Unsupervised Segmentation in Real-World Images via Spelke Object Inference
Paper and Code
May 17, 2022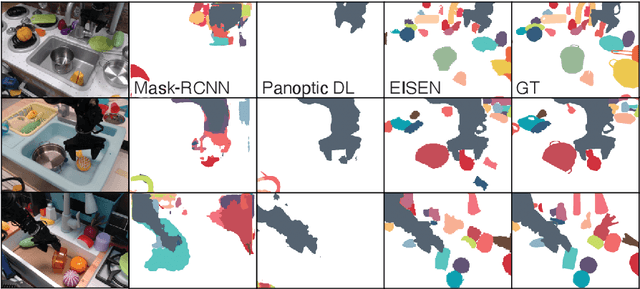
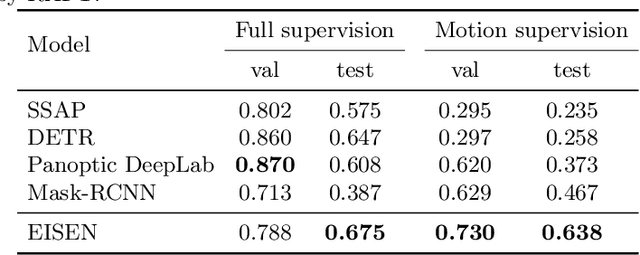
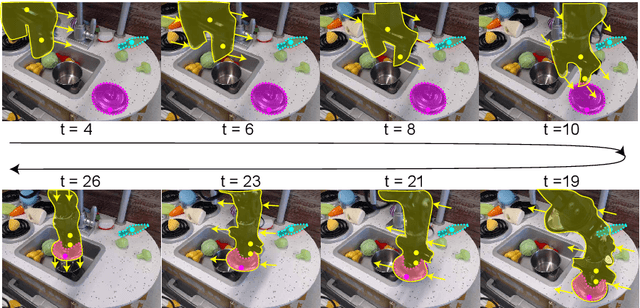
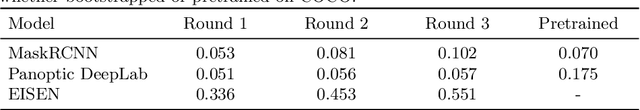
Self-supervised category-agnostic segmentation of real-world images into objects is a challenging open problem in computer vision. Here, we show how to learn static grouping priors from motion self-supervision, building on the cognitive science notion of Spelke Objects: groupings of stuff that move together. We introduce Excitatory-Inhibitory Segment Extraction Network (EISEN), which learns from optical flow estimates to extract pairwise affinity graphs for static scenes. EISEN then produces segments from affinities using a novel graph propagation and competition mechanism. Correlations between independent sources of motion (e.g. robot arms) and objects they move are resolved into separate segments through a bootstrapping training process. We show that EISEN achieves a substantial improvement in the state of the art for self-supervised segmentation on challenging synthetic and real-world robotic image datasets. We also present an ablation analysis illustrating the importance of each element of the EISEN architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge