Éric Le Ferrand
Spoken Term Detection Methods for Sparse Transcription in Very Low-resource Settings
Jun 11, 2021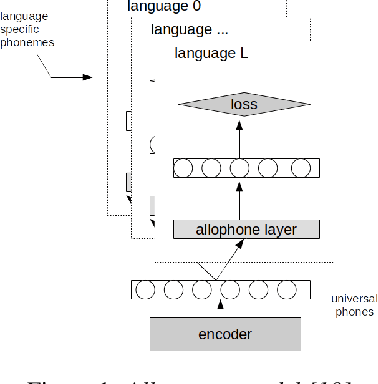
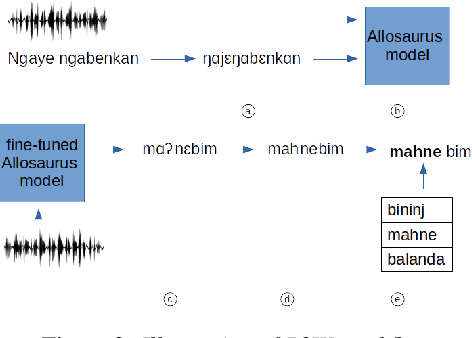
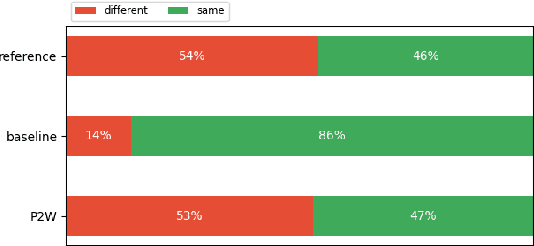
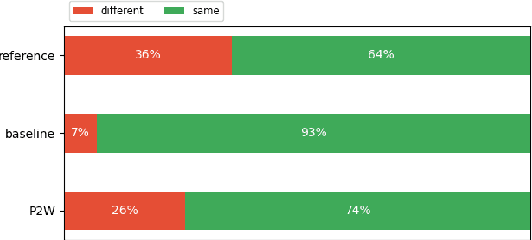
Abstract:We investigate the efficiency of two very different spoken term detection approaches for transcription when the available data is insufficient to train a robust ASR system. This work is grounded in very low-resource language documentation scenario where only few minutes of recording have been transcribed for a given language so far.Experiments on two oral languages show that a pretrained universal phone recognizer, fine-tuned with only a few minutes of target language speech, can be used for spoken term detection with a better overall performance than a dynamic time warping approach. In addition, we show that representing phoneme recognition ambiguity in a graph structure can further boost the recall while maintaining high precision in the low resource spoken term detection task.
Enabling Interactive Transcription in an Indigenous Community
Nov 12, 2020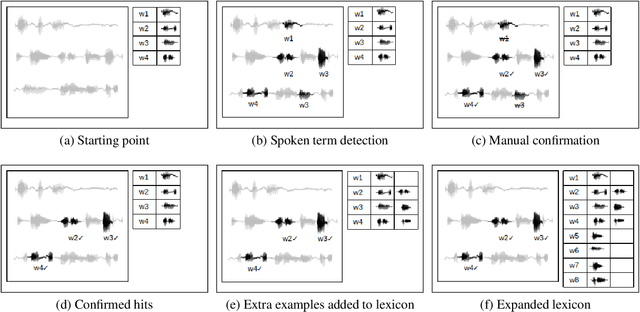

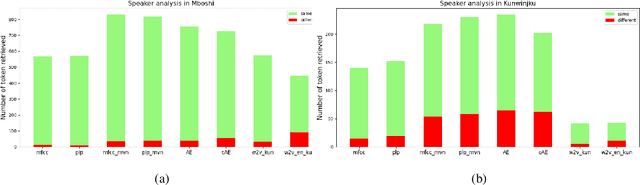
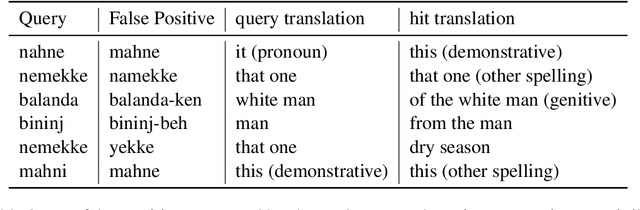
Abstract:We propose a novel transcription workflow which combines spoken term detection and human-in-the-loop, together with a pilot experiment. This work is grounded in an almost zero-resource scenario where only a few terms have so far been identified, involving two endangered languages. We show that in the early stages of transcription, when the available data is insufficient to train a robust ASR system, it is possible to take advantage of the transcription of a small number of isolated words in order to bootstrap the transcription of a speech collection.
MaSS: A Large and Clean Multilingual Corpus of Sentence-aligned Spoken Utterances Extracted from the Bible
Aug 01, 2019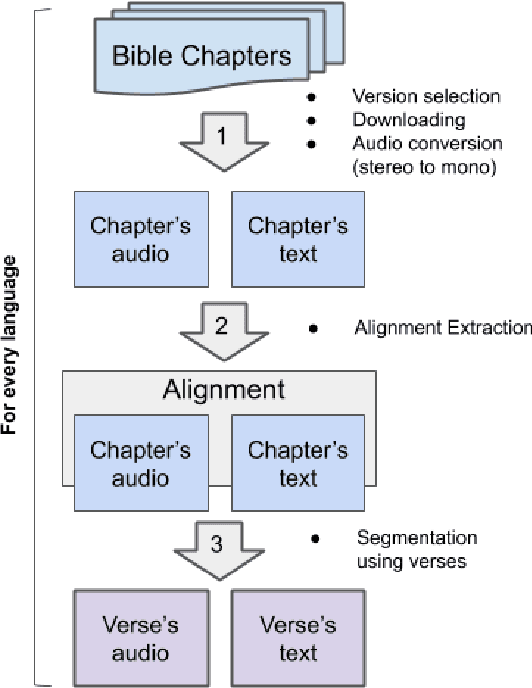
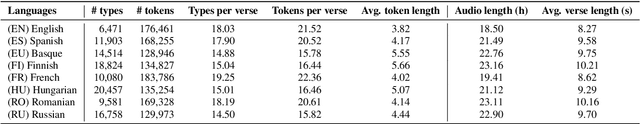
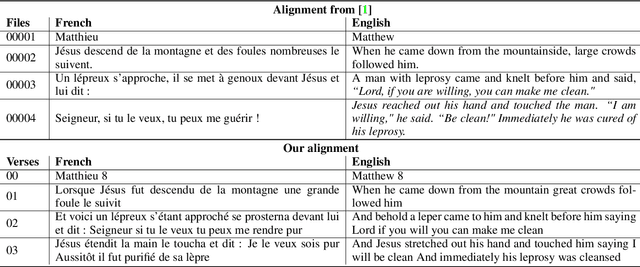
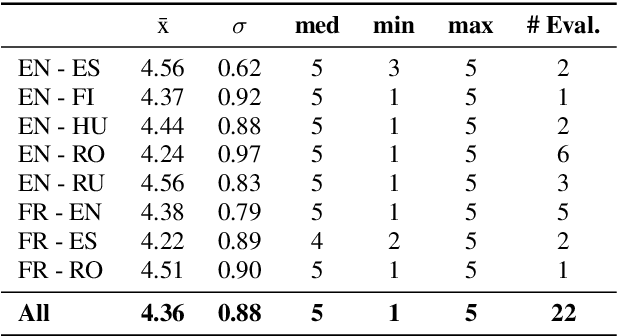
Abstract:The CMU Wilderness Multilingual Speech Dataset is a newly published multilingual speech dataset based on recorded readings of the New Testament. It provides data to build Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and Text-to-Speech (TTS) models for potentially 700 languages. However, the fact that the source content (the Bible), is the same for all the languages is not exploited to date. Therefore, this article proposes to add multilingual links between speech segments in different languages, and shares a large and clean dataset of 8,130 para-lel spoken utterances across 8 languages (56 language pairs).We name this corpus MaSS (Multilingual corpus of Sentence-aligned Spoken utterances). The covered languages (Basque, English, Finnish, French, Hungarian, Romanian, Russian and Spanish) allow researches on speech-to-speech alignment as well as on translation for syntactically divergent language pairs. The quality of the final corpus is attested by human evaluation performed on a corpus subset (100 utterances, 8 language pairs). Lastly, we showcase the usefulness of the final product on a bilingual speech retrieval task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge