Structure-Grounded Pretraining for Text-to-SQL
Paper and Code
Oct 24, 2020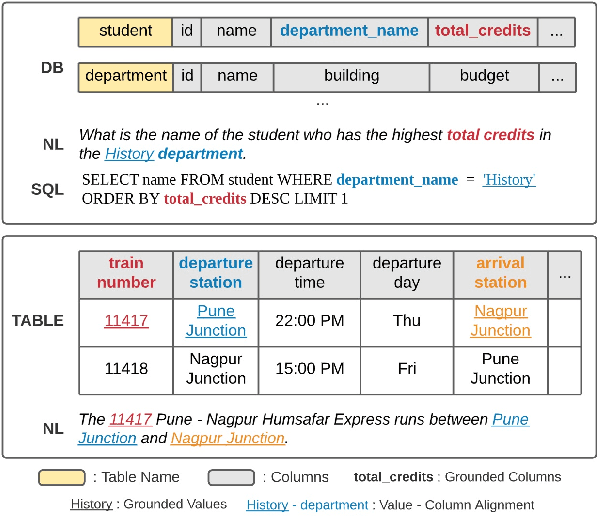
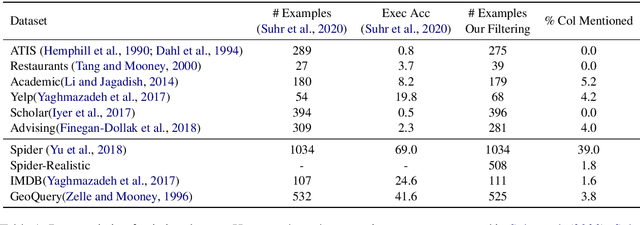
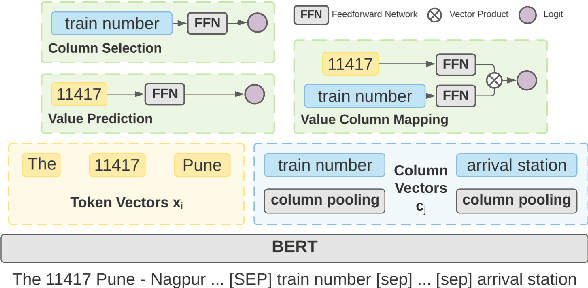

Learning to capture text-table alignment is essential for table related tasks like text-to-SQL. The model needs to correctly recognize natural language references to columns and values and to ground them in the given database schema. In this paper, we present a novel weakly supervised Structure-Grounded pretraining framework (StruG) for text-to-SQL that can effectively learn to capture text-table alignment based on a parallel text-table corpus. We identify a set of novel prediction tasks: column grounding, value grounding and column-value mapping, and train them using weak supervision without requiring complex SQL annotation. Additionally, to evaluate the model under a more realistic setting, we create a new evaluation set Spider-Realistic based on Spider with explicit mentions of column names removed, and adopt two existing single-database text-to-SQL datasets. StruG significantly outperforms BERT-LARGE on Spider and the realistic evaluation sets, while bringing consistent improvement on the large-scale WikiSQL benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge