Visual Fixation-Based Retinal Prosthetic Simulation
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2024
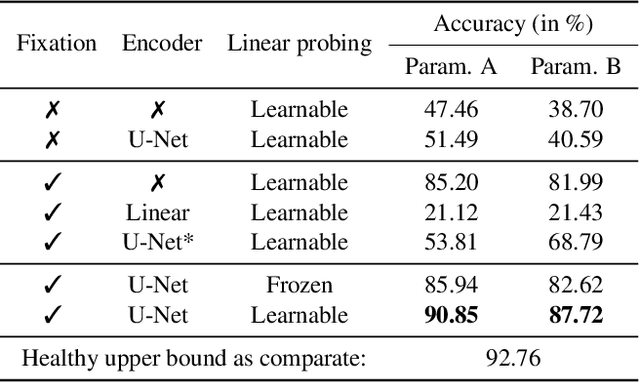
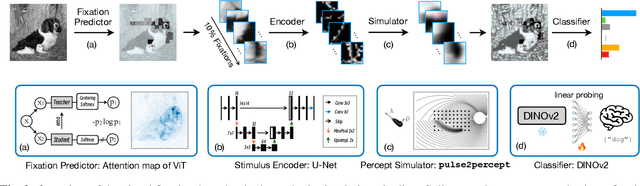
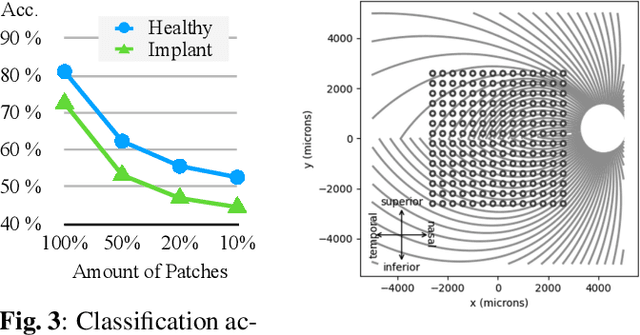
This study proposes a retinal prosthetic simulation framework driven by visual fixations, inspired by the saccade mechanism, and assesses performance improvements through end-to-end optimization in a classification task. Salient patches are predicted from input images using the self-attention map of a vision transformer to mimic visual fixations. These patches are then encoded by a trainable U-Net and simulated using the pulse2percept framework to predict visual percepts. By incorporating a learnable encoder, we aim to optimize the visual information transmitted to the retinal implant, addressing both the limited resolution of the electrode array and the distortion between the input stimuli and resulting phosphenes. The predicted percepts are evaluated using the self-supervised DINOv2 foundation model, with an optional learnable linear layer for classification accuracy. On a subset of the ImageNet validation set, the fixation-based framework achieves a classification accuracy of 87.72%, using computational parameters based on a real subject's physiological data, significantly outperforming the downsampling-based accuracy of 40.59% and approaching the healthy upper bound of 92.76%. Our approach shows promising potential for producing more semantically understandable percepts with the limited resolution available in retinal prosthetics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge