TouchUp-G: Improving Feature Representation through Graph-Centric Finetuning
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2023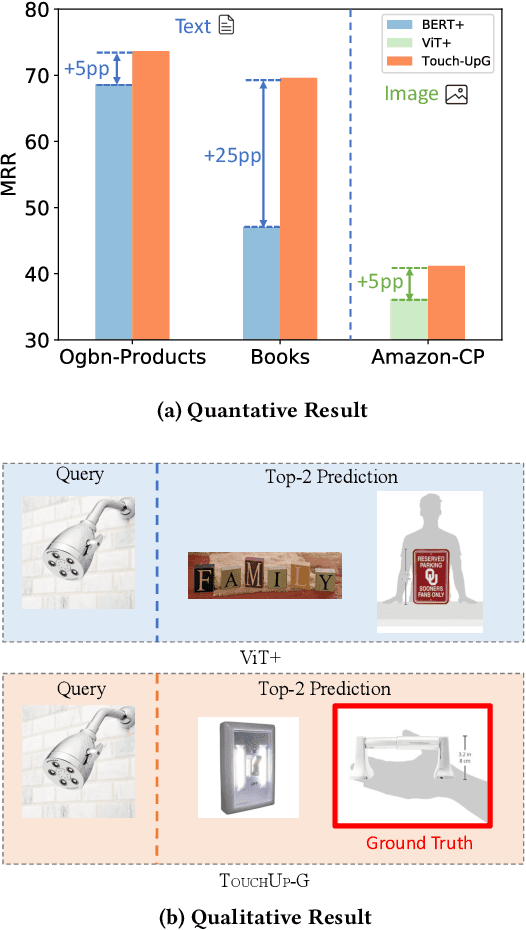
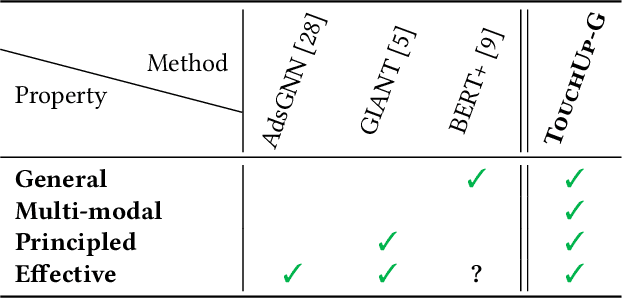
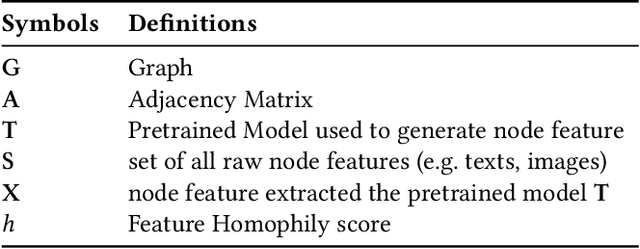
How can we enhance the node features acquired from Pretrained Models (PMs) to better suit downstream graph learning tasks? Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have become the state-of-the-art approach for many high-impact, real-world graph applications. For feature-rich graphs, a prevalent practice involves utilizing a PM directly to generate features, without incorporating any domain adaptation techniques. Nevertheless, this practice is suboptimal because the node features extracted from PM are graph-agnostic and prevent GNNs from fully utilizing the potential correlations between the graph structure and node features, leading to a decline in GNNs performance. In this work, we seek to improve the node features obtained from a PM for downstream graph tasks and introduce TOUCHUP-G, which has several advantages. It is (a) General: applicable to any downstream graph task, including link prediction which is often employed in recommender systems; (b) Multi-modal: able to improve raw features of any modality (e.g. images, texts, audio); (c) Principled: it is closely related to a novel metric, feature homophily, which we propose to quantify the potential correlations between the graph structure and node features and we show that TOUCHUP-G can effectively shrink the discrepancy between the graph structure and node features; (d) Effective: achieving state-of-the-art results on four real-world datasets spanning different tasks and modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge