$χ$-sepnet: Deep neural network for magnetic susceptibility source separation
Paper and Code
Sep 24, 2024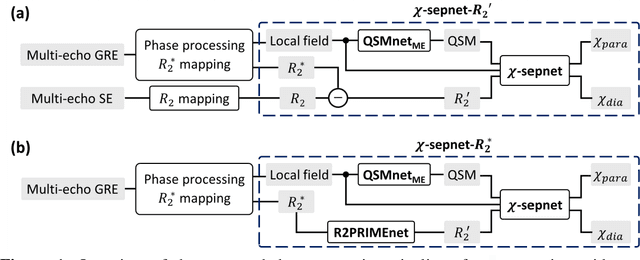
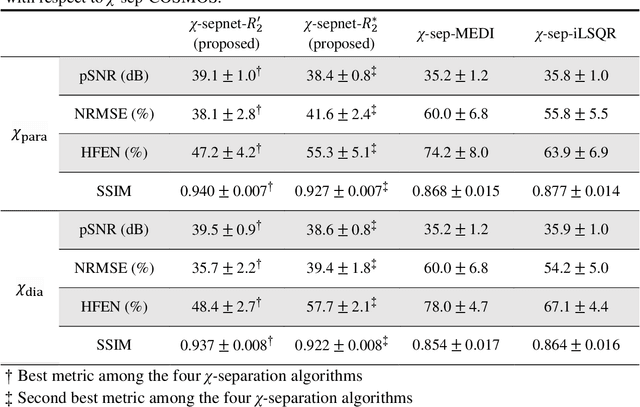
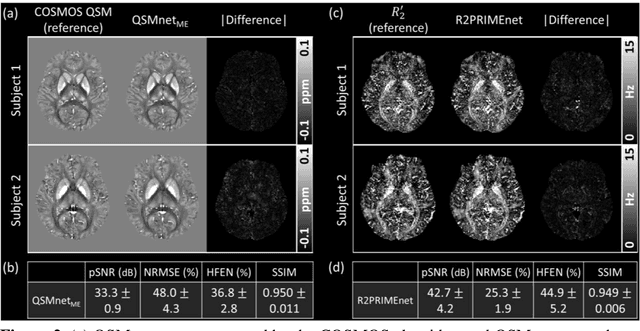
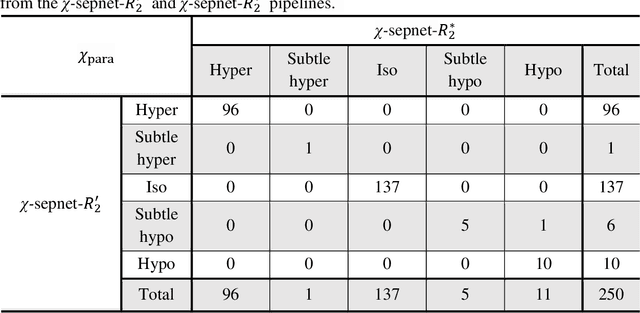
Magnetic susceptibility source separation ($\chi$-separation), an advanced quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) method, enables the separate estimation of para- and diamagnetic susceptibility source distributions in the brain. The method utilizes reversible transverse relaxation (R2'=R2*-R2) to complement frequency shift information for estimating susceptibility source concentrations, requiring time-consuming data acquisition for R2 in addition R2*. To address this challenge, we develop a new deep learning network, $\chi$-sepnet, and propose two deep learning-based susceptibility source separation pipelines, $\chi$-sepnet-R2' for inputs with multi-echo GRE and multi-echo spin-echo, and $\chi$-sepnet-R2* for input with multi-echo GRE only. $\chi$-sepnet is trained using multiple head orientation data that provide streaking artifact-free labels, generating high-quality $\chi$-separation maps. The evaluation of the pipelines encompasses both qualitative and quantitative assessments in healthy subjects, and visual inspection of lesion characteristics in multiple sclerosis patients. The susceptibility source-separated maps of the proposed pipelines delineate detailed brain structures with substantially reduced artifacts compared to those from conventional regularization-based reconstruction methods. In quantitative analysis, $\chi$-sepnet-R2' achieves the best outcomes followed by $\chi$-sepnet-R2*, outperforming the conventional methods. When the lesions of multiple sclerosis patients are assessed, both pipelines report identical lesion characteristics in most lesions ($\chi$para: 99.6% and $\chi$dia: 98.4% out of 250 lesions). The $\chi$-sepnet-R2* pipeline, which only requires multi-echo GRE data, has demonstrated its potential to offer broad clinical and scientific applications, although further evaluations for various diseases and pathological conditions are necessary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge