Towards Out-of-Distribution Adversarial Robustness
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2022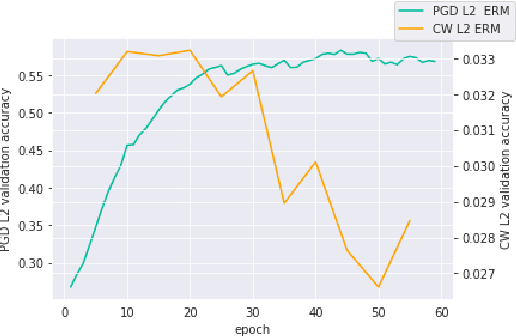
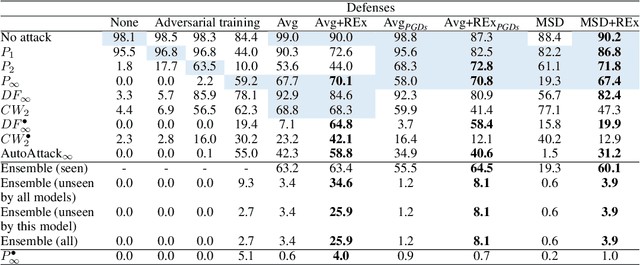
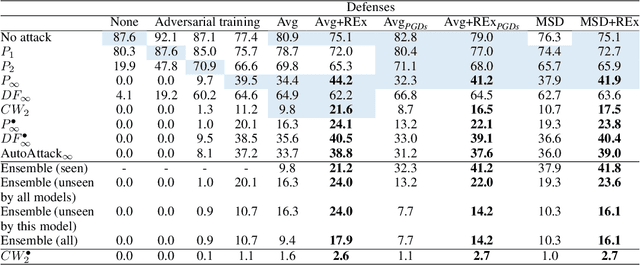
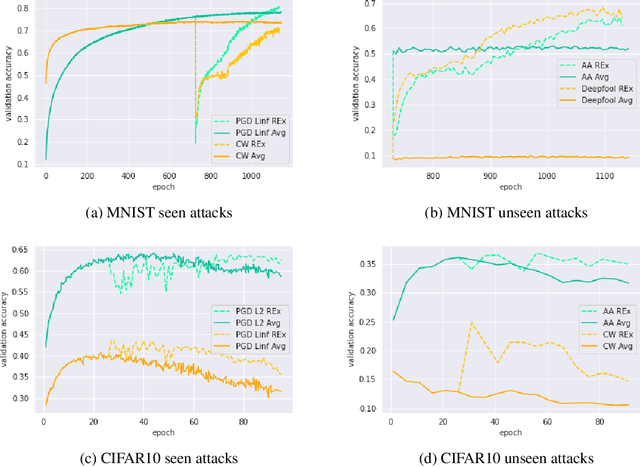
Adversarial robustness continues to be a major challenge for deep learning. A core issue is that robustness to one type of attack often fails to transfer to other attacks. While prior work establishes a theoretical trade-off in robustness against different $L_p$ norms, we show that there is potential for improvement against many commonly used attacks by adopting a domain generalisation approach. Concretely, we treat each type of attack as a domain, and apply the Risk Extrapolation method (REx), which promotes similar levels of robustness against all training attacks. Compared to existing methods, we obtain similar or superior worst-case adversarial robustness on attacks seen during training. Moreover, we achieve superior performance on families or tunings of attacks only encountered at test time. On ensembles of attacks, our approach improves the accuracy from 3.4% the best existing baseline to 25.9% on MNIST, and from 16.9% to 23.5% on CIFAR10.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge