SleePyCo: Automatic Sleep Scoring with Feature Pyramid and Contrastive Learning
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2022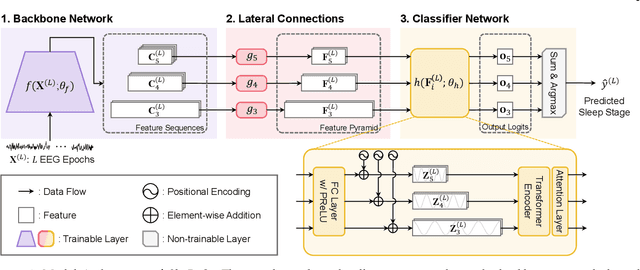
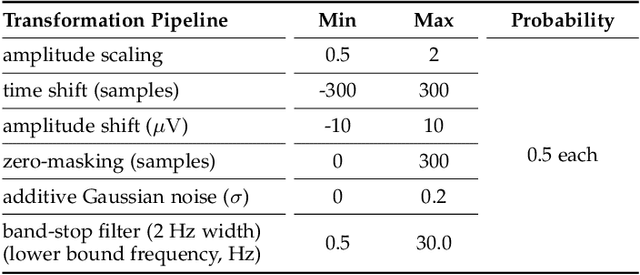
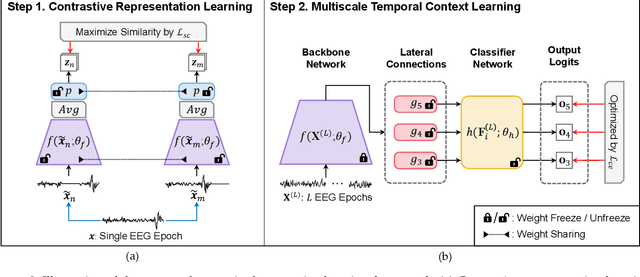

Automatic sleep scoring is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders and enables longitudinal sleep tracking in home environments. Conventionally, learning-based automatic sleep scoring on single-channel electroencephalogram (EEG) is actively studied because obtaining multi-channel signals during sleep is difficult. However, learning representation from raw EEG signals is challenging owing to the following issues: 1) sleep-related EEG patterns occur on different temporal and frequency scales and 2) sleep stages share similar EEG patterns. To address these issues, we propose a deep learning framework named SleePyCo that incorporates 1) a feature pyramid and 2) supervised contrastive learning for automatic sleep scoring. For the feature pyramid, we propose a backbone network named SleePyCo-backbone to consider multiple feature sequences on different temporal and frequency scales. Supervised contrastive learning allows the network to extract class discriminative features by minimizing the distance between intra-class features and simultaneously maximizing that between inter-class features. Comparative analyses on four public datasets demonstrate that SleePyCo consistently outperforms existing frameworks based on single-channel EEG. Extensive ablation experiments show that SleePyCo exhibits enhanced overall performance, with significant improvements in discrimination between the N1 and rapid eye movement (REM) stages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge