Situation-Aware Environment Perception Using a Multi-Layer Attention Map
Paper and Code
Dec 02, 2021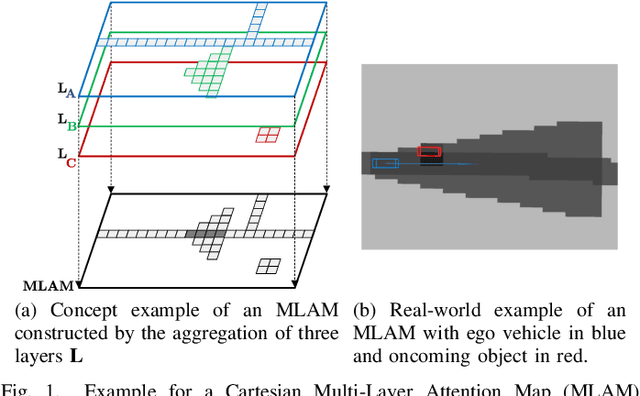
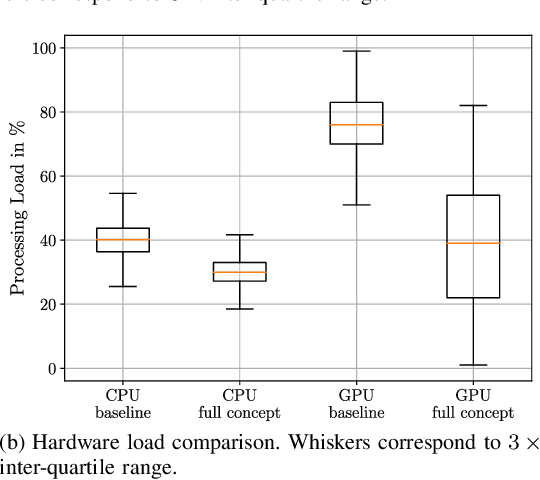
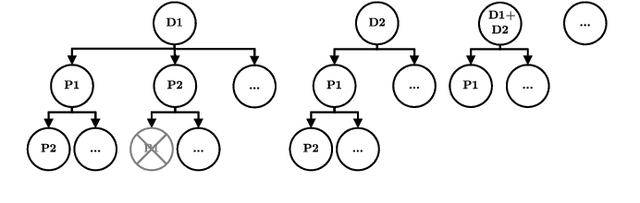
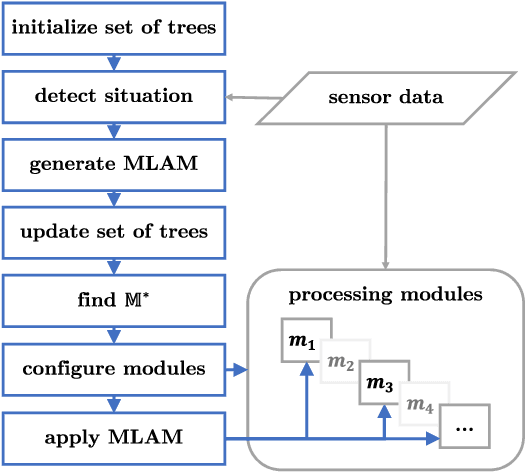
Within the field of automated driving, a clear trend in environment perception tends towards more sensors, higher redundancy, and overall increase in computational power. This is mainly driven by the paradigm to perceive the entire environment as best as possible at all times. However, due to the ongoing rise in functional complexity, compromises have to be considered to ensure real-time capabilities of the perception system. In this work, we introduce a concept for situation-aware environment perception to control the resource allocation towards processing relevant areas within the data as well as towards employing only a subset of functional modules for environment perception, if sufficient for the current driving task. Specifically, we propose to evaluate the context of an automated vehicle to derive a multi-layer attention map (MLAM) that defines relevant areas. Using this MLAM, the optimum of active functional modules is dynamically configured and intra-module processing of only relevant data is enforced. We outline the feasibility of application of our concept using real-world data in a straight-forward implementation for our system at hand. While retaining overall functionality, we achieve a reduction of accumulated processing time of 59%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge