Successive Subspace Learning for Cardiac Disease Classification with Two-phase Deformation Fields from Cine MRI
Paper and Code
Jan 21, 2023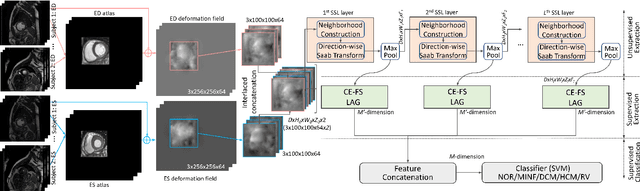
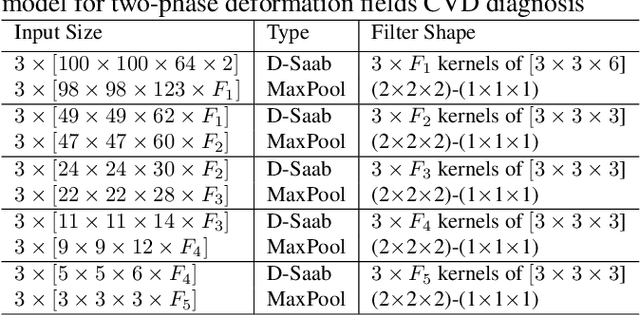
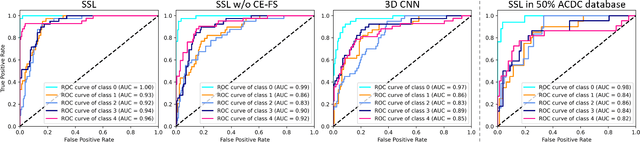
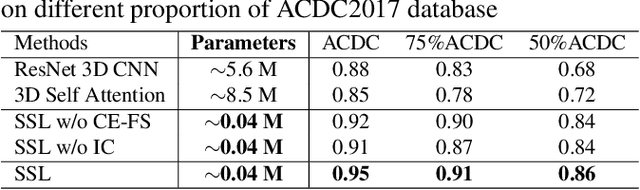
Cardiac cine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been used to characterize cardiovascular diseases (CVD), often providing a noninvasive phenotyping tool.~While recently flourished deep learning based approaches using cine MRI yield accurate characterization results, the performance is often degraded by small training samples. In addition, many deep learning models are deemed a ``black box," for which models remain largely elusive in how models yield a prediction and how reliable they are. To alleviate this, this work proposes a lightweight successive subspace learning (SSL) framework for CVD classification, based on an interpretable feedforward design, in conjunction with a cardiac atlas. Specifically, our hierarchical SSL model is based on (i) neighborhood voxel expansion, (ii) unsupervised subspace approximation, (iii) supervised regression, and (iv) multi-level feature integration. In addition, using two-phase 3D deformation fields, including end-diastolic and end-systolic phases, derived between the atlas and individual subjects as input offers objective means of assessing CVD, even with small training samples. We evaluate our framework on the ACDC2017 database, comprising one healthy group and four disease groups. Compared with 3D CNN-based approaches, our framework achieves superior classification performance with 140$\times$ fewer parameters, which supports its potential value in clinical use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge