Snomed2Vec: Random Walk and Poincaré Embeddings of a Clinical Knowledge Base for Healthcare Analytics
Paper and Code
Jul 19, 2019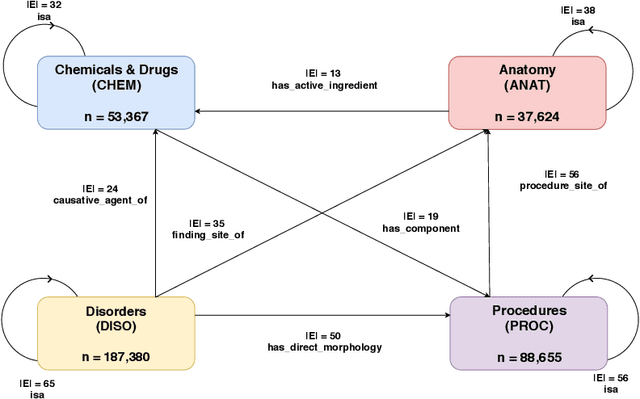
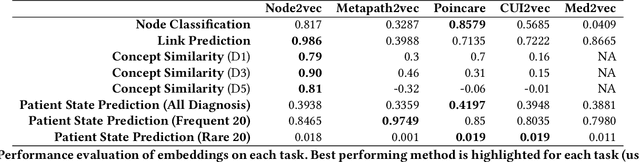
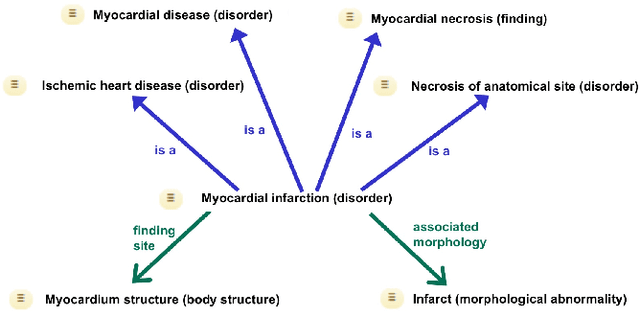
Representation learning methods that transform encoded data (e.g., diagnosis and drug codes) into continuous vector spaces (i.e., vector embeddings) are critical for the application of deep learning in healthcare. Initial work in this area explored the use of variants of the word2vec algorithm to learn embeddings for medical concepts from electronic health records or medical claims datasets. We propose learning embeddings for medical concepts by using graph-based representation learning methods on SNOMED-CT, a widely popular knowledge graph in the healthcare domain with numerous operational and research applications. Current work presents an empirical analysis of various embedding methods, including the evaluation of their performance on multiple tasks of biomedical relevance (node classification, link prediction, and patient state prediction). Our results show that concept embeddings derived from the SNOMED-CT knowledge graph significantly outperform state-of-the-art embeddings, showing 5-6x improvement in ``concept similarity" and 6-20\% improvement in patient diagnosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge