Unsupervised Adaptation with Domain Separation Networks for Robust Speech Recognition
Paper and Code
Nov 21, 2017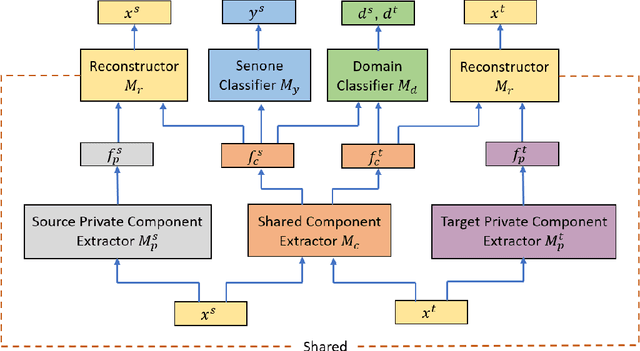
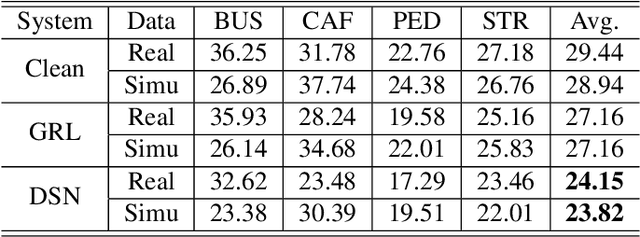
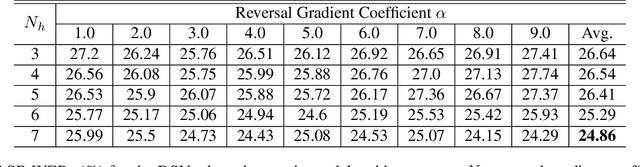
Unsupervised domain adaptation of speech signal aims at adapting a well-trained source-domain acoustic model to the unlabeled data from target domain. This can be achieved by adversarial training of deep neural network (DNN) acoustic models to learn an intermediate deep representation that is both senone-discriminative and domain-invariant. Specifically, the DNN is trained to jointly optimize the primary task of senone classification and the secondary task of domain classification with adversarial objective functions. In this work, instead of only focusing on learning a domain-invariant feature (i.e. the shared component between domains), we also characterize the difference between the source and target domain distributions by explicitly modeling the private component of each domain through a private component extractor DNN. The private component is trained to be orthogonal with the shared component and thus implicitly increases the degree of domain-invariance of the shared component. A reconstructor DNN is used to reconstruct the original speech feature from the private and shared components as a regularization. This domain separation framework is applied to the unsupervised environment adaptation task and achieved 11.08% relative WER reduction from the gradient reversal layer training, a representative adversarial training method, for automatic speech recognition on CHiME-3 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge