Towards efficient end-to-end speech recognition with biologically-inspired neural networks
Paper and Code
Oct 04, 2021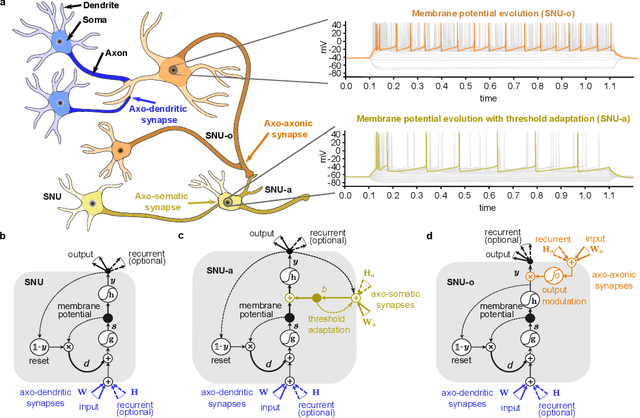
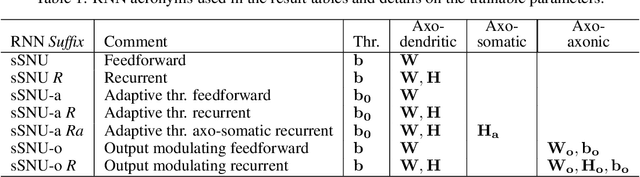
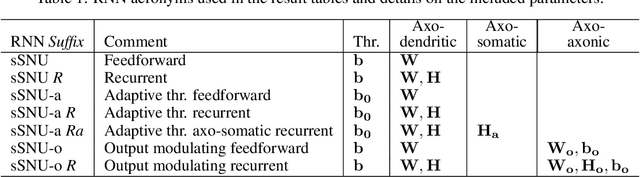
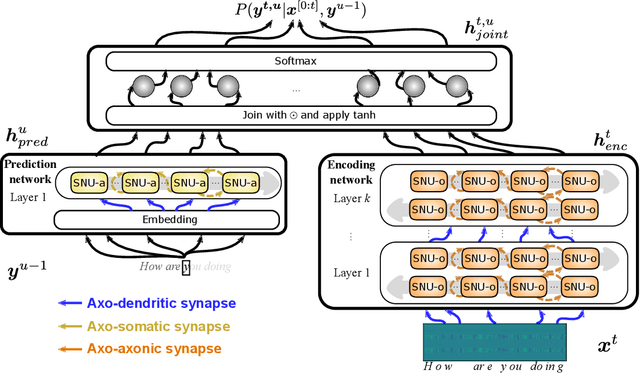
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) is a capability which enables a program to process human speech into a written form. Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) have led to high-accuracy ASR systems based on deep neural networks, such as the recurrent neural network transducer (RNN-T). However, the core components and the performed operations of these approaches depart from the powerful biological counterpart, i.e., the human brain. On the other hand, the current developments in biologically-inspired ASR models, based on spiking neural networks (SNNs), lag behind in terms of accuracy and focus primarily on small scale applications. In this work, we revisit the incorporation of biologically-plausible models into deep learning and we substantially enhance their capabilities, by taking inspiration from the diverse neural and synaptic dynamics found in the brain. In particular, we introduce neural connectivity concepts emulating the axo-somatic and the axo-axonic synapses. Based on this, we propose novel deep learning units with enriched neuro-synaptic dynamics and integrate them into the RNN-T architecture. We demonstrate for the first time, that a biologically realistic implementation of a large-scale ASR model can yield competitive performance levels compared to the existing deep learning models. Specifically, we show that such an implementation bears several advantages, such as a reduced computational cost and a lower latency, which are critical for speech recognition applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge