SENSEI: Semantic Exploration Guided by Foundation Models to Learn Versatile World Models
Paper and Code
Mar 03, 2025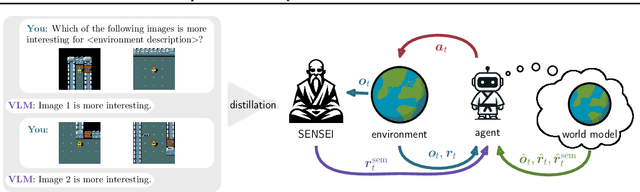
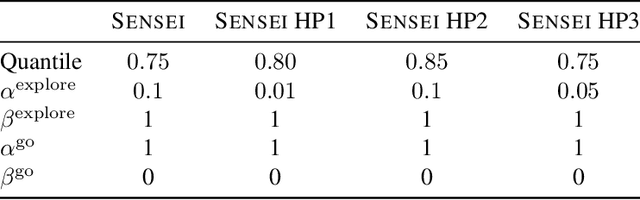
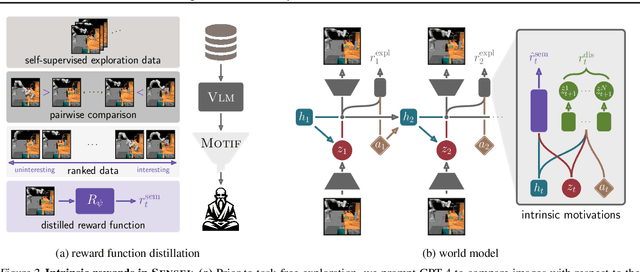
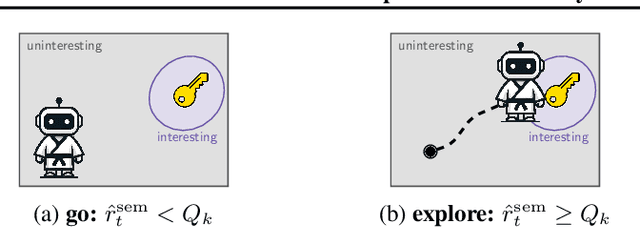
Exploration is a cornerstone of reinforcement learning (RL). Intrinsic motivation attempts to decouple exploration from external, task-based rewards. However, established approaches to intrinsic motivation that follow general principles such as information gain, often only uncover low-level interactions. In contrast, children's play suggests that they engage in meaningful high-level behavior by imitating or interacting with their caregivers. Recent work has focused on using foundation models to inject these semantic biases into exploration. However, these methods often rely on unrealistic assumptions, such as language-embedded environments or access to high-level actions. We propose SEmaNtically Sensible ExploratIon (SENSEI), a framework to equip model-based RL agents with an intrinsic motivation for semantically meaningful behavior. SENSEI distills a reward signal of interestingness from Vision Language Model (VLM) annotations, enabling an agent to predict these rewards through a world model. Using model-based RL, SENSEI trains an exploration policy that jointly maximizes semantic rewards and uncertainty. We show that in both robotic and video game-like simulations SENSEI discovers a variety of meaningful behaviors from image observations and low-level actions. SENSEI provides a general tool for learning from foundation model feedback, a crucial research direction, as VLMs become more powerful.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge