Switching Independent Vector Analysis and Its Extension to Blind and Spatially Guided Convolutional Beamforming Algorithm
Paper and Code
Nov 20, 2021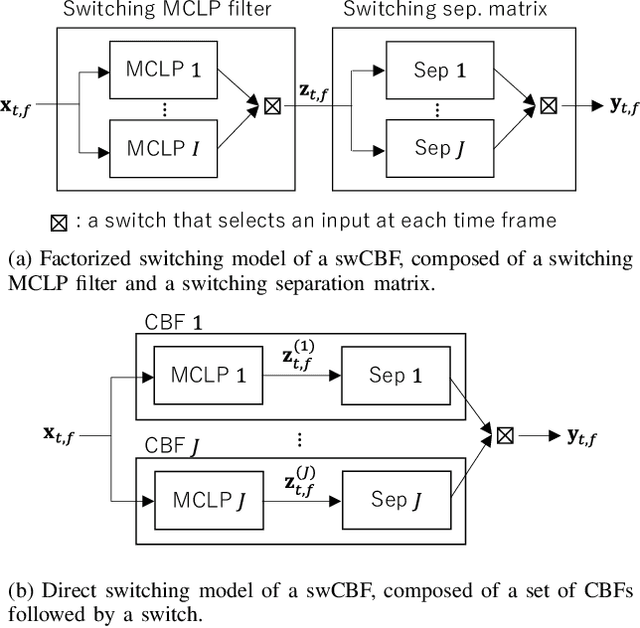
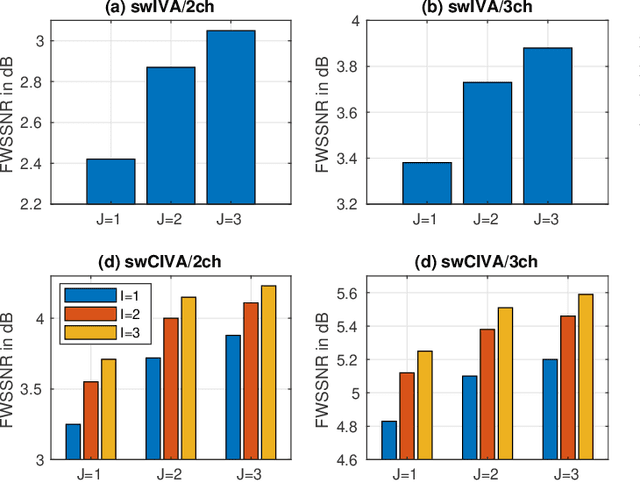
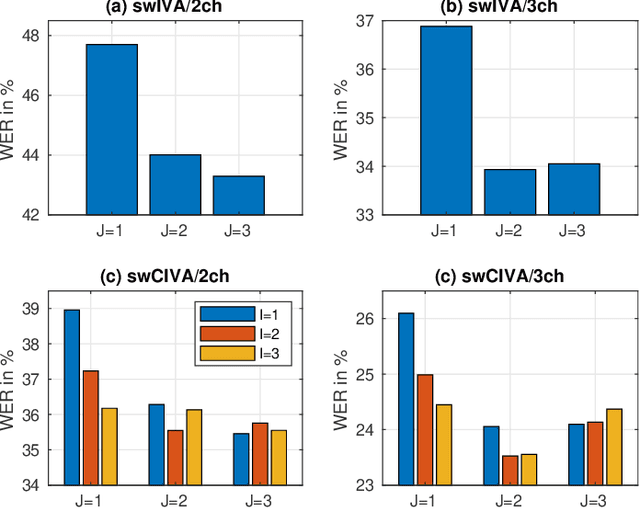
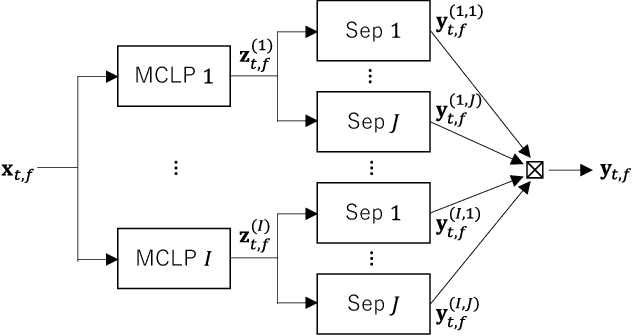
This paper develops a framework that can perform denoising, dereverberation, and source separation accurately by using a relatively small number of microphones. It has been empirically confirmed that Independent Vector Analysis (IVA) can blindly separate $N$ sources from their sound mixture even with diffuse noise when a sufficiently large number ($=M$) of microphones are available (i.e., $M\gg N)$. However, the estimation accuracy seriously degrades as the number of microphones, or more specifically $M-N$ $(\ge 0)$, decreases. To overcome this limitation of IVA, we propose switching IVA (swIVA) in this paper. With swIVA, time frames of an observed signal with time-varying characteristics are clustered into several groups, each of which can be well handled by IVA using a small number of microphones, and thus accurate estimation can be achieved by applying {\IVA} individually to each of the groups. Conventionally, a switching mechanism was introduced into a beamformer; however, no blind source separation algorithms with a switching mechanism have been successfully developed until this paper. In order to incorporate dereverberation capability, this paper further extends swIVA to blind Convolutional beamforming algorithm (swCIVA). It integrates swIVA and switching Weighted Prediction Error-based dereverberation (swWPE) in a jointly optimal way. We show that both swIVA and swIVAconv can be optimized effectively based on blind signal processing, and that their performance can be further improved using a spatial guide for the initialization. Experiments show that the both proposed methods largely outperform conventional IVA and its Convolutional beamforming extension (CIVA) in terms of objective signal quality and automatic speech recognition scores when using a relatively small number of microphones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge