TTVD: Towards a Geometric Framework for Test-Time Adaptation Based on Voronoi Diagram
Paper and Code
Dec 10, 2024


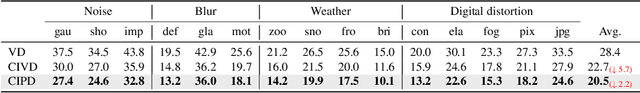
Deep learning models often struggle with generalization when deploying on real-world data, due to the common distributional shift to the training data. Test-time adaptation (TTA) is an emerging scheme used at inference time to address this issue. In TTA, models are adapted online at the same time when making predictions to test data. Neighbor-based approaches have gained attention recently, where prototype embeddings provide location information to alleviate the feature shift between training and testing data. However, due to their inherit limitation of simplicity, they often struggle to learn useful patterns and encounter performance degradation. To confront this challenge, we study the TTA problem from a geometric point of view. We first reveal that the underlying structure of neighbor-based methods aligns with the Voronoi Diagram, a classical computational geometry model for space partitioning. Building on this observation, we propose the Test-Time adjustment by Voronoi Diagram guidance (TTVD), a novel framework that leverages the benefits of this geometric property. Specifically, we explore two key structures: 1) Cluster-induced Voronoi Diagram (CIVD): This integrates the joint contribution of self-supervision and entropy-based methods to provide richer information. 2) Power Diagram (PD): A generalized version of the Voronoi Diagram that refines partitions by assigning weights to each Voronoi cell. Our experiments under rigid, peer-reviewed settings on CIFAR-10-C, CIFAR-100-C, ImageNet-C, and ImageNet-R shows that TTVD achieves remarkable improvements compared to state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, extensive experimental results also explore the effects of batch size and class imbalance, which are two scenarios commonly encountered in real-world applications. These analyses further validate the robustness and adaptability of our proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge