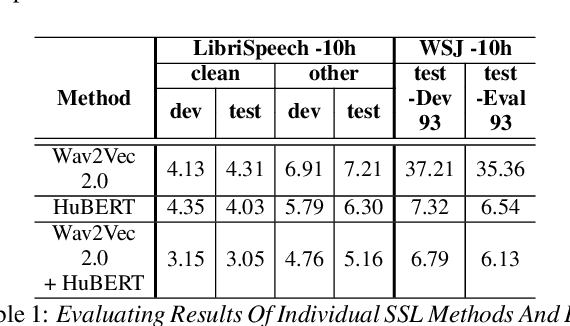
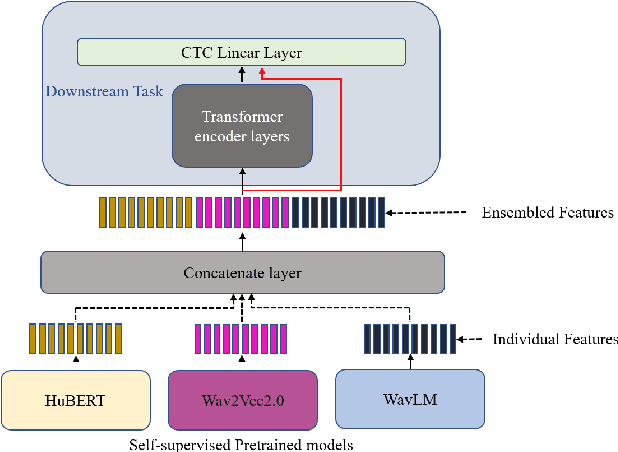
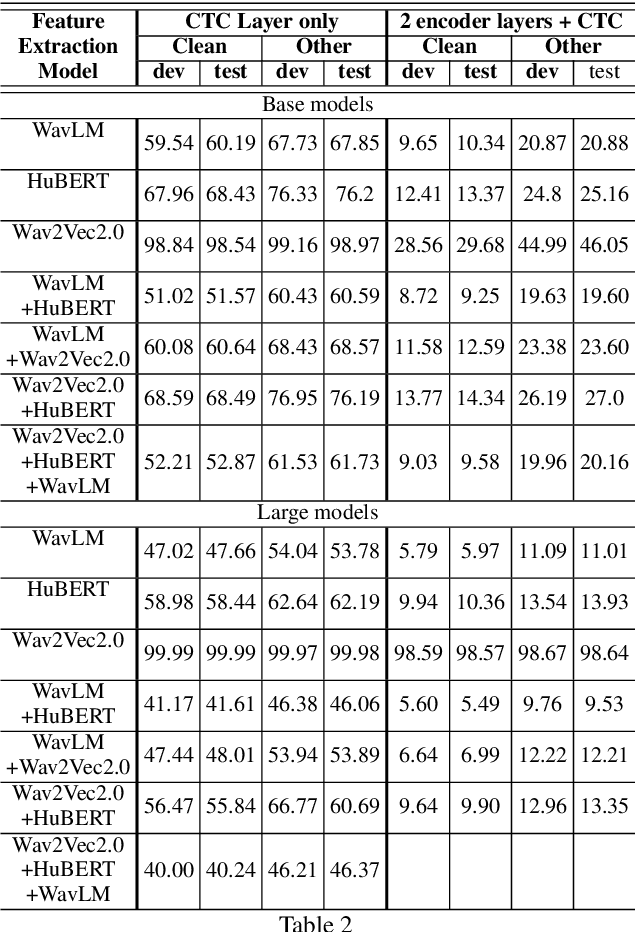
Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) based models have been shown to generate powerful representations that can be used to improve the performance of downstream speech tasks. Several state-of-the-art SSL models are available, and each of these models optimizes a different loss which gives rise to the possibility of their features being complementary. This paper proposes using an ensemble of such SSL representations and models, which exploits the complementary nature of the features extracted by the various pretrained models. We hypothesize that this results in a richer feature representation and shows results for the ASR downstream task. To this end, we use three SSL models that have shown excellent results on ASR tasks, namely HuBERT, Wav2vec2.0, and WaveLM. We explore the ensemble of models fine-tuned for the ASR task and the ensemble of features using the embeddings obtained from the pre-trained models for a downstream ASR task. We get improved performance over individual models and pre-trained features using Librispeech(100h) and WSJ dataset for the downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge