The Gap of Semantic Parsing: A Survey on Automatic Math Word Problem Solvers
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2018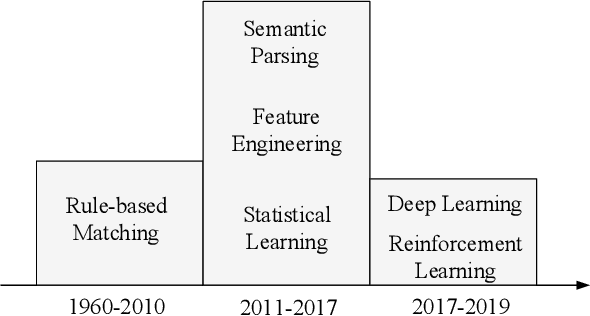
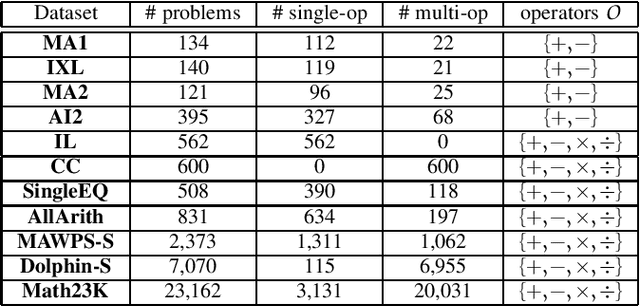
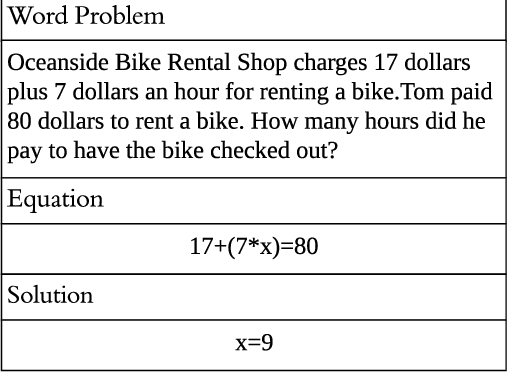
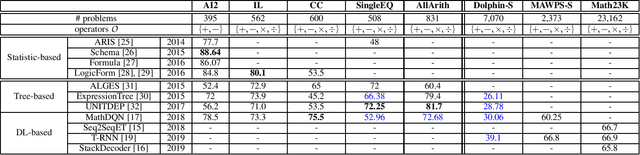
Automatically solving mathematical word problems (MWPs) is challenging, primarily due to the semantic gap between human-readable words and machine-understandable logics. Despite a long history dated back to the 1960s, MWPs has regained intensive attention in the past few years with the advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI). To solve MWPs successfully is considered as a milestone towards general AI. Many systems have claimed promising results in self-crafted and small-scale datasets. However, when applied on large and diverse datasets, none of the proposed methods in the literatures achieves a high precision, revealing that current MWPs solvers are still far from intelligent. This motivated us to present a comprehensive survey to deliver a clear and complete picture of automatic math problem solvers. In this survey, we emphasize on algebraic word problems, summarize their extracted features and proposed techniques to bridge the semantic gap, and compare their performance in the publicly accessible datasets. We will also cover automatic solvers for other types of math problems such as geometric problems that require the understanding of diagrams. Finally, we will identify several emerging research directions for the readers with interests in MWPs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge