Textual Adversarial Attack as Combinatorial Optimization
Paper and Code
Nov 10, 2019
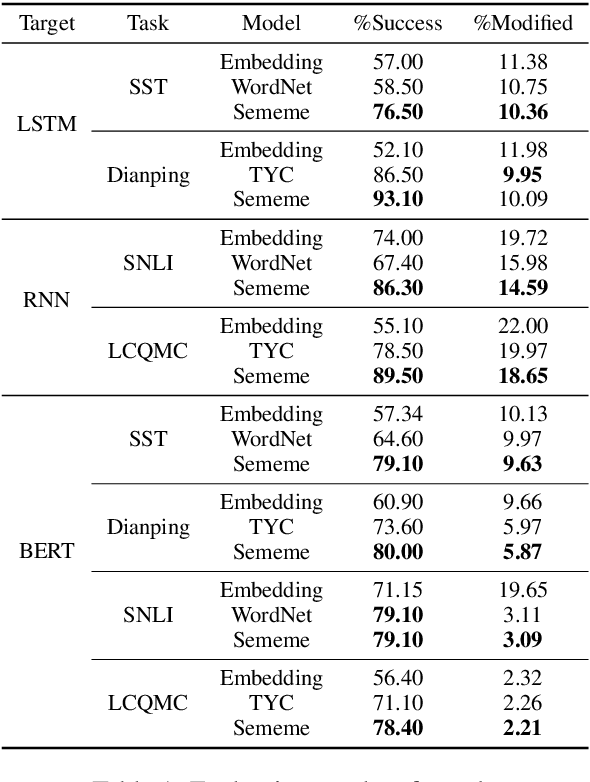
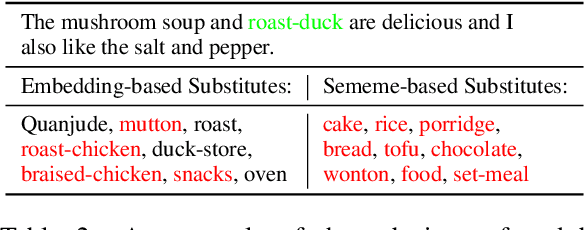
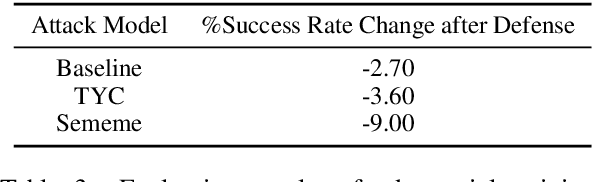
Adversarial attack is carried out to reveal the vulnerability of deep neural networks. Textual adversarial attack is challenging because text is discrete and any perturbation might bring big semantic change. Word substitution is a class of effective textual attack method and has been extensively explored. However, all existing word substitution-based attack methods suffer the problems of bad semantic preservation, insufficient adversarial examples or suboptimal attack results. In this paper, we formalize the word substitution-based attack as a combinatorial optimization problem. We also propose a novel attack model, which comprises a sememe-based word substitution strategy and the particle swarm optimization algorithm, to tackle the existing problems. In experiments, we evaluate our attack model on the sentiment analysis task. Experimental results demonstrate our model achieves higher attack success rates and less modification than the baseline methods. The ablation study also verifies the superiority of the two parts of our model over previous ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge