Unleashing OpenTitan's Potential: a Silicon-Ready Embedded Secure Element for Root of Trust and Cryptographic Offloading
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2024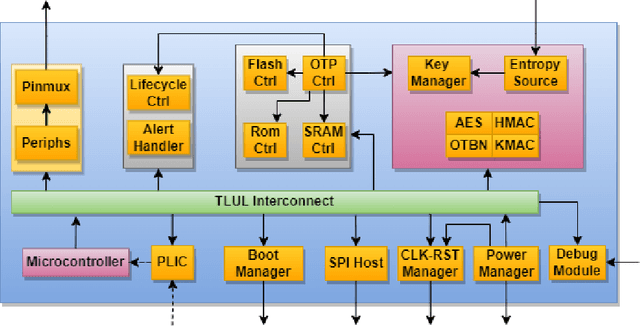
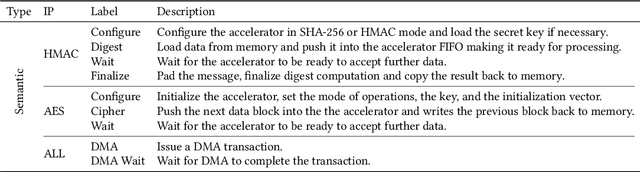
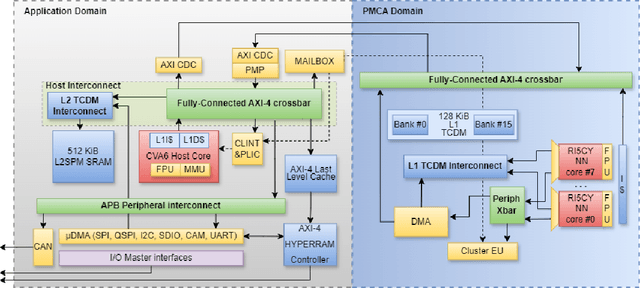
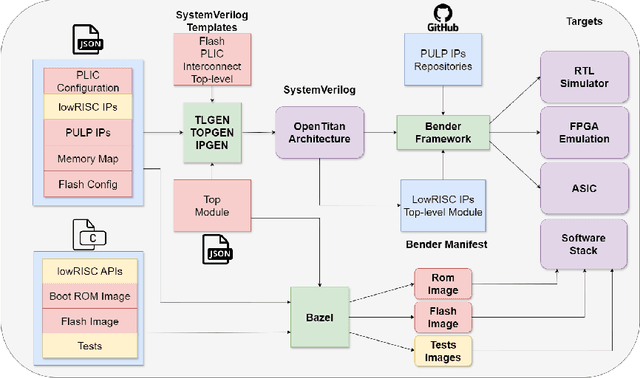
The rapid advancement and exploration of open-hardware RISC-V platforms are driving significant changes in sectors like autonomous vehicles, smart-city infrastructure, and medical devices. OpenTitan stands out as a groundbreaking open-source RISC-V design with a comprehensive security toolkit as a standalone system-on-chip (SoC). OpenTitan includes Earl Grey, a fully implemented and silicon-proven SoC, and Darjeeling, announced but not yet fully implemented. Earl Grey targets standalone SoC implementations, while Darjeeling is for integrable implementations. The literature lacks a silicon-ready embedded implementation of an open-source Root of Trust, despite lowRISC's efforts on Darjeeling. We address the limitations of existing implementations by optimizing data transfer latency between memory and cryptographic accelerators to prevent under-utilization and ensure efficient task acceleration. Our contributions include a comprehensive methodology for integrating custom extensions and IPs into the Earl Grey architecture, architectural enhancements for system-level integration, support for varied boot modes, and improved data movement across the platform. These advancements facilitate deploying OpenTitan in broader SoCs, even without specific technology-dependent IPs, providing a deployment-ready research vehicle for the community. We integrated the extended Earl Grey architecture into a reference architecture in a 22nm FDX technology node, benchmarking the enhanced architecture's performance. The results show significant improvements in cryptographic processing speed, achieving up to 2.7x speedup for SHA-256/HMAC and 1.6x for AES accelerators compared to the baseline Earl Grey architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge