Waypoint Planning Networks
Paper and Code
May 01, 2021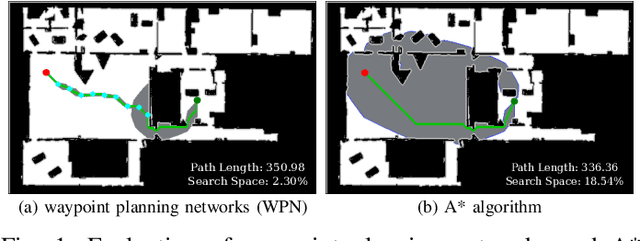
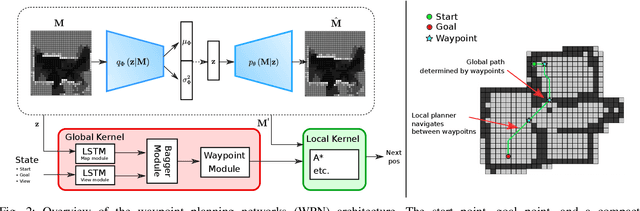
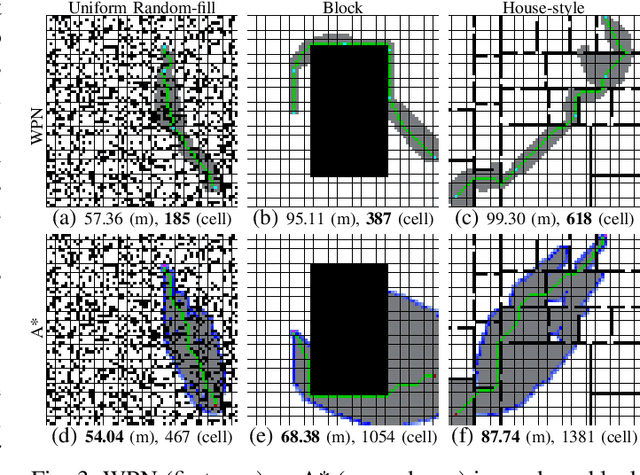
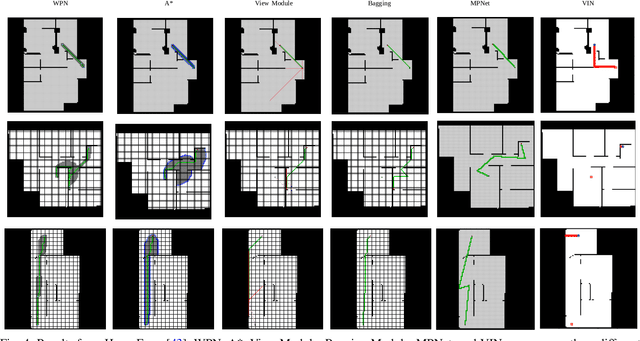
With the recent advances in machine learning, path planning algorithms are also evolving; however, the learned path planning algorithms often have difficulty competing with success rates of classic algorithms. We propose waypoint planning networks (WPN), a hybrid algorithm based on LSTMs with a local kernel - a classic algorithm such as A*, and a global kernel using a learned algorithm. WPN produces a more computationally efficient and robust solution. We compare WPN against A*, as well as related works including motion planning networks (MPNet) and value iteration networks (VIN). In this paper, the design and experiments have been conducted for 2D environments. Experimental results outline the benefits of WPN, both in efficiency and generalization. It is shown that WPN's search space is considerably less than A*, while being able to generate near optimal results. Additionally, WPN works on partial maps, unlike A* which needs the full map in advance. The code is available online.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge