Štefan Beňuš
Language Proficiency and F0 Entrainment: A Study of L2 English Imitation in Italian, French, and Slovak Speakers
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:This study explores F0 entrainment in second language (L2) English speech imitation during an Alternating Reading Task (ART). Participants with Italian, French, and Slovak native languages imitated English utterances, and their F0 entrainment was quantified using the Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) distance between the parameterized F0 contours of the imitated utterances and those of the model utterances. Results indicate a nuanced relationship between L2 English proficiency and entrainment: speakers with higher proficiency generally exhibit less entrainment in pitch variation and declination. However, within dyads, the more proficient speakers demonstrate a greater ability to mimic pitch range, leading to increased entrainment. This suggests that proficiency influences entrainment differently at individual and dyadic levels, highlighting the complex interplay between language skill and prosodic adaptation.
ART: The Alternating Reading Task Corpus for Speech Entrainment and Imitation
Apr 03, 2024Abstract:We introduce the Alternating Reading Task (ART) Corpus, a collection of dyadic sentence reading for studying the entrainment and imitation behaviour in speech communication. The ART corpus features three experimental conditions - solo reading, alternating reading, and deliberate imitation - as well as three sub-corpora encompassing French-, Italian-, and Slovak-accented English. This design allows systematic investigation of speech entrainment in a controlled and less-spontaneous setting. Alongside detailed transcriptions, it includes English proficiency scores, demographics, and in-experiment questionnaires for probing linguistic, personal and interpersonal influences on entrainment. Our presentation covers its design, collection, annotation processes, initial analysis, and future research prospects.
Relationship between auditory and semantic entrainment using Deep Neural Networks (DNN)
Dec 27, 2023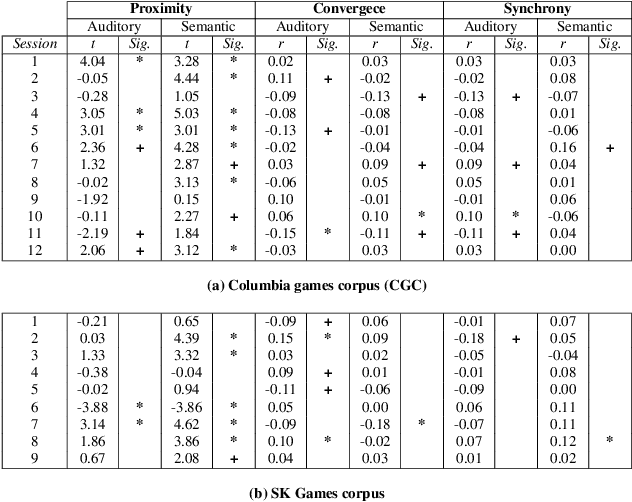
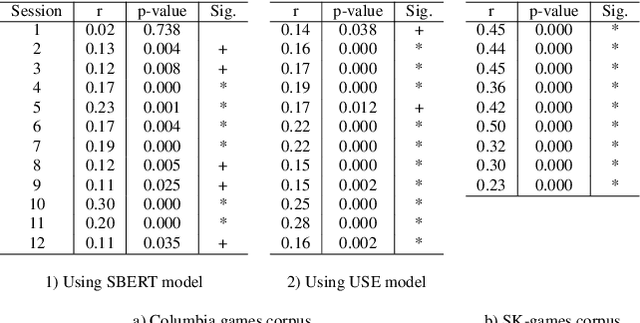
Abstract:The tendency of people to engage in similar, matching, or synchronized behaviour when interacting is known as entrainment. Many studies examined linguistic (syntactic and lexical structures) and paralinguistic (pitch, intensity) entrainment, but less attention was given to finding the relationship between them. In this study, we utilized state-of-the-art DNN embeddings such as BERT and TRIpLet Loss network (TRILL) vectors to extract features for measuring semantic and auditory similarities of turns within dialogues in two comparable spoken corpora of two different languages. We found people's tendency to entrain on semantic features more when compared to auditory features. Additionally, we found that entrainment in semantic and auditory linguistic features are positively correlated. The findings of this study might assist in implementing the mechanism of entrainment in human-machine interaction (HMI).
Entrainment profiles: Comparison by gender, role, and feature set
May 29, 2018



Abstract:We examine prosodic entrainment in cooperative game dialogs for new feature sets describing register, pitch accent shape, and rhythmic aspects of utterances. For these as well as for established features we present entrainment profiles to detect within- and across-dialog entrainment by the speakers' gender and role in the game. It turned out, that feature sets undergo entrainment in different quantitative and qualitative ways, which can partly be attributed to their different functions. Furthermore, interactions between speaker gender and role (describer vs. follower) suggest gender-dependent strategies in cooperative solution-oriented interactions: female describers entrain most, male describers least. Our data suggests a slight advantage of the latter strategy on task success.
* Accepted Manuscript for Speech Communication (Elsevier), 25 April 2018
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge